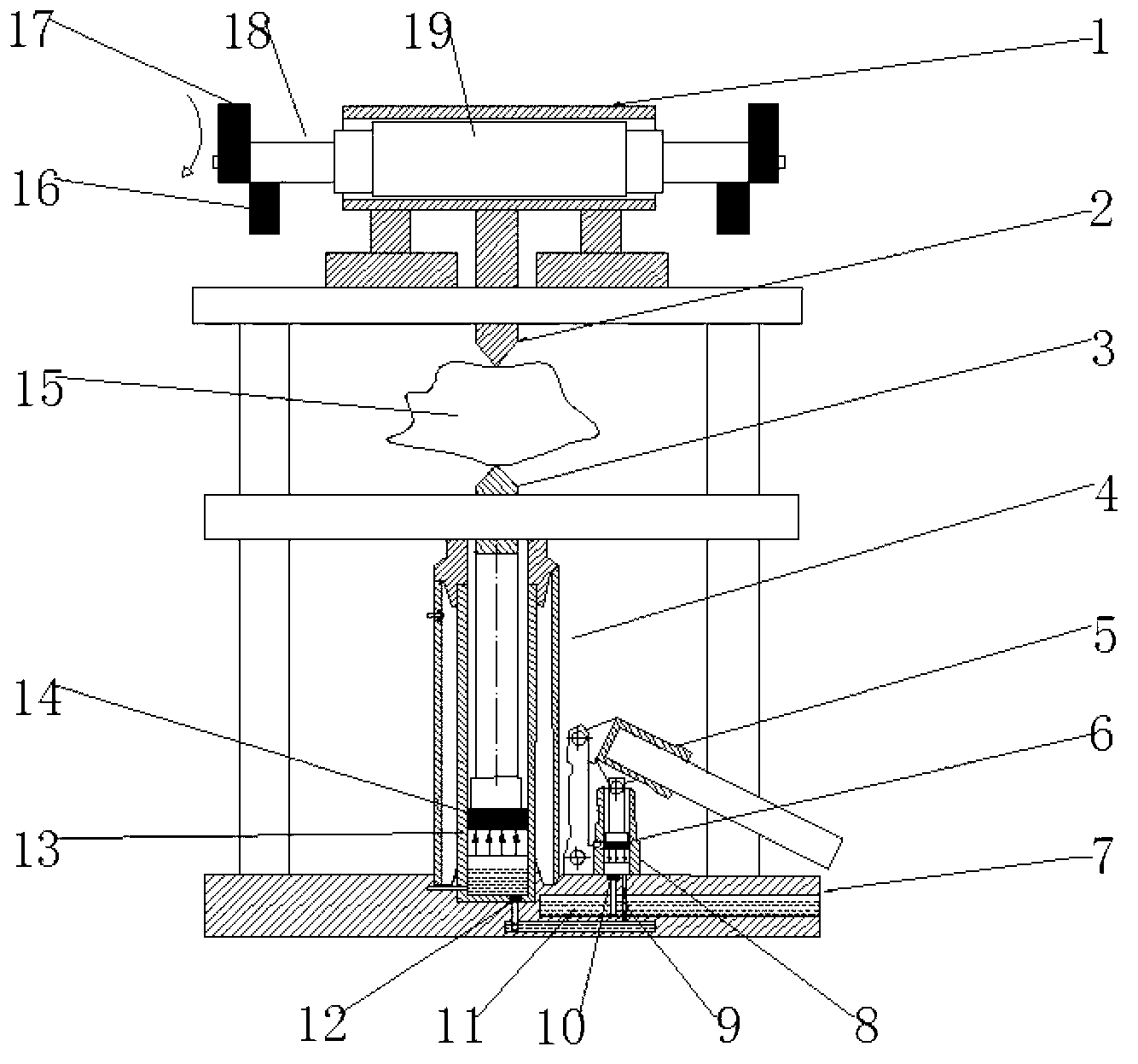
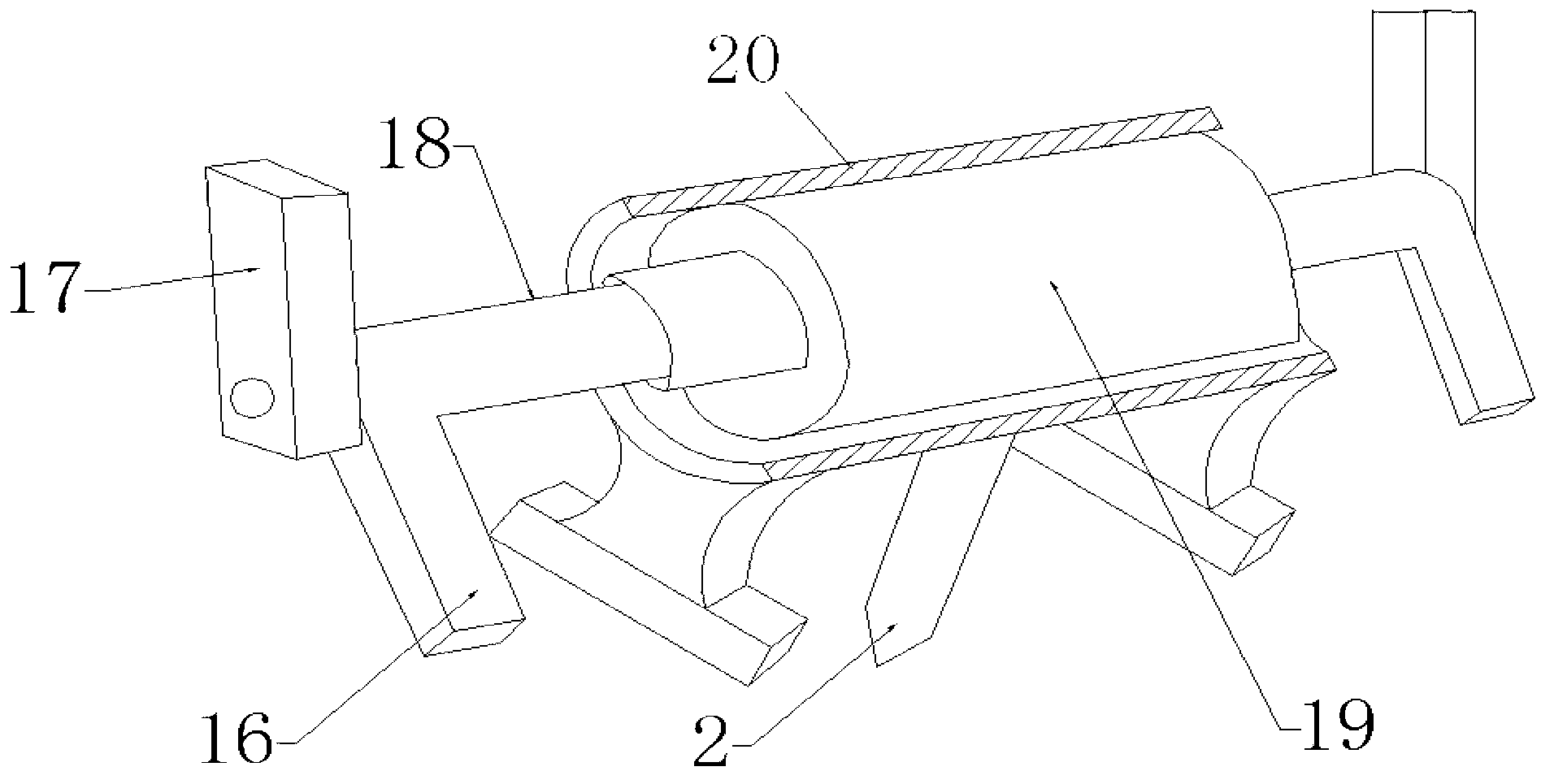
Vibration type point load tester
A point load and tester technology, applied in the direction of testing material strength by applying repetitive force/pulsation force, testing material strength by applying stable tension/compression, etc., can solve the problem that the strength or failure performance cannot be given, and the sample is not considered Mechanical properties and other issues, to achieve the effect of light and easy to carry the instrument, and improve the speed of testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1. Utilize the device to study the point load strength of rock under static load
[0029] (1) Select one of the first group of specimens, take the direction of the minimum size of the specimen as the loading direction, place the specimen between the upper and lower pressure cones, and adjust the static pressure device to raise the lower pressure cone, and finally The upper and lower pressure cones are in close contact with the upper and lower surfaces of the irregular block.
[0030] (2) Record the distance D between the vertices of the upper and lower pressure cones, with an error of no more than ±2%; record the minimum specimen width W perpendicular to the loading direction, with an error of no more than ±5%; if the sides are not parallel to each other, Then W presses (W 1 +W 2 ) / 2 calculation.
