Patents
Literature
61 results about "Cytoskeletal Filaments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Eukaryotic cells contain three main kinds of cytoskeletal filaments: microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. Each cytoskeletal filament type is formed by polymerization of a distinct type of protein subunit and has its own characteristic shape and intracellular distribution.
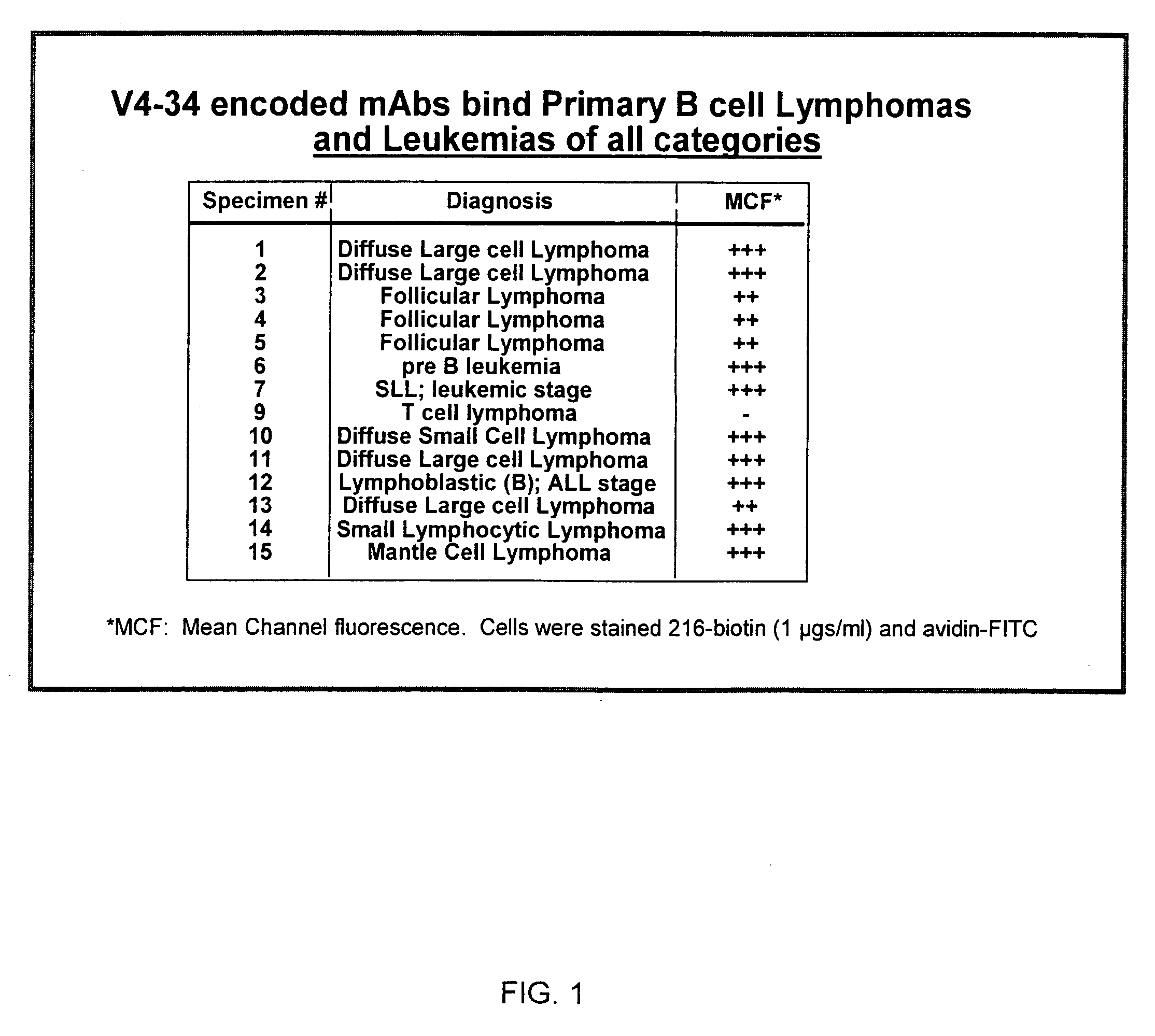
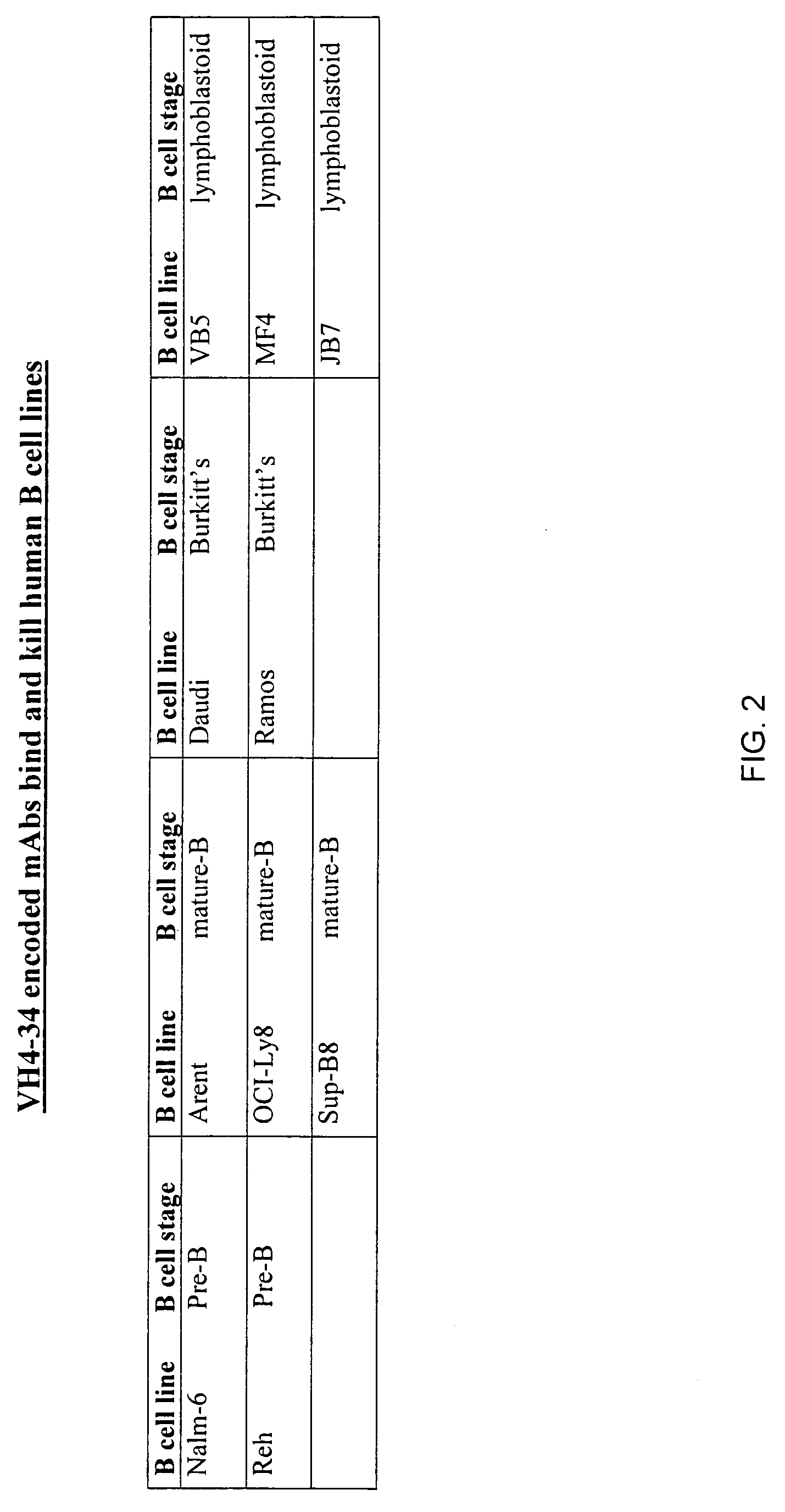
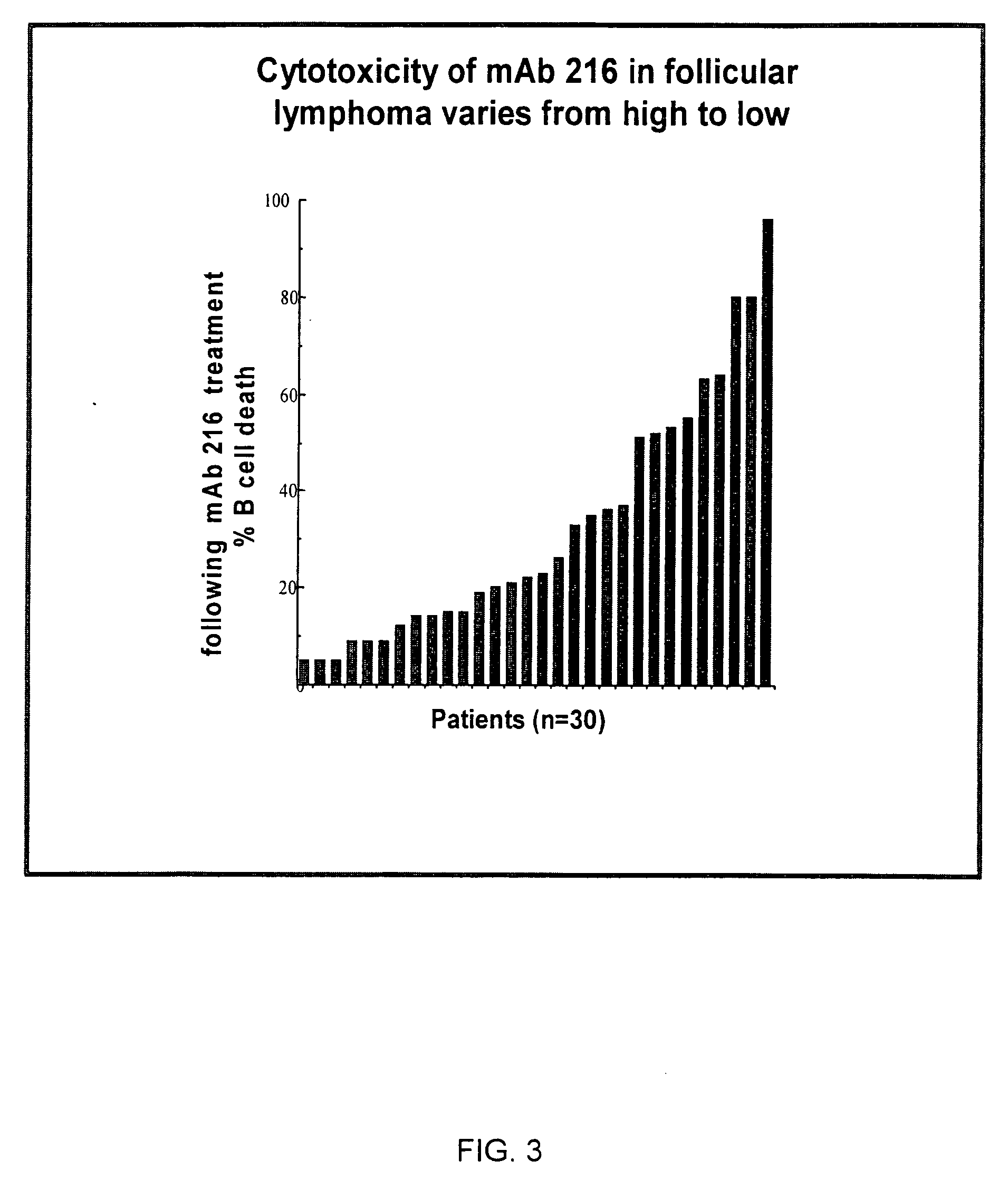
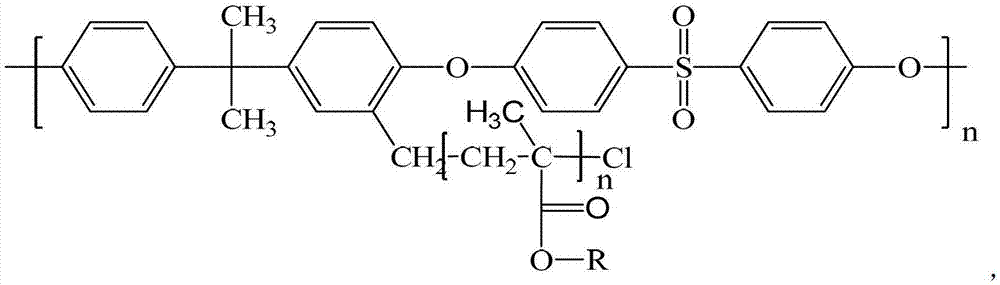
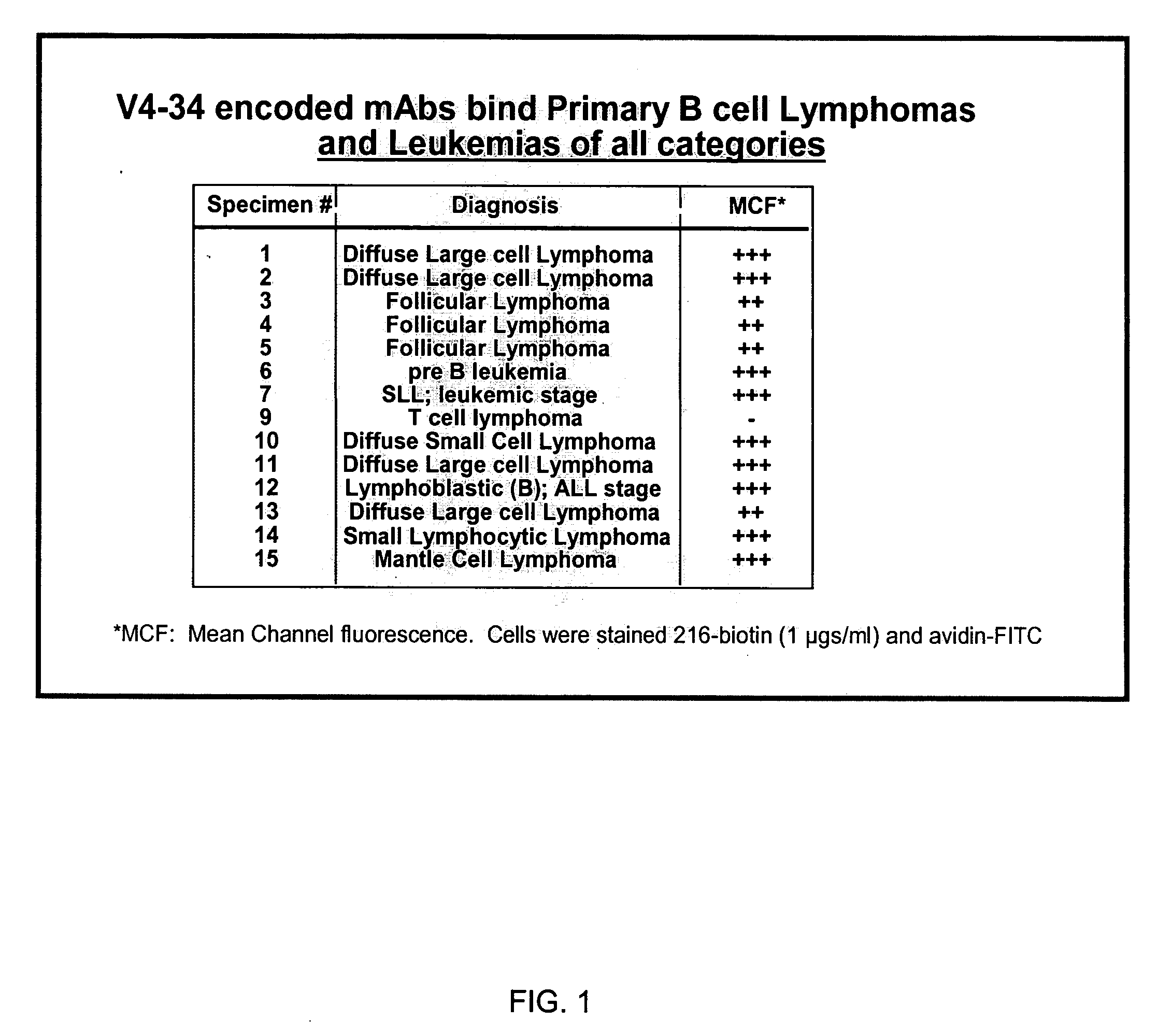
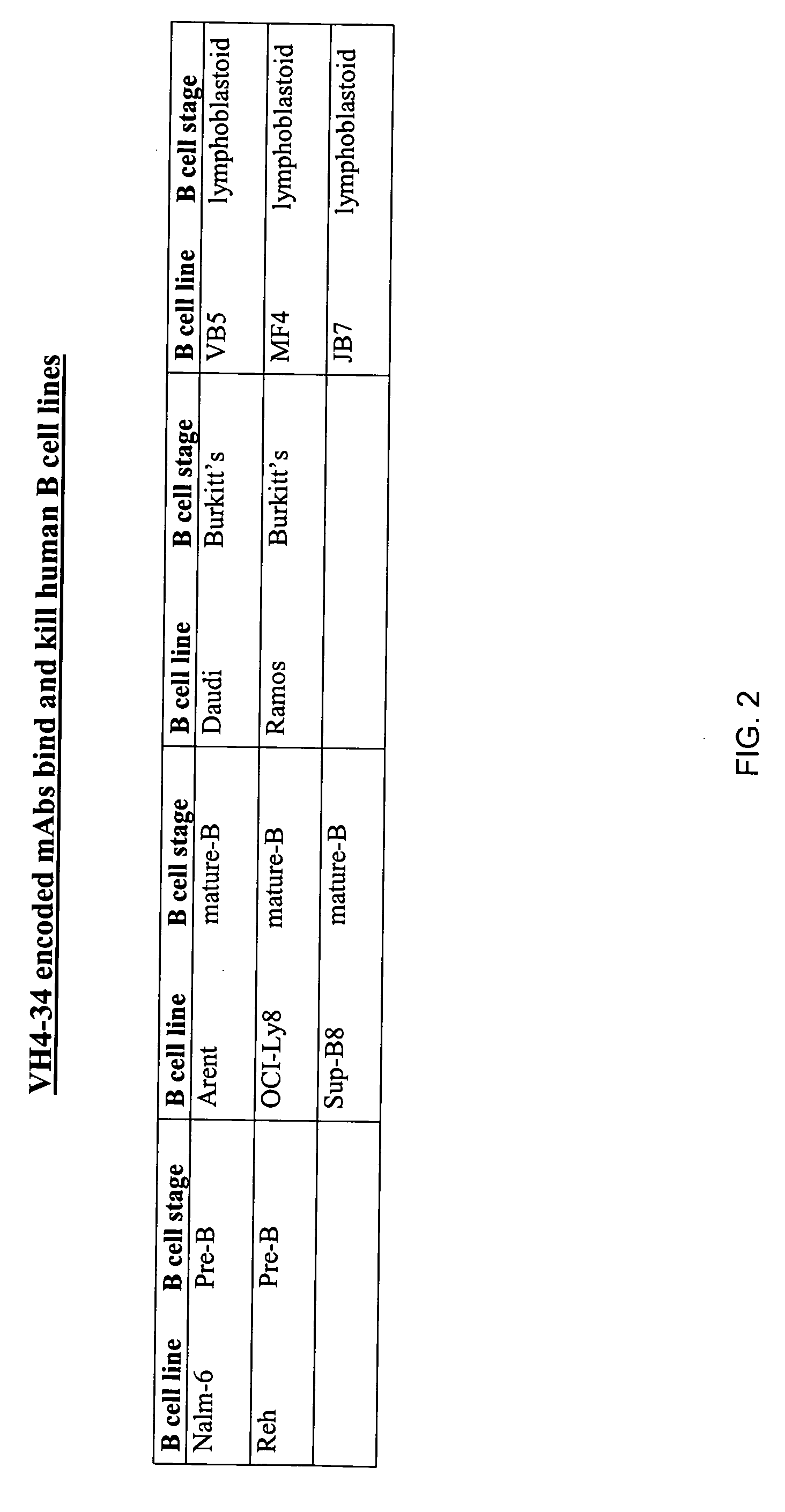
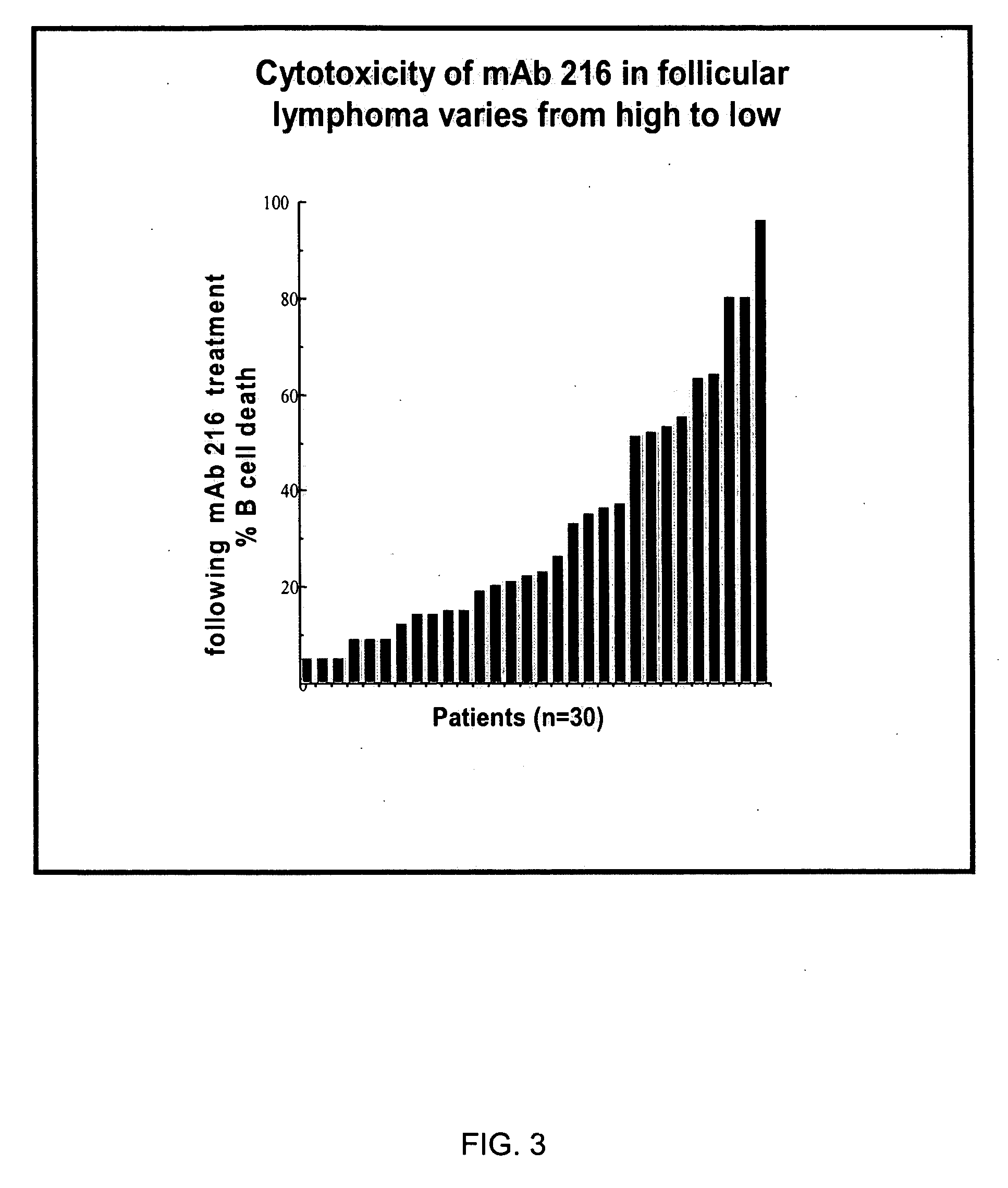
Enhanced B cell cytotoxicity of CDIM binding antibody
InactiveUS20050112130A1Good curative effectStrong cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionCytotoxicity
Formulations and methods of treating human patients suffering from a condition characterized by lymphoid cancer, autoimmune disease or B cell hyperproliferation are disclosed, the treatment comprising administering (1) a cytotoxic amount of an antibody having specific binding for CDIM epitopes on a B cell, and (2) a cytotoxic agent, including a chemotherapeutic agent, radioactive isotope, cytotoxic antibody, immunoconjugate, ligand conjugate, immunosuppressant, cell growth regulator and / or inhibitor, toxin, or mixtures thereof, including agents that disrupt the cytoskeleton of B cells, particularly vinca alkaloids or colchicine.
