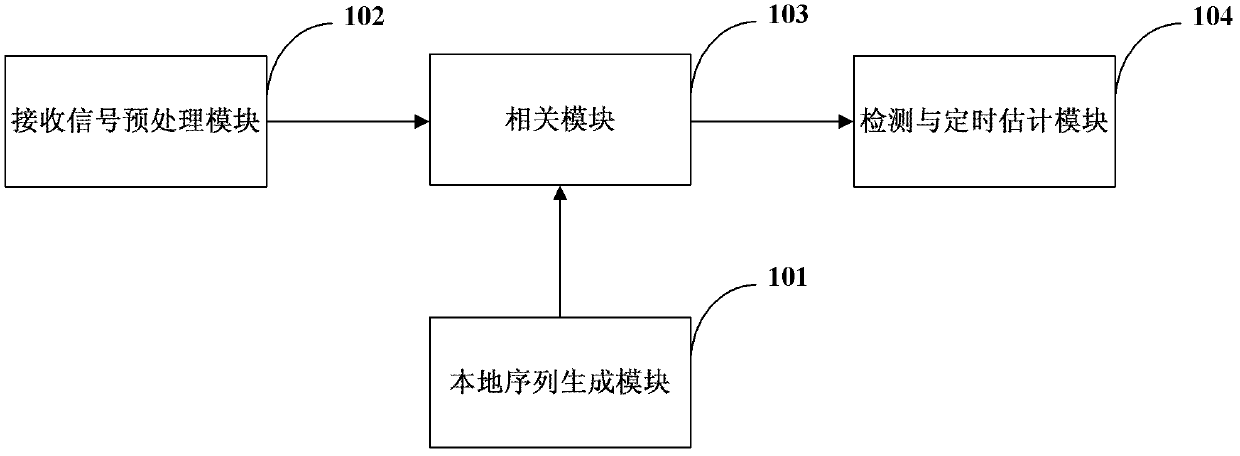
Method for inhibiting random access code false alarm
A technology of random access and random access preamble, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as the chance of users losing access, reduce the probability of multi-user normal access, and reduce the probability of multi-user detection, and achieve the effect of suppressing false alarms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
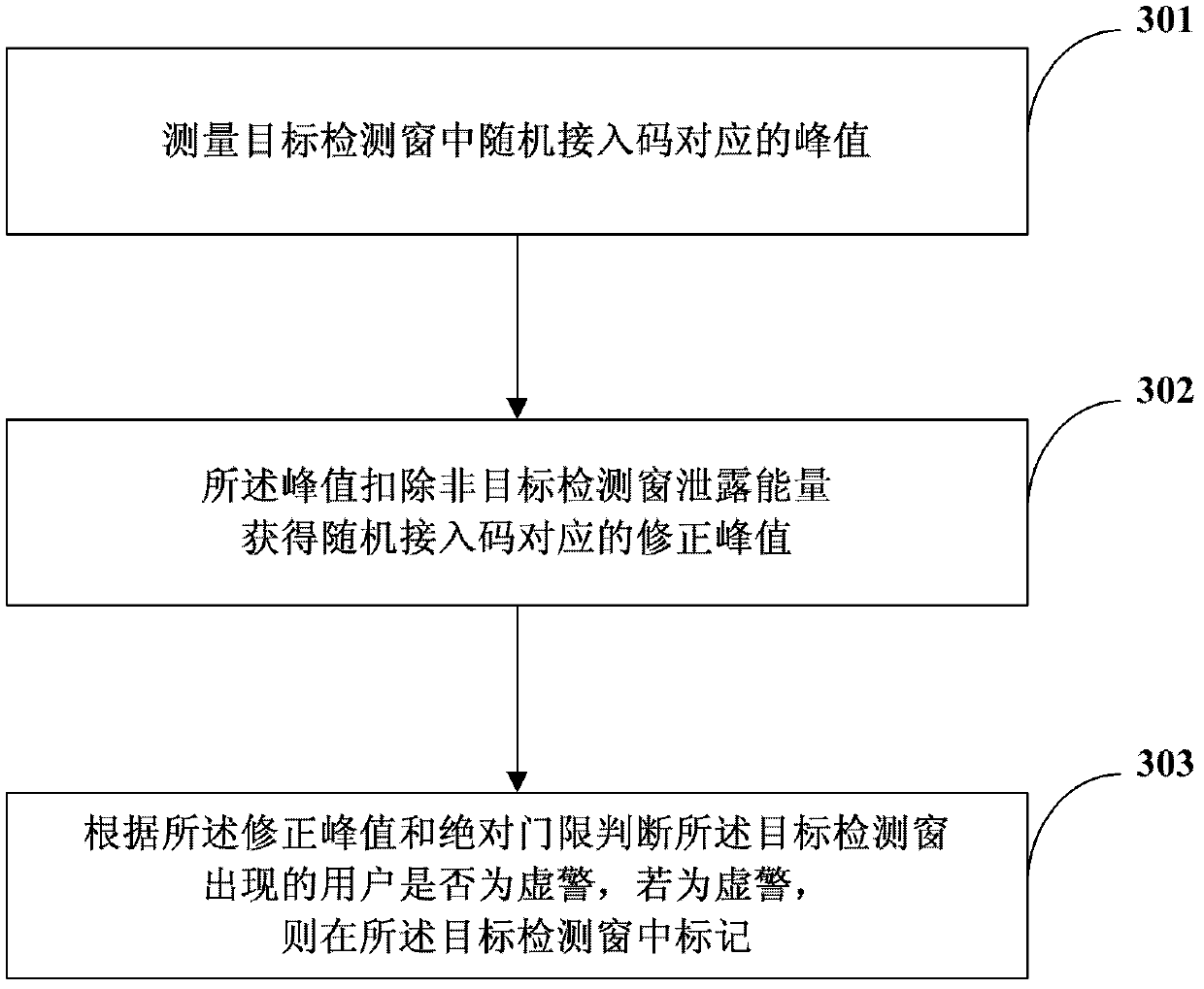
[0070] In the case of a high SNR, there are N detection windows corresponding to the root parameter u of the current random access code (detection window indexes are 1, 2, 3..., N). First, all detection windows are pre-detected to obtain the user's decision flag (flag=1 indicates that the peak value has been detected; flag=0 indicates that the peak value has not been detected).