[0031] (3) Increase the load steadily so that the specimen fails within 10 to 60 seconds. Record the reading F of the oil pressure gauge when the specimen is d...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2. Using the device to study the influence of different exciting forces on the rock point load strength
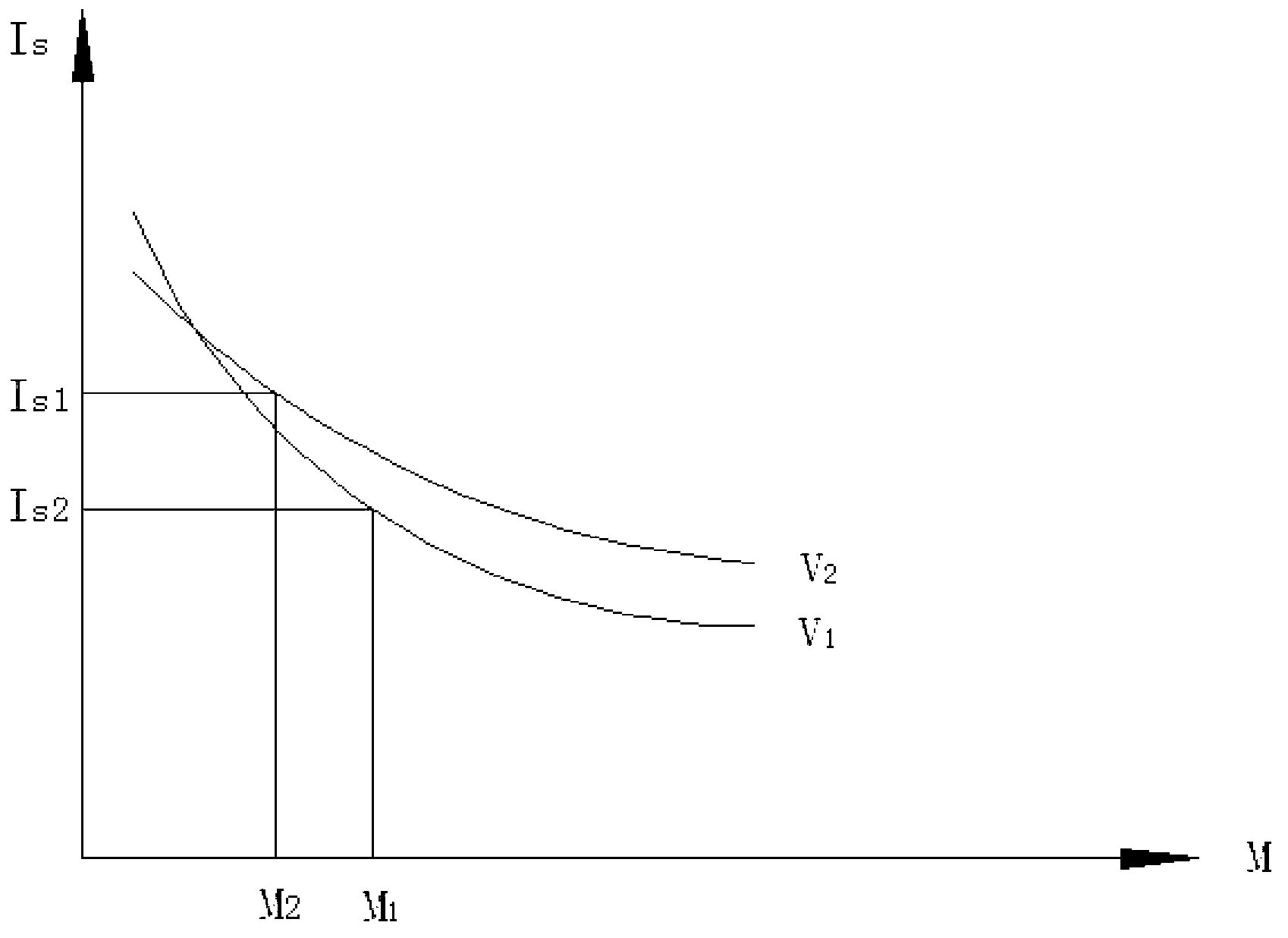
[0047] Take one test piece from the second set of test pieces. After installing the test piece, turn on the vibration motor, keep the vibration frequency unchanged, and choose an exciting force M 1 , apply the static load at the same loading rate as the static load test until the specimen fails. Follow the same steps to keep the vibration frequency ν 1 unchanged, changing the excitation force (M 2 , M 3 ...), to test other specimens.
[0048] During the experiment, in addition to recording the parameters F, W, and D of the specimen required for the above-mentioned static load experiment, it is also necessary to record the speed n of the vibration motor (for calculating the vibration frequency ν) and the exciting force M. See Appendix 2 for the experimental data recording form. The calculation method of the point load strength of the specimen is simi...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3. Using the device to study the influence of different vibration frequencies on the rock point load strength
[0051] Take one test piece from the third set of test pieces. After installing the test piece, turn on the vibration motor, keep the exciting force constant, and select a vibration frequency ν 1 , apply the static load at the same loading rate as the static load test until the specimen fails. Follow the same steps, keep the exciting force constant, change the vibration frequency (ν 2 、ν 3 ...) to complete the tests on other specimens.
[0052] During the experiment, in addition to recording the parameters F, W, and D of the specimen, it is also necessary to record the excitation force and speed n of the vibration motor (used to calculate the vibration frequency ν). See Appendix 3 for the experimental data recording form. The calculation method of the point load strength of the specimen is the same as in Example 2.
[0053] If the data in Appen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com