Owner:PALIGEN INC +2
Bifunctional rho kinase inhibitor compounds, composition and use
InactiveUS20130131106A1Lower eye pressureEffective treatmentBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseOpen angle glaucoma
This invention relates to synthetic bifunctional compounds comprising a first rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibiting compound and a second pharmaceutically active compound with complementary activity; the first and the second compounds are covalently linked by a biologically labile bond. This invention also relates to methods of making such compounds. The invention also relates to methods of using such bifunctional compounds in the prevention or treatment of diseases or conditions that are affected or can be assisted by altering the integrity or rearrangement of the cytoskeleton. Particularly, this invention relates to methods of treating ophthalmic diseases such as disorders in which intraocular pressure is elevated, for example primary open-angle glaucoma, using the bifunctional compounds.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
Nano artificial dura mater capable of being used as medicine sustained-release system and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a nano artificial dura mater capable of being used as a medicine sustained-release system, having the structure which comprises at least two layers, i.e. a hydrophobic anti-blocking electro-spun layer which faces the cerebrum, and a hydrophilic nano cytoskeleton layer which backs on to the cerebrum; and cell factors and / or medicines are arranged in any layer of the artificial dura mater by way of blended spinning. The invention also provides a method for preparing the nano biomimic artificial dura mater. Compared with an artificial mater prepared by the single utilization of the electro-spinning technology, the artificial mater to which the medicines and the cell factors are added by blending technology can effectively prevent infection and faster promote the regeneration process of the artificial mater. The invention also provides a novel medicine loading and releasing mode for treating cerebral diseases, the loaded medicines can be directly and efficiently transferred into the cranial cavity along with the implantation of the dura mate and can be released according to requirements, and therefore the invention realizes favorable treatment effect and has broad application prospect.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Photo-crosslinking sericin protein hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106075598AGood controlled drug release propertiesGood biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiocompatibility TestingIn vivo
The invention relates to photo-crosslinking sericin protein hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that methyl propenyl modified sericin protein is prepared into a solution to be mixed with a photoinitiator (Irgacure 2959) solution, and the sericin protein hydrogel is obtained through ultraviolet irradiation. The obtained sericin protein hydrogel has the good biodegradability, autofluorescence characteristic and injectable property, and wounds caused by implanting or taking out biomaterials can be effectively reduced. Most importantly, the sericin protein hydrogel has good biocompatibility both in vivo and in vitro, and adhesion of carried cells can be effectively promoted. Serving as 2D and 3D cytoskeleton, the sericin protein hydrogel can effectively promote proliferation of the carried cells and promote the carried cells to form functional tissue under the condition of being free of serum support; serving as wound accessories, the sericin protein hydrogel can repair skin wounds and can serve as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine biological materials.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
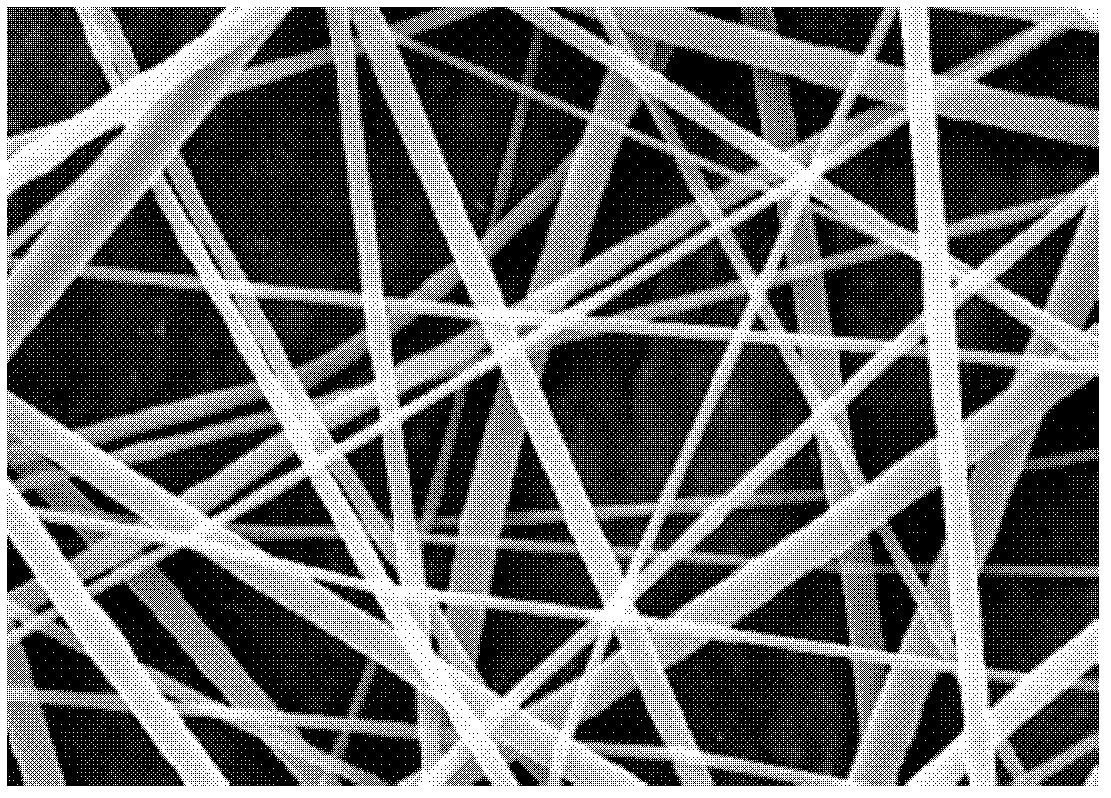
Three-dimensional large-aperture nanoscale fibrous scaffold and method for preparing same
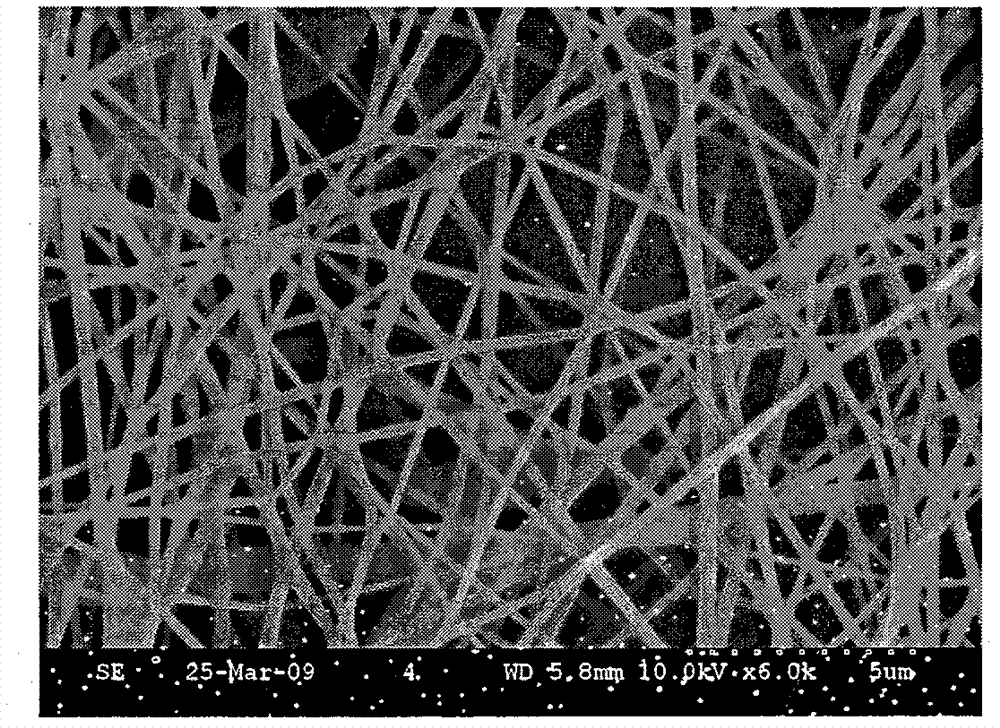
The invention discloses a three-dimensional large-aperture nanoscale fibrous scaffold and a method for preparing the same. The average diameter of fibers in the scaffold is about 1 nanometer to 900 nanometers, the voidage is about 50%-98%, the scaffold is of a three-dimensional structure, and the thickness of the scaffold is 0.01 micrometer to 10 centimeters. The method includes the following steps of dissolving biodegradable polyester and additives into organic solvent to prepare spinning solution. An electrostatic spinning process is used for spinning the spinning solution to obtain nanoscale / submicron-order fibrofelt. The fibrofelt is soaked in solvent within 48 hours after being spun, is pre-frozen at first, and then is frozen and dried, so that the three-dimensional fibrous scaffold with mutually communicated large holes is obtained. The three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffold material with the communicated large holes is prepared, the structures of the internal holes are uniform, and the three-dimensional large-aperture nanscale fibrous scaffold can be used as a tissue engineering cytoskeleton for bones, cartilages, blood vessels, hearts, nerves and the like, and is suitable for growth of various cells.
Owner:冯淑芹
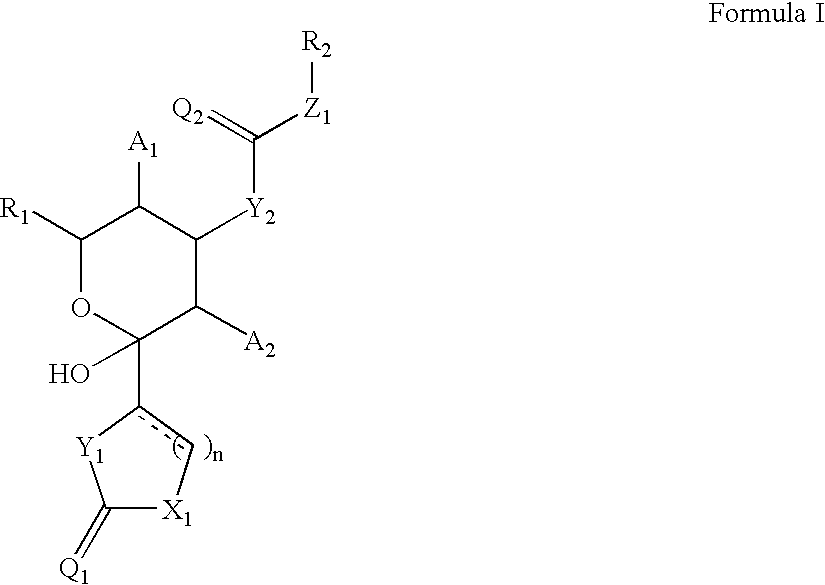
Chiral supermolecule hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103694131AEasy to operateHigh purityOrganic compound preparationVertebrate cellsAdhesiveStructural formula
The invention provides a chiral supermolecule hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the chiral supermolecule hydrogel is shown in the specification, wherein R1 is H or COOEtOEtOH, and R2 is H or COOEtOEtOH. The invention also relates to the preparation method and application of the chiral supermolecule hydrogel. The chiral supermolecule hydrogel can be used as a cytoskeleton material; the process of regulating and controlling the cell selective adhesion by the chiral supermolecule hydrogel is carried out in physiological environment and is convenient to operate; the chiral supermolecule hydrogel has practical application value; the preparation method does not need complicated synthesis steps and is beneficial for large scale industrial production; the prepared product has high purity and good dispersibility, and is applicable to cell culture and controllable adhesives in commerce.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
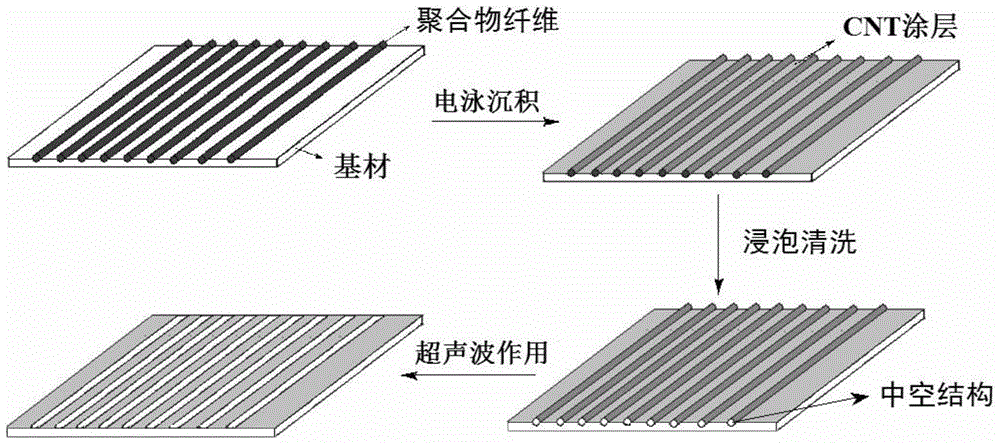
Nerve conduit material having topological structure and modified by CNT/conducting polymer composite coating and preparation method of nerve conduit material
The invention provides a nerve conduit material having a topological structure and modified by a CNT (Carbon Nano Tube) / conducting polymer composite coating and a preparation method of the nerve conduit material. With electro-spun polymer fibers as templates, CNTs are deposited on the surface of a substrate by use of an electrophoresis method so as to form a three-dimensional porous network CNT coating, next, solvent cleaning and ultrasonic stripping are carried out to form the CNT coating with a directional groove structure, then a conducting polymer is deposited by use of electro-chemical impulse polymerization, and the conducting polymer is coaxially wound around the surface of the CNT bundle to form the nerve conduit material modified by the CNT / conducting polymer composite coating having the directional groove structure. The surface of the nerve conduit material has two layers in the topological structure: at micrometer scale, the coating is provided with a patterned micrometer-scale groove for guiding the rearrangement of a neural cytoskeleton; at nanometer scale, the coating is provided with a nanometer-scale porous network structure for guaranteeing the physical conditions for the attachment and growth of nerve cells and excellent electrochemical properties of the nerve conduit.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional stephanoporate organization engineering bracket material, fibre cementing method preparing same and applications thereof
InactiveCN101249277AAdjust the micropore sizeRegulates biodegradation rateBone implantPorosityRoom temperature
The invention relates to a three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stent material, a fiber-gluing preparation method thereof and the application thereof, The material comprises poly butylene succinate and polycaprolactone; the weight portion is: poly butylene succinate 90 to 10 parts, polycaprolactone 10 to 90 parts; preparation: 1) mixing poly butylene succinate and polycaprolactone to obtain fiber by melt spinning; 2) cutting fiber and filling the fiber into a module, the fiber being arranged in an even structure; 3) putting the mould into a vacuum oven with 50 to 90 DEG C and keeping for 5 minutes to 1 hour, demoulding at room temperature and drying in vacuum after cooling, and obtaining three-dimensional tissue engineering stent material; 4) sterilizing and packing the three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stent material; The material has the application of being used as bone or cartilage tissue engineering cytoskeleton for repairing and rebuilding of bone or cartilage tissue organ. The tissue engineering stent material has evenly structured, internal pores that communicate with each other. The aperture of the pores is 10 to 500 Mum, and the porosity changes between 70 to 91 percent, so that the systematic structure of the stent is stable and easy to produce.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
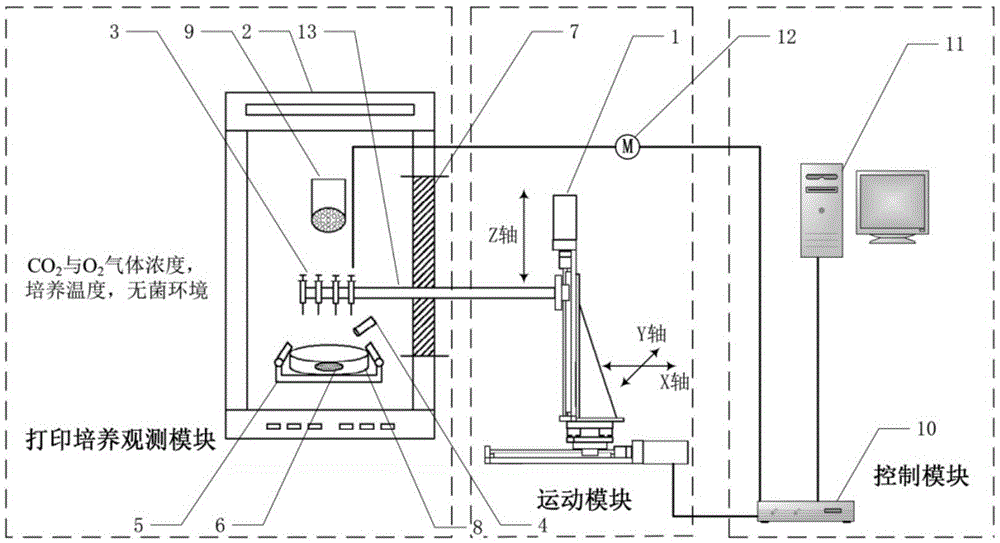
An ultra-clean high-stability biological 3D printing-culturing integrated system and a method therefor
ActiveCN105524831AEasy to useExtend your lifeAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue/virus culture apparatusCell activityEngineering
The invention provides an ultra-clean high-stability biological 3D printing-culturing integrated system and a method therefor, and overcomes problems namely environment pollution and equipment corrosion which are caused by separation of biological printing from culturing systems. The integrated system can achieve synchronous printing of various cells and cytoskeletons in a biological printing system, namely integration of 3D printing and culturing. Cell activity in a printing process and functions and differentiation of printed cells can be ensured and are protected from being influenced by outer environments. The integrated system adopts a design that culturing and printing driving are separated. Printing nozzles and a clamp are embedded in the biological culturing system, and therefore a sterile culture environment is protected from being damaged by printing equipment and the outer environment on the basis of ensuring barrier-free printing, and integration of high-precision cell printing and culturing is achieved. Special requirements of biological culturing temperature and humidity on materials, dimension, designs, and the like of workbench components are reduced through the integrated system. The integrated system improves positioning precision of a workbench, increases the speed, and the like, prolongs the service lifetime of a driving module, and greatly reduces the cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Nerve conduit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104689376AImmune rejectionFree from virus transmissionTubular organ implantsMedicineElectrospinning
The invention provides a nerve conduit. The nerve conduit is characterized by comprising an inner layer, an outer layer and a cavity; the outer surface of the inner layer is wrapped with the outer layer; the cavity is formed between the inner layer and the outer layer; the inner layer is a hydrophilic cytoskeleton layer manufactured by the electrostatic spinning method; the outer layer is a hydrophobic nerve conduit skeleton layer by the electrostatic spinning method; the cavity is used for storing a bioactive factor solution. The nerve conduit has the characteristics of being proper in strength and hardness, degradable, capable of providing proper neurotrophic active substances, ideal in double-layer or multi-layer structure, semi-permeable, low in cost, short in production cycle, easy to be stored and transported, free of viruses, free of immunological rejection or extremely small in immunological rejection, and wide in applicable scope; the requirement on nerve regeneration process can be met well.