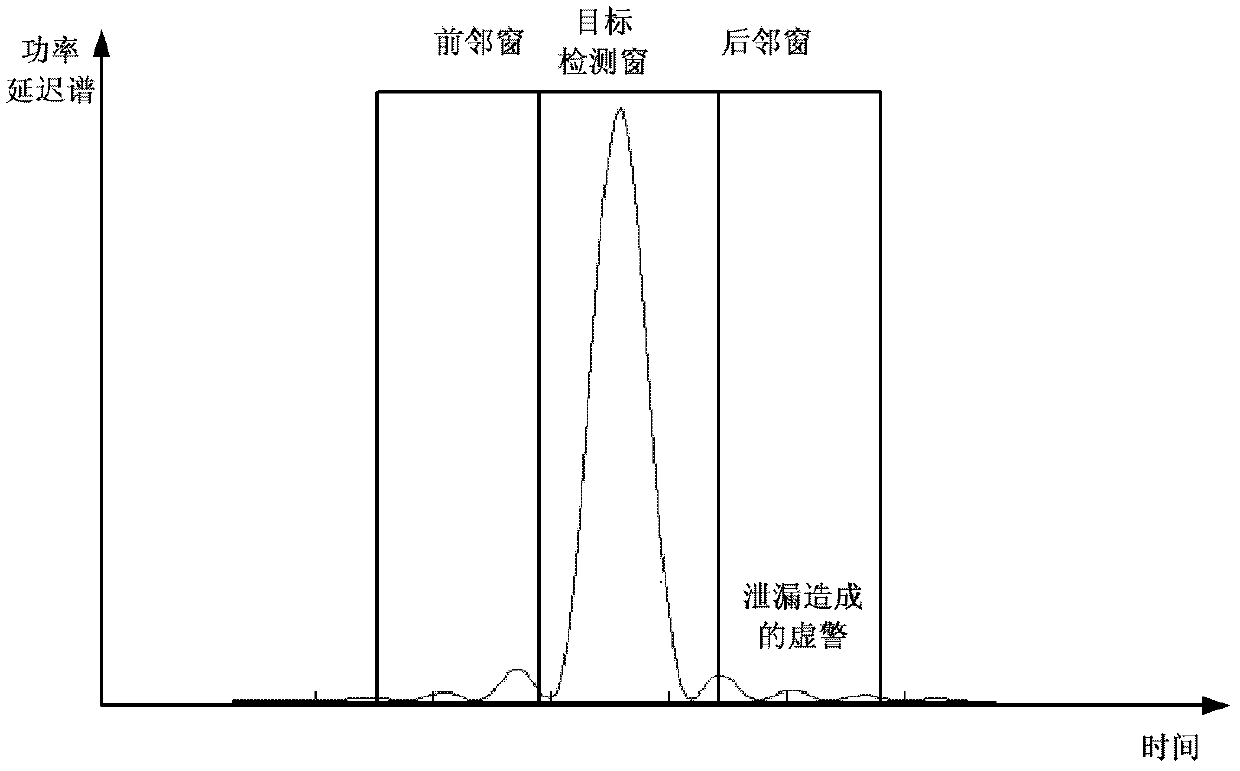
[0071] A user appears in the Kth detection window, and its pre-detection flag flag K = 1, the Kth detection window may be a real user, or it may be caused by the energy leakage of its adjacent detection windows.
[0072] The peak value (or other detection amount) of the Kth user is Maxvalue K , record its corrected peak value (or other detection amount) as Maxvalue_r K , Maxvalue_r K is the Maxvalue K It is obtained after deducting the possible adjacent window energy leakage in .
[0073] The transmitter transmits a random access preamble, and measures the peak value of each detection window. Af...
example 2
[0087] Both Example 2 and Embodiment 1 are applicable to the case of high signal-to-noise ratio. In the second embodiment, there are at least 3 adjacent windows, that is, N≥4. Because in specific cases, when the suppression factors include G1 and G2, the amount of calculation is too large. In order to avoid a large number of calculations, only considering the influence G2 between adjacent windows can set G2=0. The determination method of G1 is the same as that in the first embodiment. Of course, under the condition that the calculation amount is not considered and the accuracy is ensured, it is the best to adopt the solution in the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0089] In the environment of frequency offset (residual frequency offset and Doppler frequency shift), the detection window corresponding to the root parameter u is detected to obtain the user's decision flag flag. if flag K =1, the peak position is Maxindex K . Max index k ±(d u , 2d u ......nd u ) may cause false alarms in other detection windows. But as n increases, the leaked energy will become smaller and smaller. Therefore, when using single-window detection, the main consideration is the distance from the main peak ±d u The influence of the energy leakage at the position on other detection windows can be used to obtain the Flasealarm_index set of locations where flag=1 may cause false alarms for all users. If need to consider ±2d u ,3d u ......nd u Flasealarm_index can be expanded for the energy leakage at the position.
[0090] If the three-window combined detection is used, the user's judgment flag flag is obtained. When using three-window combined detectio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com