Modularized embedded control system for multi-finger myoelectric artificial hand with various sensing functions
An embedded control and sensing function technology, applied in the direction of electrical program control, comprehensive factory control, comprehensive factory control, etc., can solve the problems of poor real-time performance and large size, and achieve real-time improvement, volume reduction, and easy development, improvement and customization The effect of production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
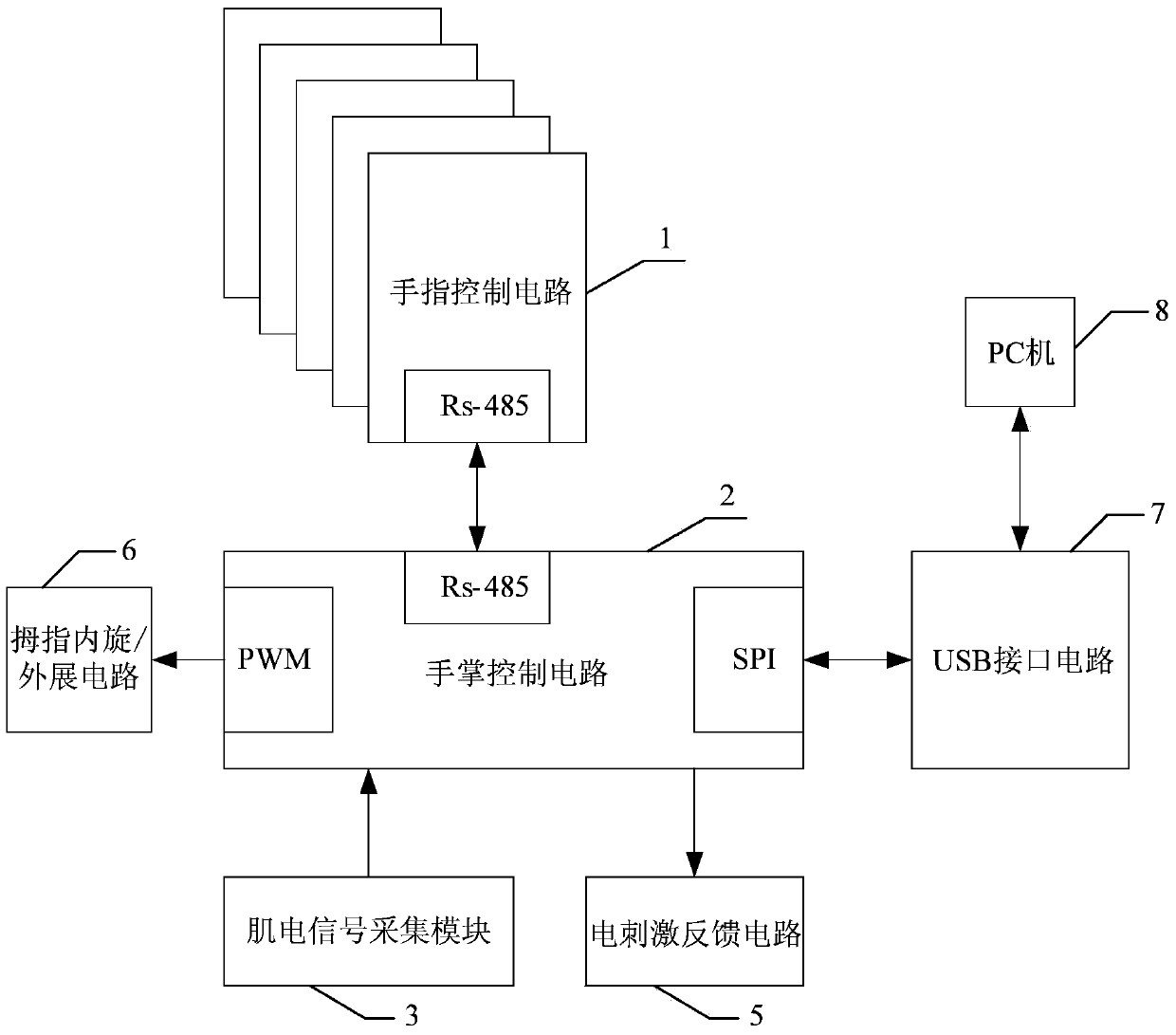
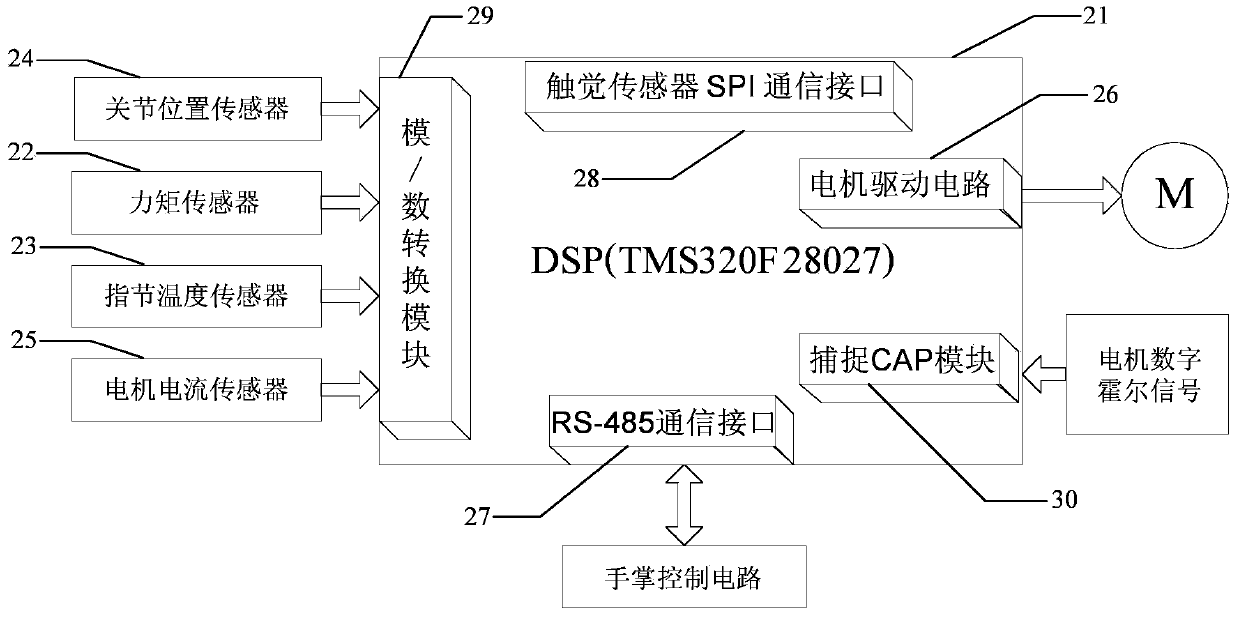
[0044] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figures 1 to 5Illustrate this specific embodiment, the multi-finger myoelectric prosthetic hand modular embedded control system with multiple sensory functions is characterized in that: it includes finger control circuit 1, palm control circuit 2, myoelectric signal acquisition module 3, thumb internal rotation / Outreach circuit 6, USB interface circuit 7 and PC 8;