Owner:邹蓉
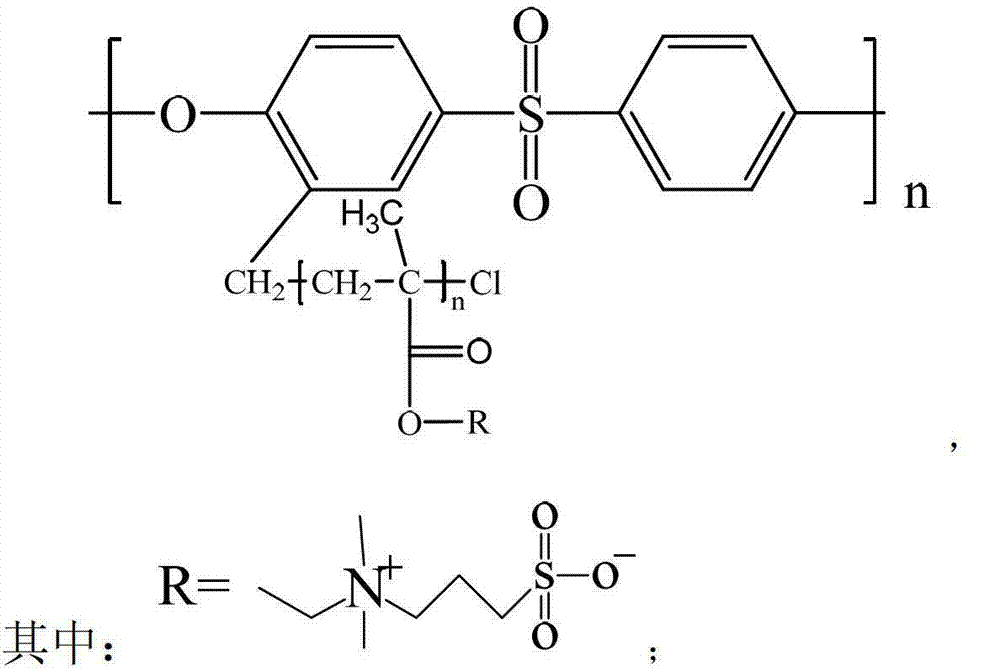
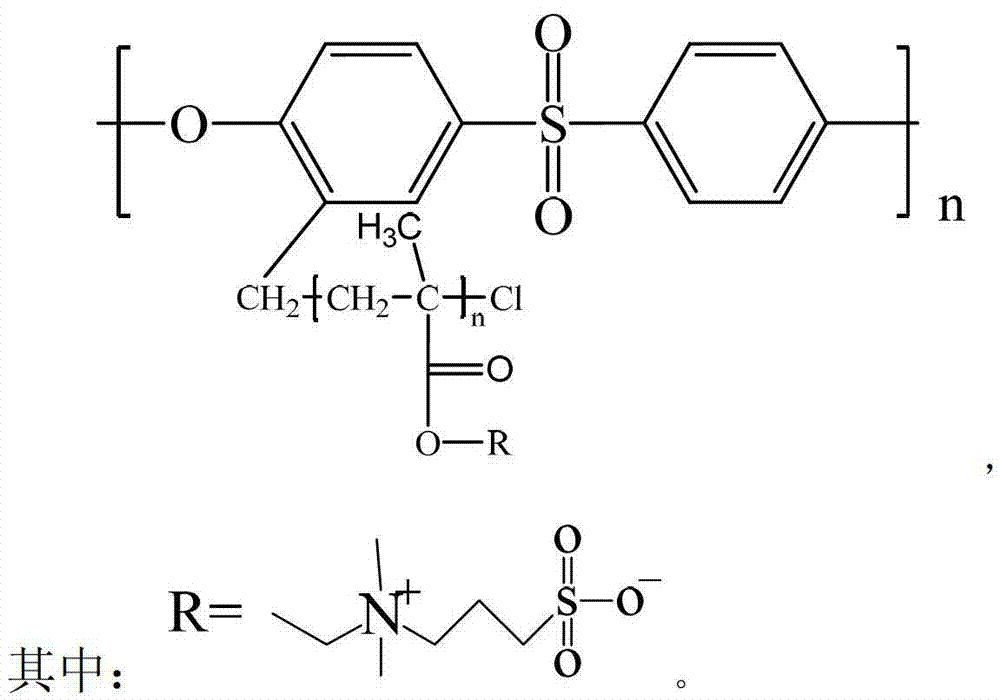
Sulphobetaine metacrylic acid ester grafted polysulfone copolymer as well as preparation method and application of polysulfone copolymer
The invention discloses a sulphobetaine metacrylic acid ester grafted polysulfone copolymer as well as a preparation method and an application of the polysulfone copolymer. The copolymer disclosed by the invention is prepared by implementing solution radical polymerization under the action of a catalyst by taking SBMA (Sulphobetaine Metacrylic Acid) and PSU (Polysulfone) as raw materials and dimethylsulfoxide as a solvent. The copolymer disclosed by the invention is a white amorphous solid at normal temperature, can be dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide and N-methylpyrrolidone and cannot be dissolved in water and alcohol. The copolymer and the PSU can be prepared to flat sheet membranes and hollow fiber membranes to a scale. Due to the excellent capability of resisting pollutants such as protein and soterocyte, the flat sheet membranes and the hollow fiber membranes prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used as materials contacted to the blood, cytoskeletons, separated biomass fermentation solution materials and water treatment materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Antibody induced cell membrane wounding
ActiveUS20060153854A1Enhanced cell membrane wounding and killing of cellReduced viabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntigenCell Surface Antigens
Compositions and methods for inducing cell membrane wounding, cell permeabilization and cell killing are provided. The composition comprises a polyvalent agent that binds to a highly expressed cell surface antigen present on the surface of a cell. Preferably, the cell surface antigen is associated with the cytoskeleton of the cell. A preferred polyvalent agent is an IgM, and enhanced cell wounding and killing can be provided by the addition of a crosslinking agent. At sublethal concentrations in vivo, the cell wounding antibodies permeabilize cells and dramatically enhance response to chemotherapeutic agents, even in patients refractory to the chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:MCURE BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Livestock embryo vitrifying freeze process on metal surface
InactiveCN101066052AImprove survival ratePromote commercial applicationDead animal preservationEmbryoDomestic animal
The present invention is livestock embryo vitrifying freeze process on metal surface, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The livestock embryo vitrifying freeze process includes replacing freeze protectant for liquid inside and outside the embryo cell and fast freezing of the embryo liquid drop. During the fast freezing, the embryo liquid drop is dropped onto the exposed upper surface of one metal block with lower part soaked inside liquid nitrogen. The present invention can cool embryo in high speed while avoiding contamination of impurity in liquid nitrogen to the embryo. Besides, adding cytochalasin B as cytoskeleton protectant into the frozen liquid can raise the freezeproof capacity of the embryo and raise vitrification freezing effect. The present invention is used for freezing livestock embryo.
