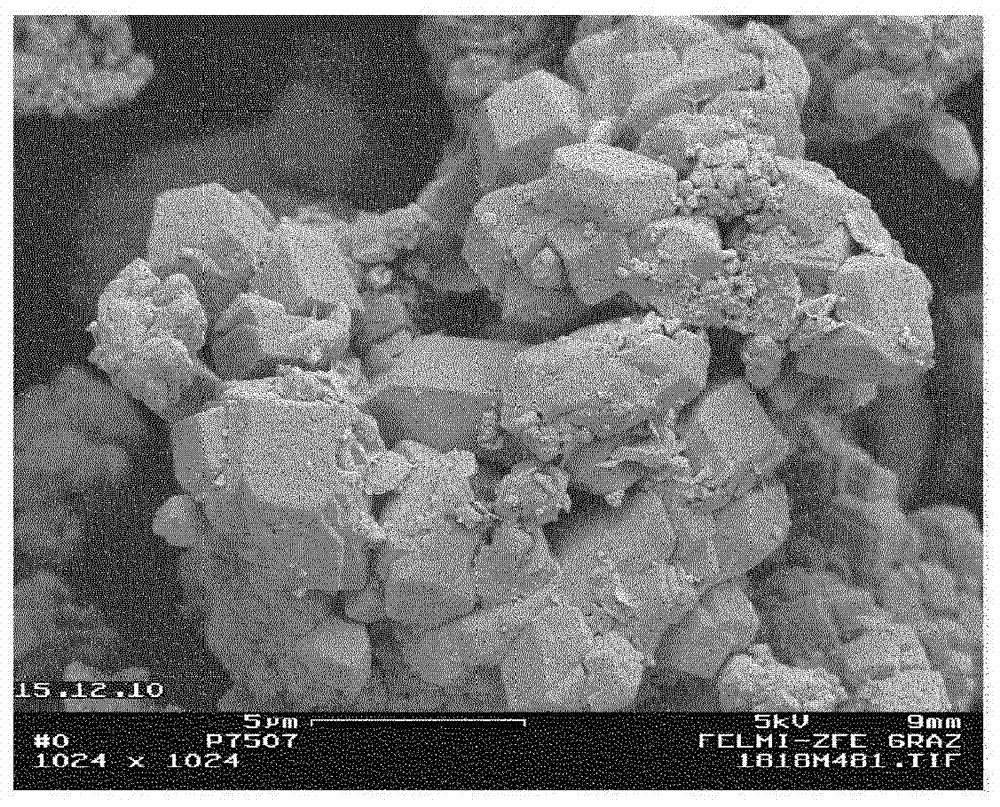
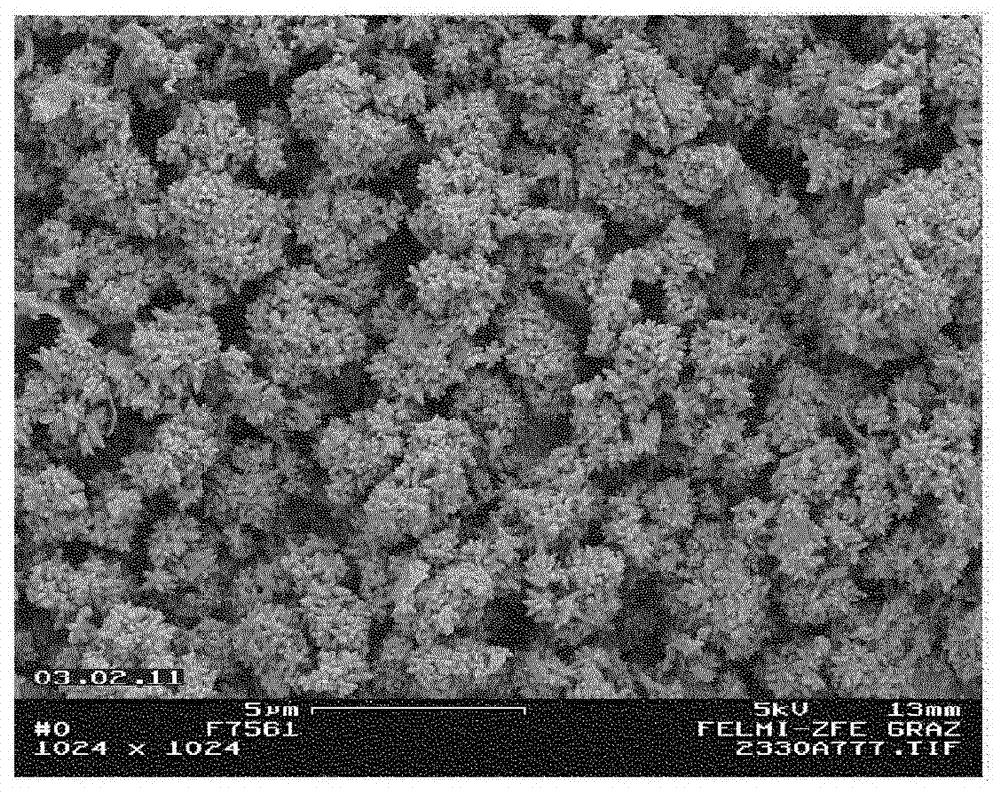
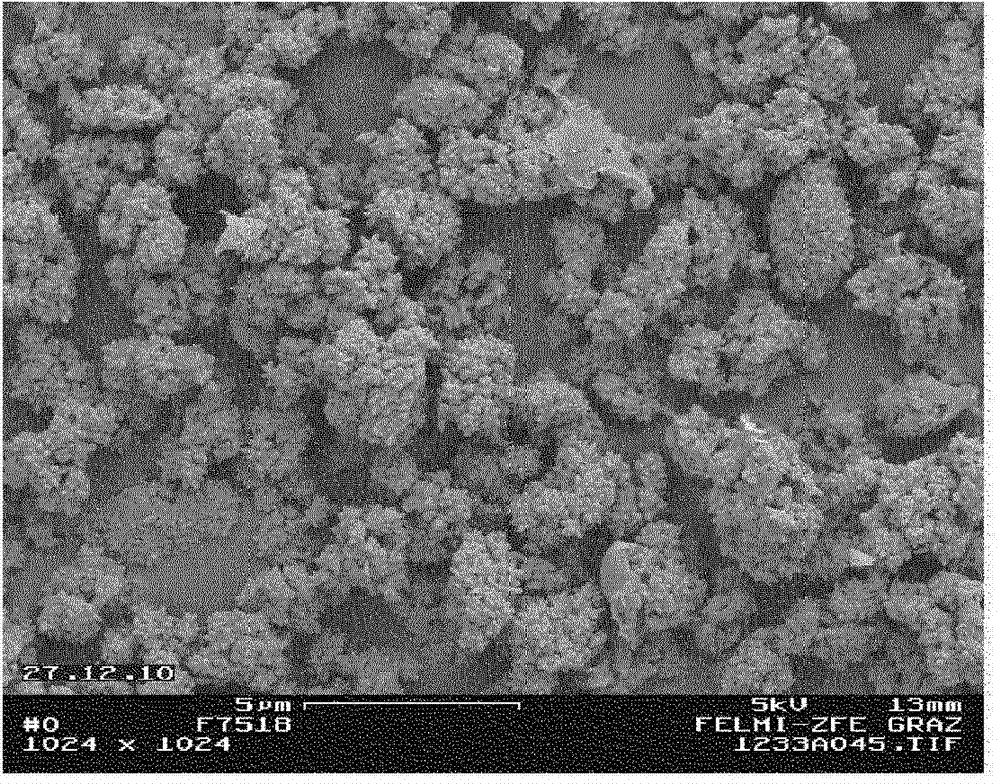
Precipitated calcium carbonate from pulp grinding waste with improved brightness, process for its manufacture and use thereof
A waste, whiteness technology, applied in the field of mineral pigments, can solve the problems that do not involve the properties of precipitated calcium carbonate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0081] The following examples are intended to illustrate specific embodiments of the invention and are not to be construed as limiting the invention in any way.
[0082] For the purposes of the present invention, the parameter d 50 The value of (%) is obtained from the particle size measurement values of which 50% by mass of the particles each have a diameter smaller than or equal to the value.
[0083]The term w / w refers to the mass fraction of the material and is defined as the material mass m mat Specific mass of the total mixture m tot score.
[0084] Measurement methods:
[0085] Suspension pH measurement
[0086] The pH of the suspension was measured at 25°C using a Mettler Toledo Seven Easy pH meter with a Mettler Toledo Expert Pro pH electrode measurement.
[0087] The instrument was first calibrated at three points (according to the segment method) using commercially available buffer solutions (from Aldrich) with pH values of 4, 7 and 10 at 20°C.
[0088...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 - Example of the invention