[0045] The finger control circuit 1 includes a thumb control circuit, an index finger control circuit, a middle finger control circuit, a ring finger control circuit and a little finger control circuit;
[0046] The thumb control circuit is used to control the action of the thumb of the prosthetic hand, and is also used to communicate with the palm control circuit 2 through the RS-485 bus;
[0047] The index finger control circuit is used to control the action of the index finger of the prosthetic hand, and is also used to communicate with the palm control circ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
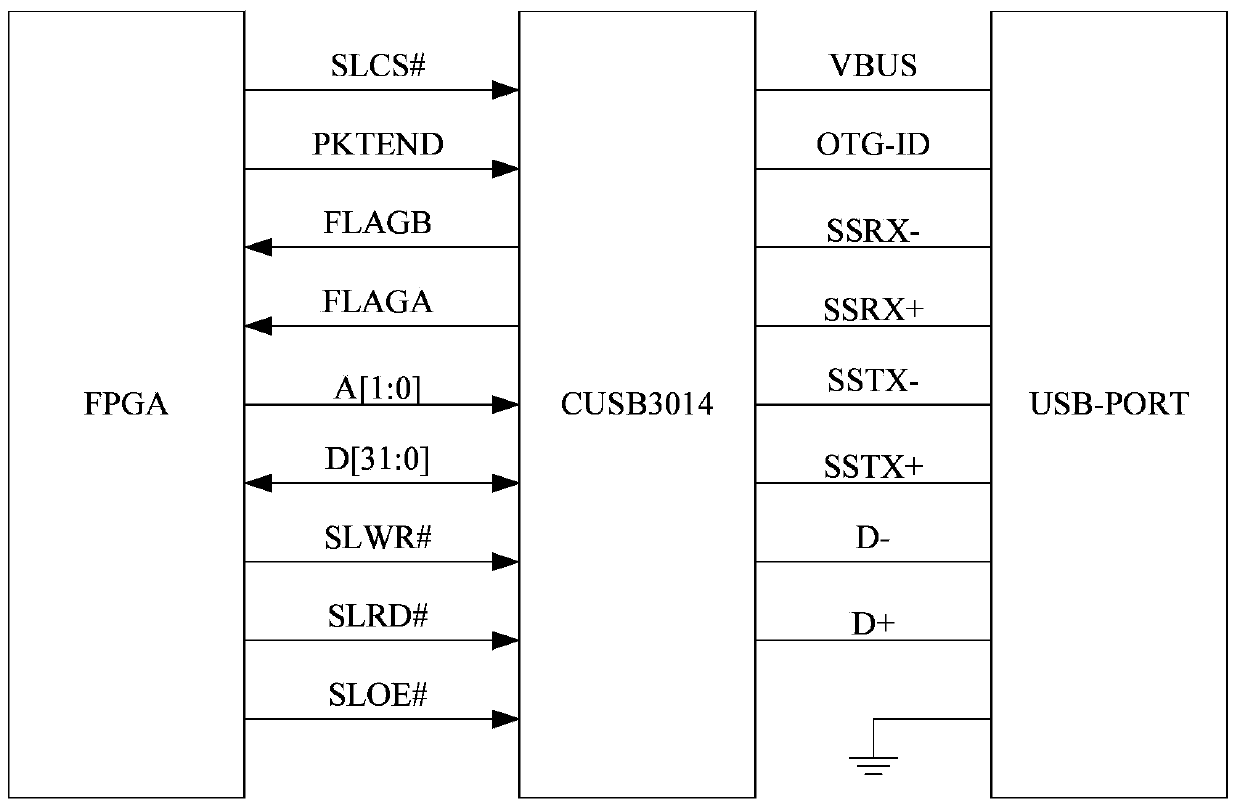
[0055] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the multi-finger myoelectric prosthetic hand modular embedded control system with multiple sensing functions described in Embodiment 1 is that the palm control circuit 2 is realized by FPGA.
[0056] The FPGA chip is connected to the voltage conversion chip 33 through the SPI interface of 3.3 volts, and the other end of the voltage conversion chip 33 is connected to the ADC chip 32 through the SPI interface of 5 volts;
[0057] The FPGA converts the SPI signal from 3.3 volts to 5 volts through the voltage conversion chip 33 to control the ADC chip 32, collects 8 road myoelectric signals, and then converts the SPI signal of 5 volts to the SPI signal of 3.3 volts by the voltage conversion chip 33. The collected 8 channels of myoelectric digital signals are transmitted to FPGA.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0058] Specific Embodiment Three. The difference between this specific embodiment and the multi-finger myoelectric prosthetic hand modular embedded control system with multiple sensory functions described in specific embodiment one is that it also includes an electrical stimulation feedback module 5. The stimulation feedback module 5 is used for sending electrical stimulation feedback signals to the human body.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com