Method and system for predictive modeling
A predictive model and predictive analysis technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as not allowing user experiments, long response time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
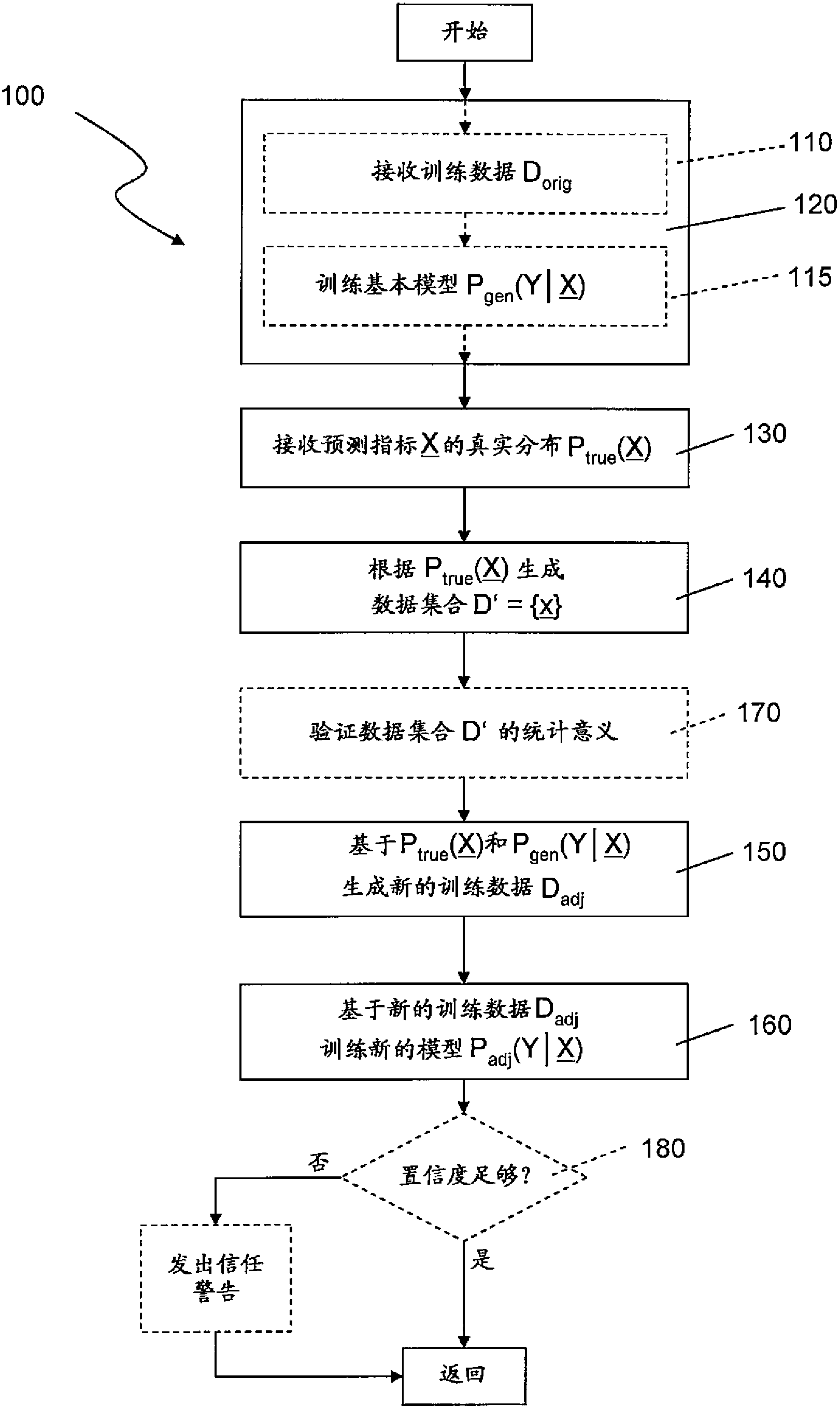
[0024] Figure 1a Depicts the probability distribution P(Y| X A schematic flow diagram of a method 100 for predicting a given feature X The probability of a specific outcome Y for a predefined set. here, X refers to a vector of variables (indicators) describing the influencer and a single variable Y (value) describing the prediction. Note that in the following, variables will be referred to by the term "feature" X , "predictor" and "indicator" are interchangeable; and the variable Y will be referred to by the terms "value", "label" or "prediction". All variables can be numeric or categorical. If the value variable Y is categorical, the method solves a classification problem, and if the value variable Y is numerical, the method solves a regression problem. Both cases can be handled in a similar manner.
[0025] The modeling process is based on the original set of training data D orig ;D orig Contains have the form ( x , a tuple of y), where x ∈ X (which is, x is an ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com