Owner:BEIJING JINXIU DADI AGRI CO LTD
Cell-based composite materials with programmed structures and functions
ActiveUS9273305B1Stabilized structure and functionStable structureSamplingOn/in inorganic carrierLipid formationEntire cell
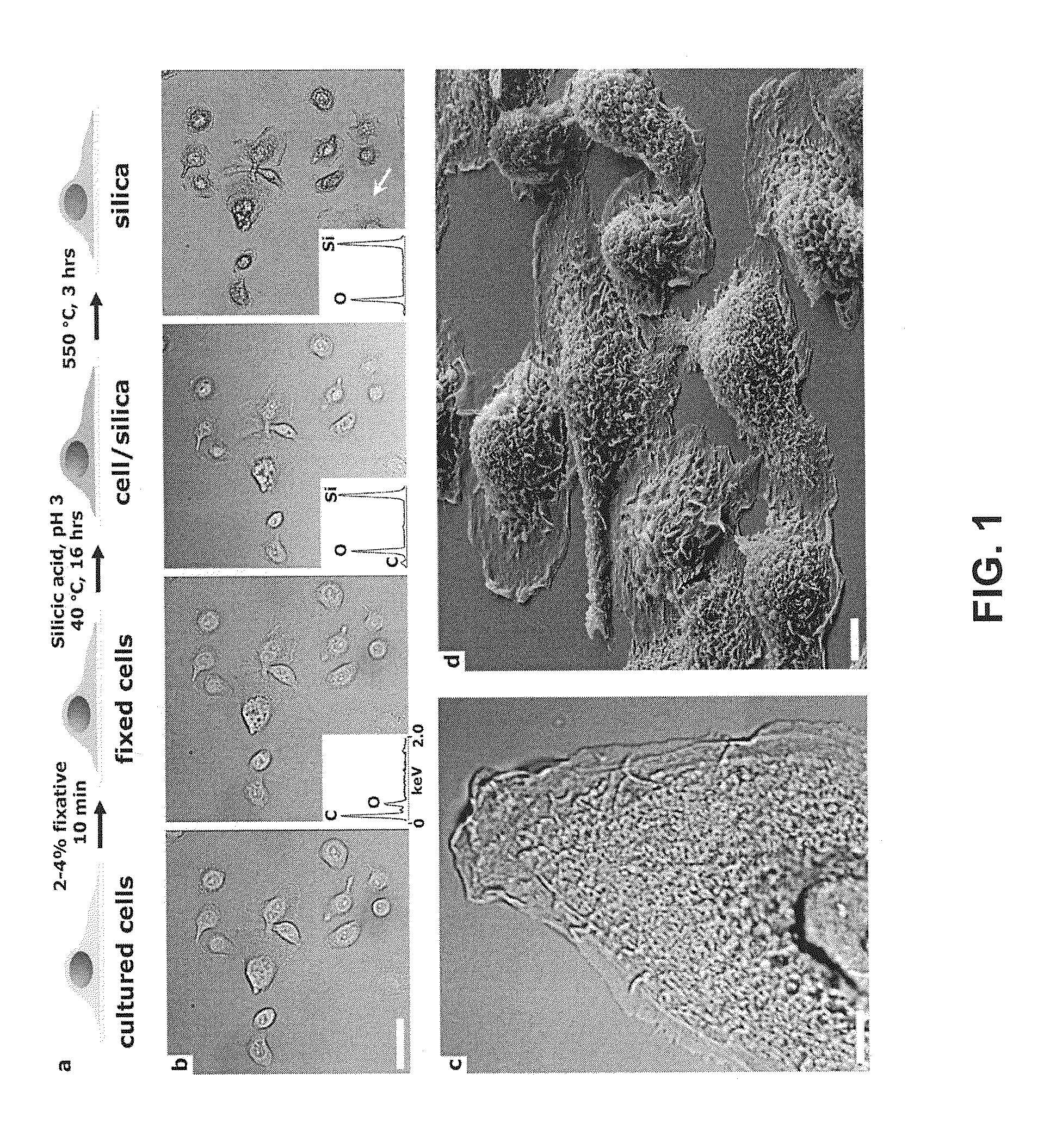
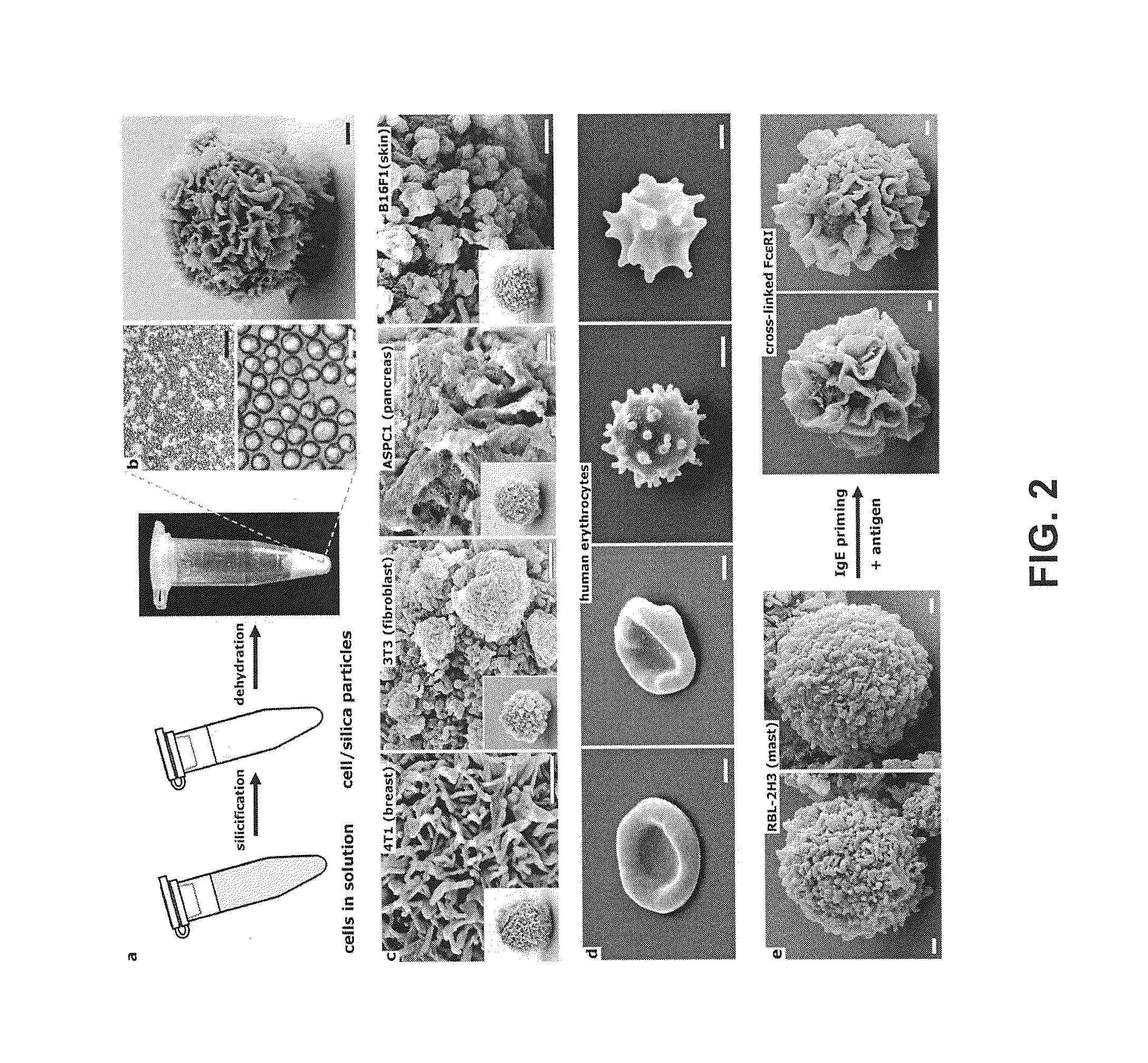
The present invention is directed to the use of silicic acid to transform biological materials, including cellular architecture into inorganic materials to provide biocomposites (nanomaterials) with stabilized structure and function. In the present invention, there has been discovered a means to stabilize the structure and function of biological materials, including cells, biomolecules, peptides, proteins (especially including enzymes), lipids, lipid vesicles, polysaccharides, cytoskeletal filaments, tissue and organs with silicic acid such that these materials may be used as biocomposites. In many instances, these materials retain their original biological activity and may be used in harsh conditions which would otherwise destroy the integrity of the biological material. In certain instances, these biomaterials may be storage stable for long periods of time and reconstituted after storage to return the biological material back to its original form. In addition, by exposing an entire cell to form CSCs, the CSCs may function to provide a unique system to study enzymes or a cascade of enzymes which are otherwise unavailable.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
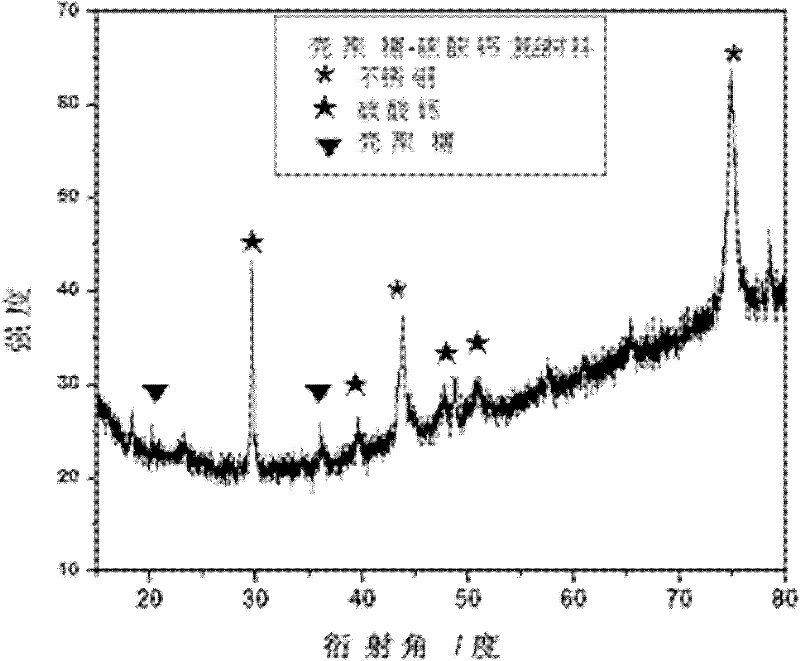
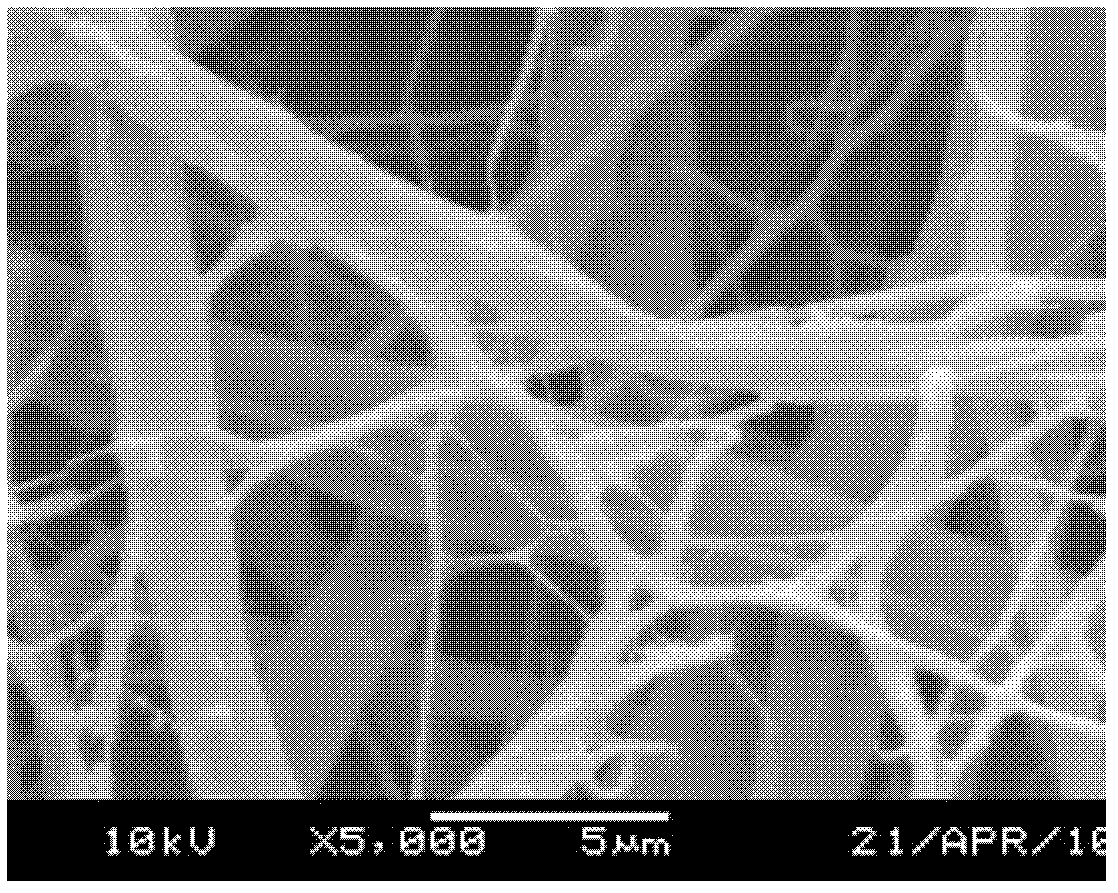
Three-dimensional network-like chitosan-calcium carbonate nano composite material as well as preparation method and cell compatibility thereof
InactiveCN102343115ACompact structureEvenly distributedElectrolytic coatingsTissue/virus culture apparatusCalcium Chloride HexahydrateBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a three-dimensional network-like chitosan-calcium carbonate nano composite material as well as a preparation method and cell compatibility thereof. In the preparation method, the chitosan-calcium carbonate nano composite material is prepared by taking chitosan as a carbon source, calcium chloride dehydrate, ammonium bicarbonate and secondary distilled water as raw materials on the surface of stainless steel by virtue of a one-step coelectrodeposition method. The biocompatibility of the chitosan-calcium carbonate network-like nano composite structure is studied by virtue of in-vitro cell culture. The electrodeposition method is simple and controllable; and the chitosan-calcium carbonate fibrous network-like structure is firmly combined with a substrate, and has strong mechanical performance and excellent biocompatibility. A good experimental result is achieved by using the chitosan-calcium carbonate fibrous network-like structure as a cytoskeleton material. The preparation method is simple in process, low in cost and environmentally-friendly; and the three-dimensional network-like chitosan-calcium carbonate nano composite material is in accordance with the standard of a biomaterial of a cell culture medium in tissue engineering, and can be applied to bone repair.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Detection conjugate
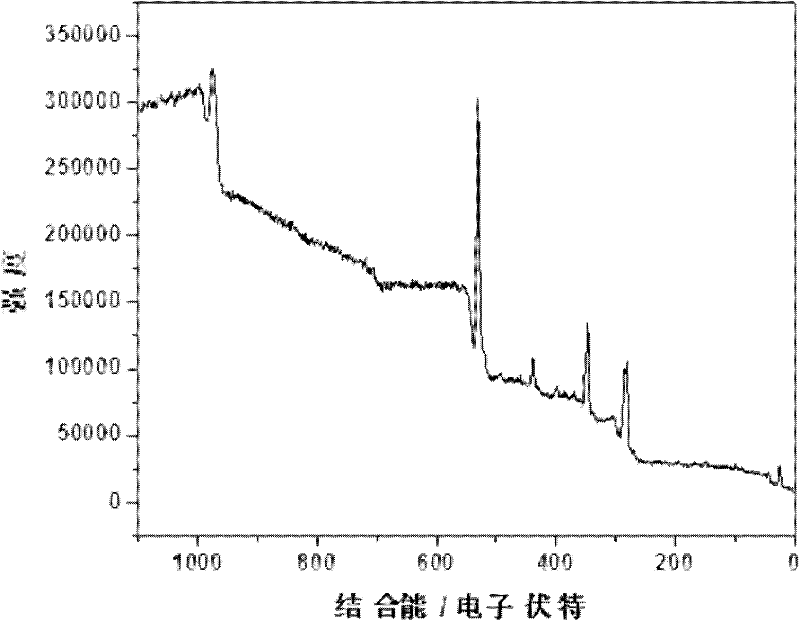
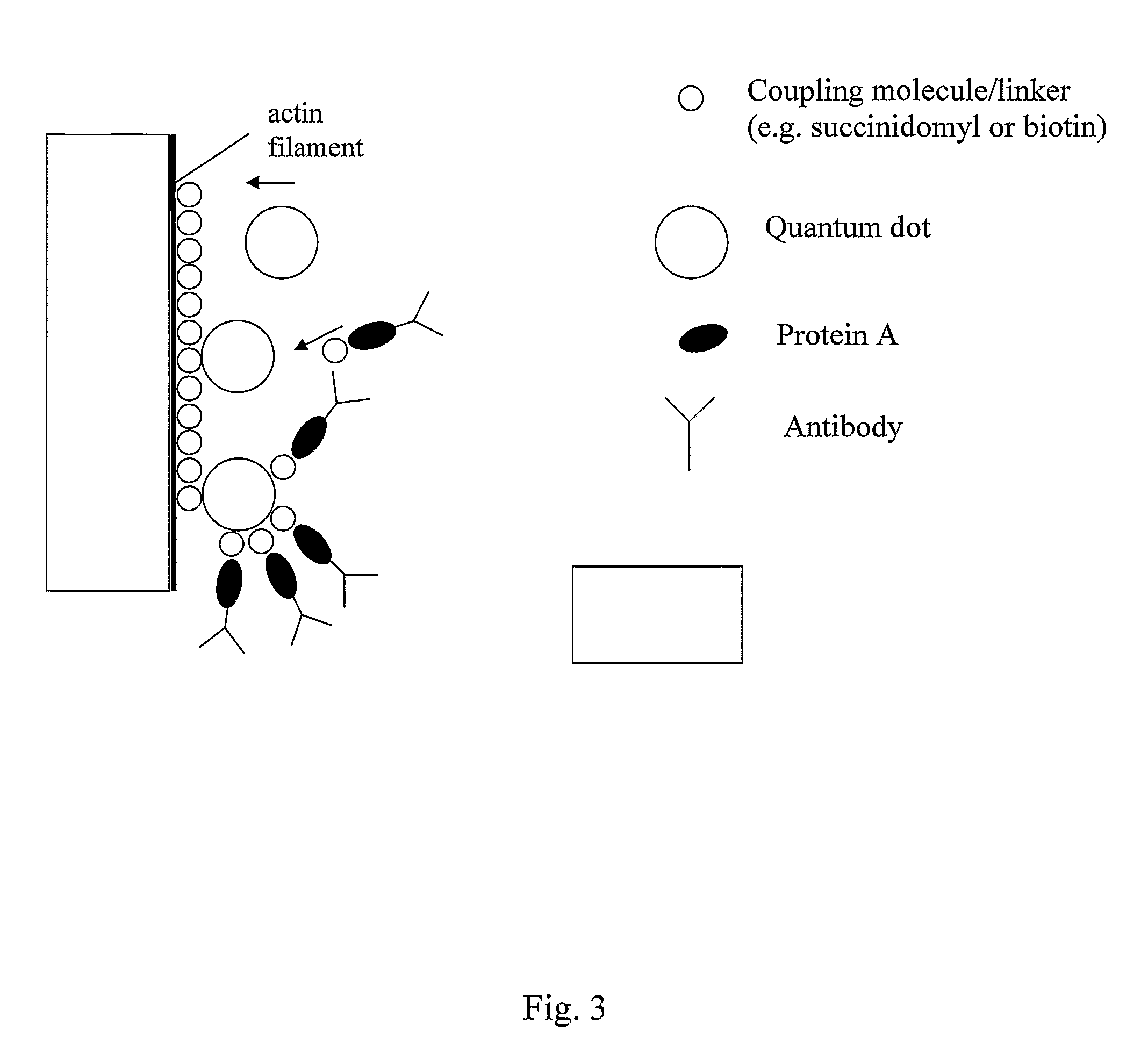
InactiveUS8658381B2High sensitivityLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsActin myofilamentCytoskeletal Filaments