[0119] This example relates to the inventive process for the manufacture of calcium carbonate products starting from calcium carbonate obtained from pulp grinding waste, wherein the calcium carbonate obtained from pulp grinding waste is calcined to obtain pulp grinding waste lime (CaO), slaked, and subsequently The resulting milk of lime is carbonated and processed to obtain a specific pulp grinding waste precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) characterized by ultrafine discrete particles. The resulting material is then subjected to a carbonation reaction with an aqueous slurry of high-purity calcium hydroxide (the so-called "milk of lime").
Embodiment 1
[0120] The low-purity spent CaCO of embodiment 1 3(which is typically discharged from the chemical recovery process of kraft pulp milling of Klabin Papeís S.A., Telemaco Borba Mill) is calcined in a rotary kiln at a temperature in the range of 900°C to 1300°C and pre-crushed on a hammer mill to obtain Low-purity pulp grinding waste CaO. 200 kg of this spent CaO (quicklime) were added to 1800 liters of 70°C tap water in a stirred slaking reactor. The quicklime was slaked for 30 minutes under continuous stirring, and the resulting slurry ("milk of spent lime") was recovered in the form of an aqueous suspension of calcium hydroxide. 1800 liters of this milk of spent lime were added to the carbonator, and the temperature of the milk of spent lime was adjusted to 20°C. Before carbonation, 1.3 liters of a 70% w / w aqueous sugar alcohol solution (Sorbitol 80%, Brenntag CEE GmbH) was added.
[0121] Carbonation was carried out in the same manner as described in Example 1. The carbo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com