The invention relates to a detection conjugate composed of a filament fragment, e.g. a cytoskeletal filament such as actin filaments or microtubules, and recognition elements bound to this fragment as well as kits comprising said detection conjugate and methods how to use said detection conjugate as well as the use for the detection of one or more compounds present within a sample, such as a biological sample.
Owner:MANSSON ALF +1
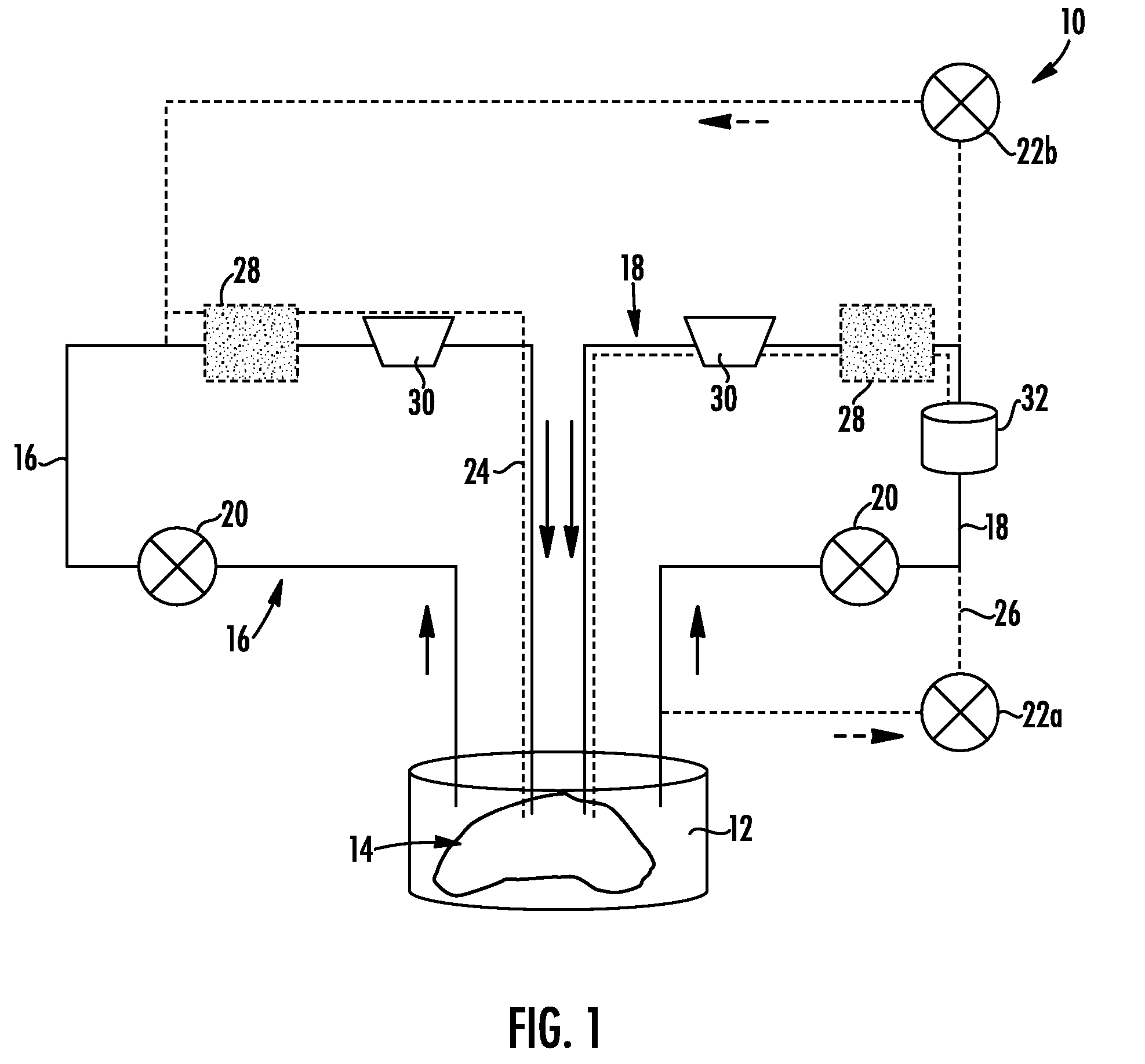
Composition and Method for the Restoration and Preservation of Transplant Organs Procured from DCD Donors
ActiveUS20070026376A1Improve preservationImprove viabilityDead animal preservationMachine perfusionOrgan Viability
The present invention provides a perfusion solution comprising specific metabolic agents, antioxidant agents, and membrane stabilizer agents that can help improve preservation, organ viability, and in some cases recover organs that would otherwise being unusable for transplantation. In a further embodiment, the perfusion solution can be used in combination with hypothermic machine perfusion. It has been found that combination of the perfusion solution and hypothermic machine perfusion can help prevent or reduce further damage to the organ and restore the organ's anti-oxidant system, stabilize the cellular cytoskeleton and cellular membranes, inhibit arachidonic acid pathway, provide oncotic support, reduce interstitial edema formation, and help restore energy stores within the organ. As a result, the method can be used to improve the viability of otherwise marginal donor organs.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
Preparation method of temperature-sensitive cellulose quaternary ammonium salt/beta-sodium glycerophosphate hydrogel
ActiveCN102432895AEasy to joinGood biocompatibilityQuaternary ammonium cationSodium glycerophosphate
The invention which discloses a preparation method of a temperature-sensitive cellulose quaternary ammonium salt / beta-sodium glycerophosphate hydrogel belongs to fields of the biological technology and tissue engineering. A 10-60wt% sodium glycerophosphate solution is added to a 1.5-5.5wt% cellulose quaternary ammonium salt solution drop by drop at 0-20DEG C to prepare a cellulose quaternary ammonium salt / beta-sodium glycerophosphate mixed solution, and the mixed solution is rapidly cured at the body temperature to form the hydrogel. The liquid state of the cellulose quaternary ammonium salt / beta-sodium glycerophosphate solution can be maintained at room temperature, so it is very convenient to add cells, proteins, enzymes and therapeutic medicines to the solution, thereby the obtained solution can be used as a cytoskeleton material or a medicine carrier. The cellulose derivative which has very good biological compatibility is very suitable for the fields of the biological technology and tissue engineering.
Owner:HUBEI GEDIAN HUMANWELL PHARMA EXCIPENTS
Cherkasky fusion proteins containing antibody-, antigen- and microtubule-binding regions and immune response-triggering regions
The invention relates to the fields of tumour physiology and biotechnology. The object of the invention is to develop effective and selective novel fusion proteins and fusion protein-antibody complexes against various types of leukaemia and solid tumours. Selectivity is achieved by cell-specific or tumour-specific ligands of the fusion proteins or by antibodies of the fusion protein-antibody complexes. Effectiveness is achieved on the one hand by the direct binding of the microtubules or cytoskeleton elements to the microtubule-binding regions and on the other hand by induction, as well as by the reinforcement of the immune reaction by regions that trigger the immune reaction on the target cells.
Owner:CHERKASKY ALEXANDER
Three-dimensional non-support bone repairing patch and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a three-dimensional non-support bone repairing patch and a preparation method thereof. The patch is composed of nanometer fibre with an extracellular matrix, wherein the nanometer fibre is composed of polycaprolactone and polyglycolic acid which are blended in proportion by weight according to (1:9) to (9:1). The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving two polymers in an organic solvent, and stirring to prepare a transparent and uniform electrostatic spinning solution; spinning the spinning solution by utilizing an electrostatic spinning process, and receiving to obtain a fibre support; and soaking, drying, tailoring and disinfecting the fibre support, and culturing by utilizing marrow mesenchmal stem cells to manufacture a three-dimensional bone patch repairing material. The three-dimensional non-support repairing patch provided by the invention can regulate pore diameter and void percentage at discretion according to need, can be used as nerve conduits and tissue engineering cytoskeletons of bones, blood vessels, hearts, nerves and the like, and is suitable for growth of multiple cells; and the preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, and good application prospects.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Cytoskeletal active compounds, compositions and use
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
Polyether sulfone copolymer modified by sulphobetaine metacrylic acid ester as well as preparation method and application of polyether sulfone copolymer
The invention discloses a polyether sulfone copolymer modified by sulphobetaine metacrylic acid ester as well as a preparation method and an application of the polyether sulfone copolymer. The polyether sulfone copolymer disclosed by the invention is prepared by taking sulphobetaine metacrylic acid ester and polyether sulfone as raw materials, taking dimethylsulfoxide as a solvent and carrying out free radical polymerization under the action of a catalyst. The polyether sulfone copolymer disclosed by the invention is white solid at normal temperature, is soluble in dimethylsulfoxide and N-methylpyrrolidone and is insoluble in water, methyl alcohol and alcohol. Flat sheet membranes and hollow fiber membranes prepared by the polyether sulfone copolymer disclosed by the invention are excellent in capability of resisting pollutants such as protein and thrombocyte, so that the flat sheet membranes and the hollow fiber membranes can be used as materials directly contacted to the blood, cytoskeletons, separated organism fermentation liquid or water treatment materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Small-bore artificial blood vessel with micropatterned inner wall
InactiveCN107789666ASolve the mechanical propertiesFix compatibility issuesCoatingsProsthesisBlood Vessel TissueBiological materials
The invention relates to the technical field of biological materials, and provides a small-bore artificial blood vessel with a micropatterned inner wall. The small-bore artificial blood vessel has a two-layer structure. An outer layer is an electrospun microfiber layer, the mechanical properties of the small-bore artificial blood vessel are improved, and the stability of a tubular structure is maintained. An inner layer is a coating layer having a micro-patterned structure, so adhesion, spreading and growth of endothelial cells are facilitated, the extension of an endothelial cytoskeleton canbe promoted and the oriented growth of the endothelial cells can be guided, and the normal exertion of cell functions is ensured. However, the mechanical properties of conventional products and researched small-bore artificial blood vessels are relatively poor, the clinical requirements cannot be completely met, and the oriented growth of the endothelial cells and the normal exertion of the cell functions cannot be promoted. The small-bore artificial blood vessel with the micropatterned inner wall has good mechanical and biological properties, and is suitable for repairing and replacing small-bore blood vessel tissues with injury or lesion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Biocompatible bone graft and preparation method thereof
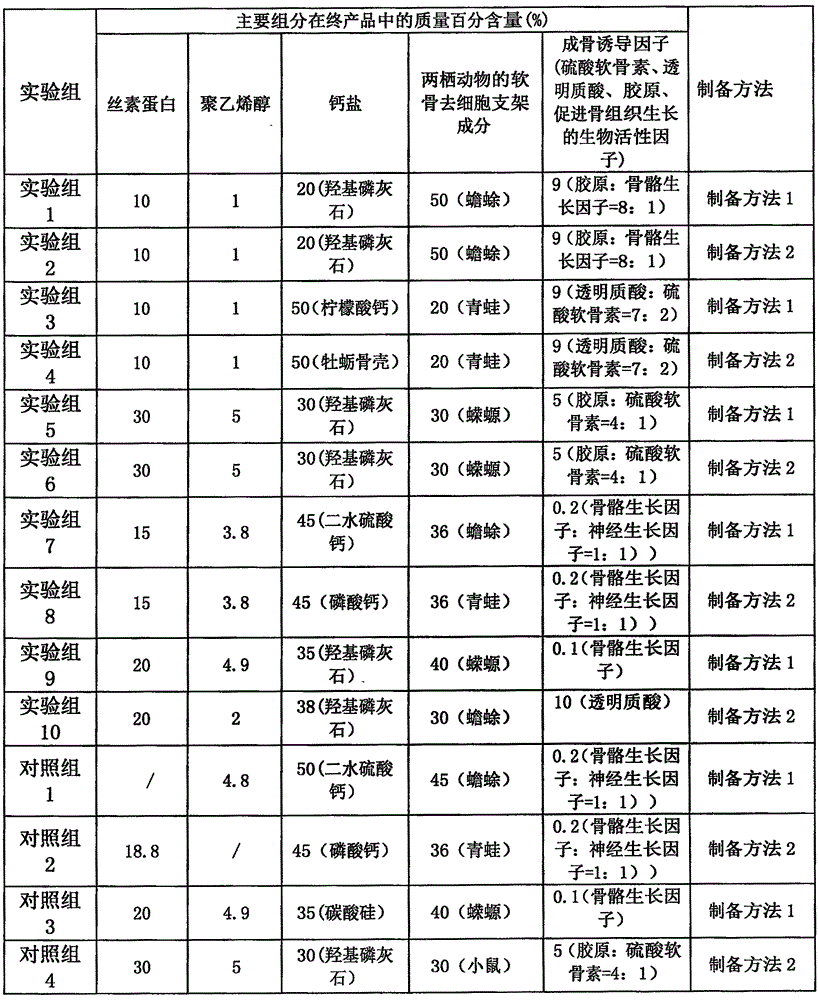
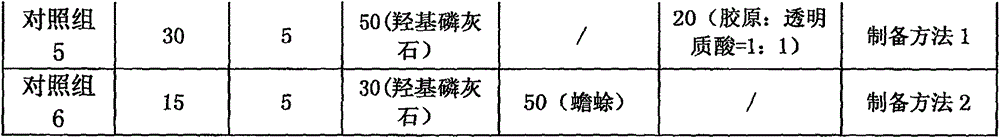
ActiveCN106492281AWide variety of sourcesIncrease elastic strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisCartilage cellsPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides a biocompatible bone graft. The main components of the stent include silk fibroin, polyvinyl alcohol, calcium salt, cartilage cytoskeleton-removed component of amphibian and an osteogenic induction factor; and the mechanical strength and degradation speed of the bone graft can be controlled by changing the proportion of the components. The biocompatible bone graft is of a three-dimensional solid shape and has good mechanical properties; and dense holes in the surface promote the adhesion and regeneration of cartilage cells. In the preparation process of the biocompatible bone graft, heating is not needed, no chemical or enzyme crosslinking agent is used, and the activity of each component is maintained. The biocompatible bone graft gives play to the collaborative advantage of each component and is applied to the substitute graft of bone tissue defect.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Dynamic bidirectional-stretch in-situ online-observation cell biomechanics loading device
ActiveCN103184144ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell biomechanicsMorphologic change
The invention discloses a dynamic bidirectional-stretch in-situ online-observation cell biomechanics loading device. The loading device comprises a base film for the growth of an adherent cell used for being observed; two fixing clips for clamping the two sides of the base film respectively, two displacement support arms for supporting the fixing clips respectively, and a driving part, wherein the fixing clips are movably arranged on a rail, and the driving part is used for driving the displacement support arms to perform symmetrical opposite-direction displacement on the rail so as to conduct bidirectional-stretch on the base film. According to the invention, by conducting the stretch with a certain frequency and a certain range on the cell growing on the biocompatible film, morphologic change, cytoskeleton reorganization, signal transduction and other responses of the cell in different action times can be observed.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
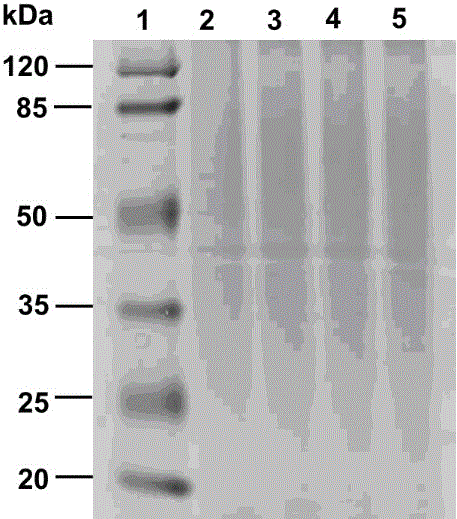
Gel electrophoresis method useful for resolution and characterization of nerve tissue ultra high molecular weight protein aggregates
The instant disclosure describes an electrophoretic procedure capable of resolving and isolating ultra high molecular weight (MW) protein aggregates from nerve tissue. The procedure is based on the use of composite agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (CAPAGE) and resolves proteins and protein aggregates over the range of from approximately 225 kDa to approximately 30,000 kDa. Triton X-100 precipitation is used to obtain a cytoskeleton protein fraction that is subsequently resuspended and subjected to gel electrophoresis. This method demonstrates that a protein aggregate of approximately 30,000 kDa is characteristic of normal murine spinal cord tissue and that the amount of said protein aggregate is increased in spinal cord homogenate obtained from transgenic mice bearing copies of a mutant human gene characteristic of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. This method for separating nerve tissue ultra high MW cytoskeleton protein aggregates can prove useful in a variety of future biophysical and pharmacological studies related to the etiologies of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diseases based on expansions in tandem DNA repeats, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedreich's ataxia, giant axon neuropathy, juvenile ceroid-lipofuscinosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetic polyneuropathy and Down's syndrome.
Owner:SHAPIRO HOWARD K
Preparation method for antibacterial collagen
The invention relates to a preparation method for antibacterial collagen. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving collagen in a buffer solution and controlling the mass concentration of collagen to be 0.1%-15%, thereby obtaining a collagen solution; (2) adding modified triclosan into the collagen solution obtained in the step (1), increasing the temperature to 25-50 DEG C and reacting for 0.1-48h, thereby obtaining an antibacterial collagen solution; (3) dialyzing the antibacterial collagen solution obtained in the step (2) for 0.5-96h at 0-4 DEG C, and then freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the antibacterial collagen. The antibacterial collagen prepared according to the method has the advantages that the antibacterial components are firmly combined with collagen through covalent bonds; the antibacterial effect is long-lasting; if the antibacterial collagen is prepared into the biomedical materials, including antibacterial collagen gel, collagen sponge, wound dressing, cytoskeleton of tissue engineering, and the like, the material has an antibacterial effect in the whole use period.
Owner:山东济清科技服务有限公司
Method for observing microtubule structure of cytoskeleton in liver tissue of animals
ActiveCN104133068AEasy to masterPrecise positioningPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingExtensibilityMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a method for observing a microtubule structure of a cytoskeleton in a liver tissue of animals. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning the liver tissue of animals with PBS, fixing for 8-12h with 4v / v% of paraformaldehyde water solution, and carrying out paraffin embedding and serial sectioning; (2) dewaxing the obtained paraffin sections, and carrying out antigen retrieval, closing and fluorescently labeled antibody incubation; (3) for specimens sealed by glycerol, observing through a laser scanning confocal microscope within 24h, respectively exciting 488 and 4' 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole under 488nm and 405nm, and observing and shooting at once at room temperature in a dark room environment. The method is fast, simple, intuitive and accurate, is strong in practicality and extensibility, and can research the dose-effect changing relationship of the cytoskeleton under stress of pollutants.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
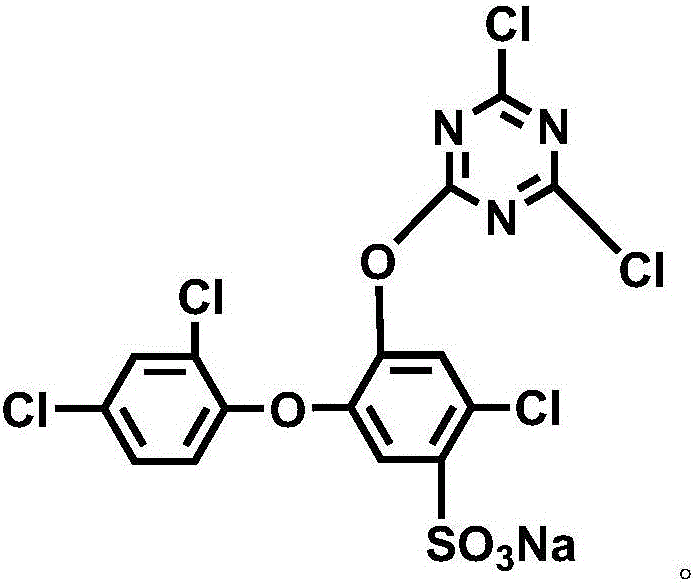
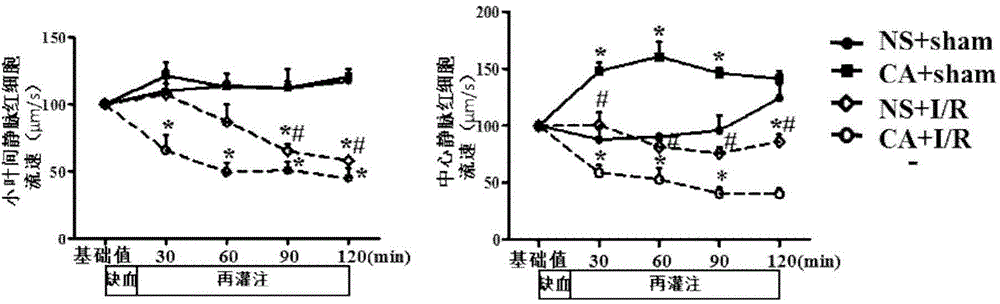
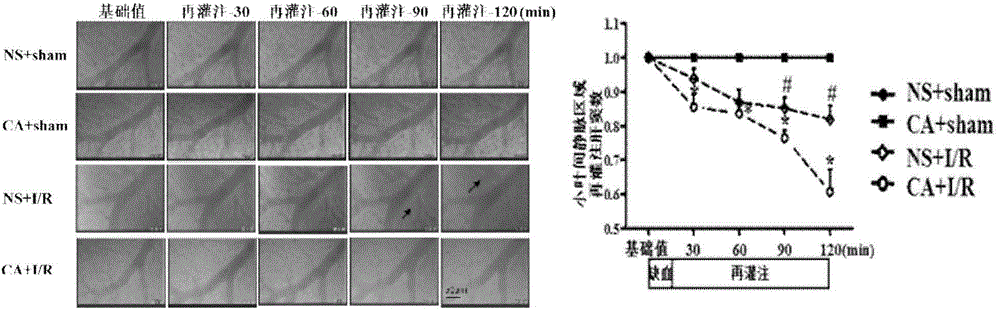
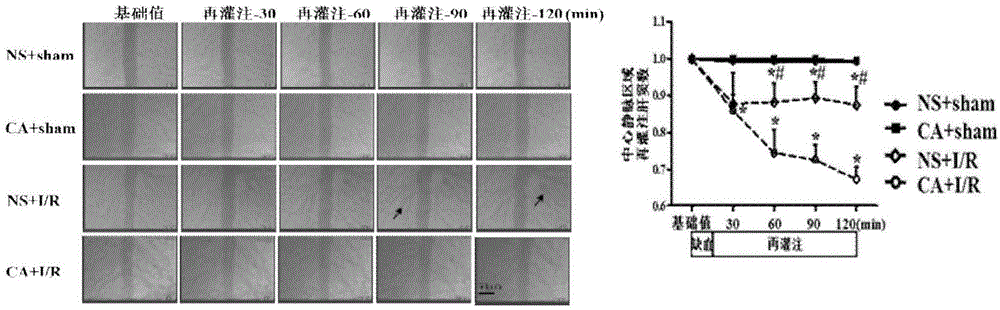
Application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury
The invention relates to an application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury. Through a series of observation of caffeic acid on hepatic ischemia reperfusion rats, caffeic acid is found to improve the hepatic surface blood flow quantity by the action routes: AMPK[alpha] phosphorylation and PKC[delta] membrane translocation are inhibited, NADPH subunit P41 and P47 membrane translocation is inhibited and NADPH-derived peroxides are inhibited; the activity of a hepatic ischemia reperfusion rat mitochondria respiratory chain is improved, and peroxide production caused by mitochondria injury is reduced, so as to increase the production of ATP; hepatocyte apoptosis caused by ischemia reperfusion is inhibited; and hepatic cell internal cytoskeleton injury caused by ischemia reperfusion is attenuated. The new application in preparation of the drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
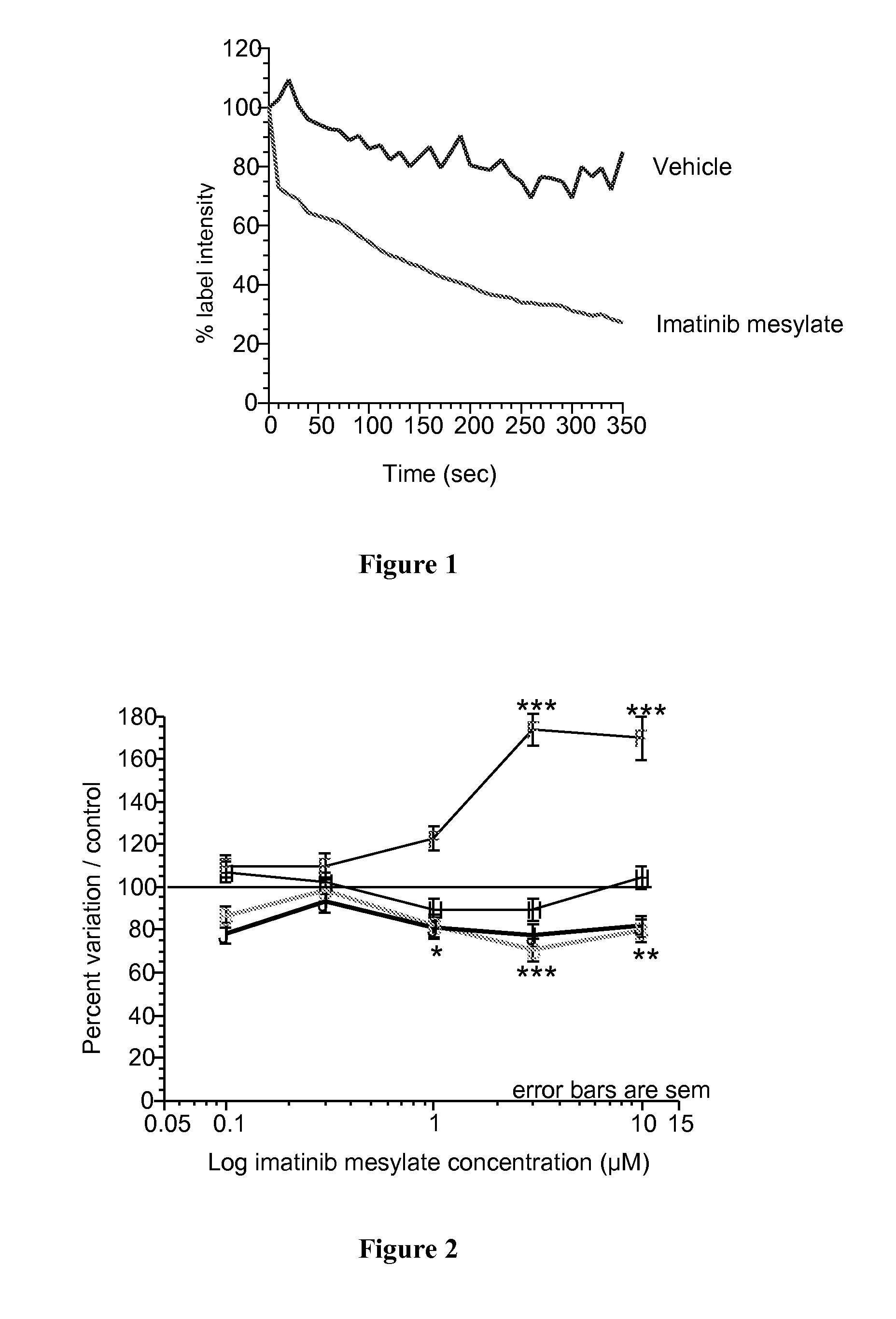
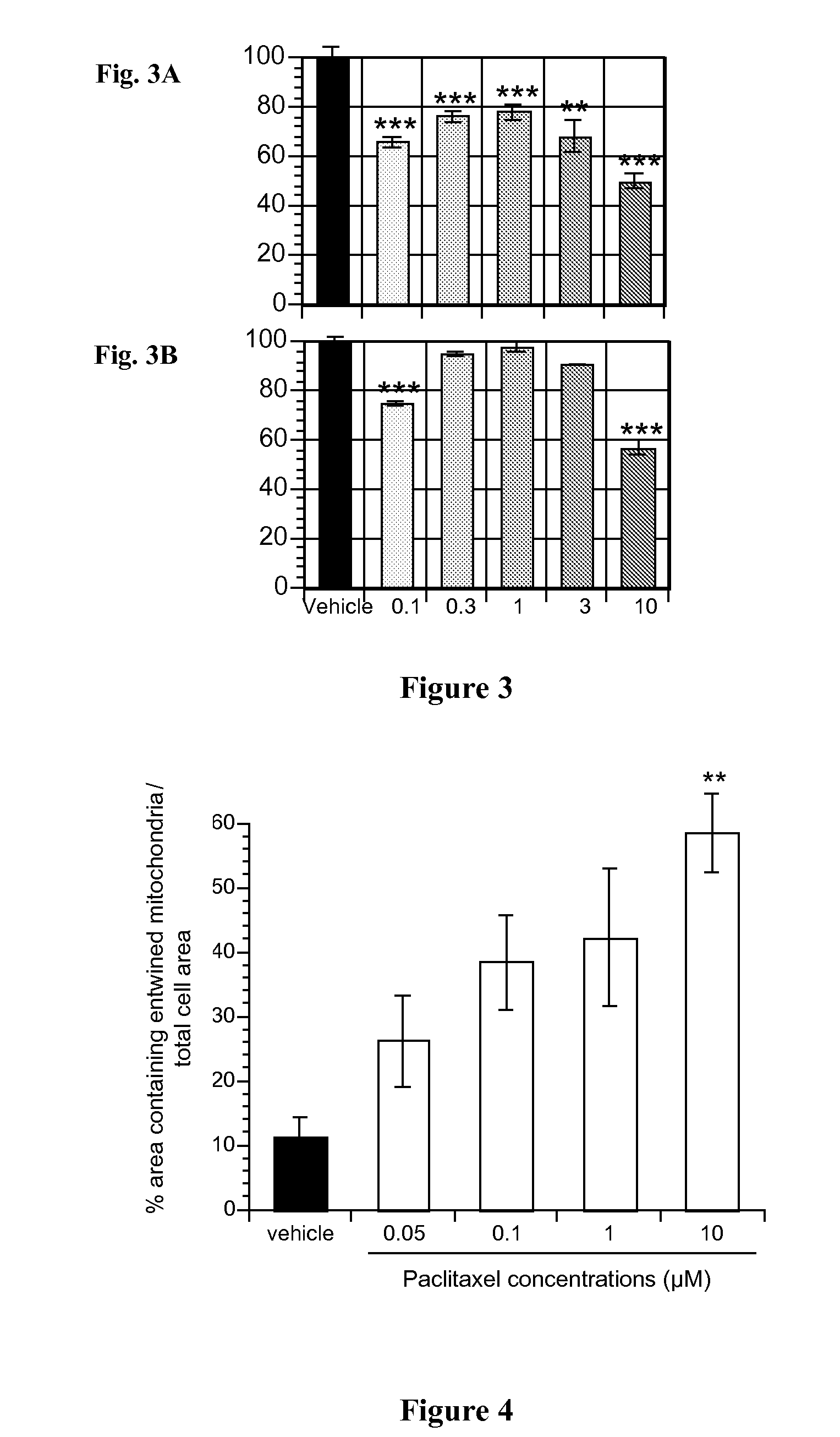
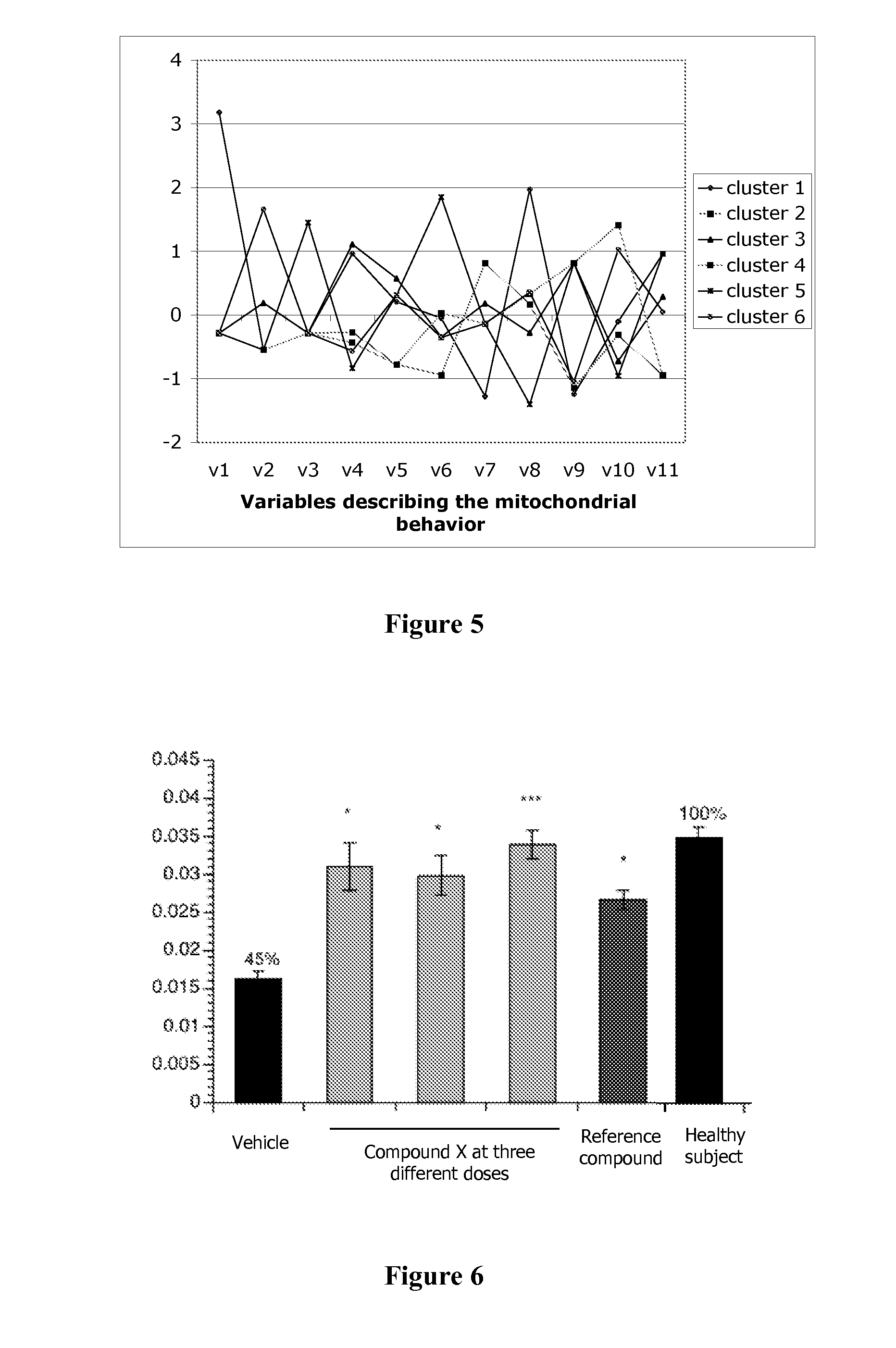
Method to predict toxicity using the analysis of dynamic organelle behaviour
The present invention provides an in vitro method to predict the effect of an exogenous element on an animal or human organism. This method is based on the analysis of variations of an organelle behaviour represented by at least two characteristics in isolated cells induced by the contact with the exogenous element and the determination of the cluster membership of the exogenous element which is representative of the effect of said element. Analyzed characteristics are selected from the group consisting of the motility, the morphology, the relationship with the cell cytoskeleton and the membrane permeability of said organelle. This method may be used to predict the efficacy or the toxicity of an element, such as a drug.
Owner:INNOVATIVE CONCEPTS IN DRUG DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com