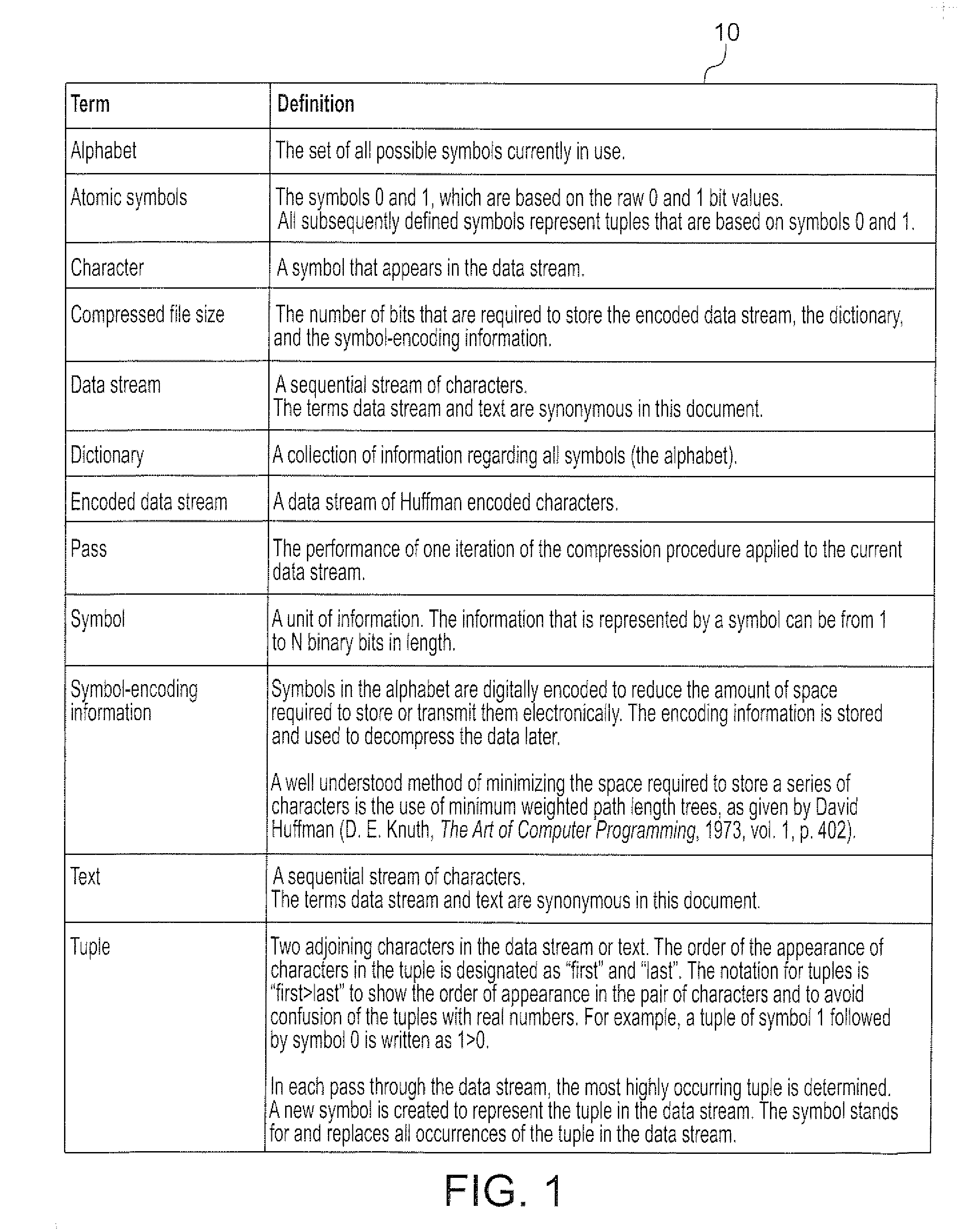
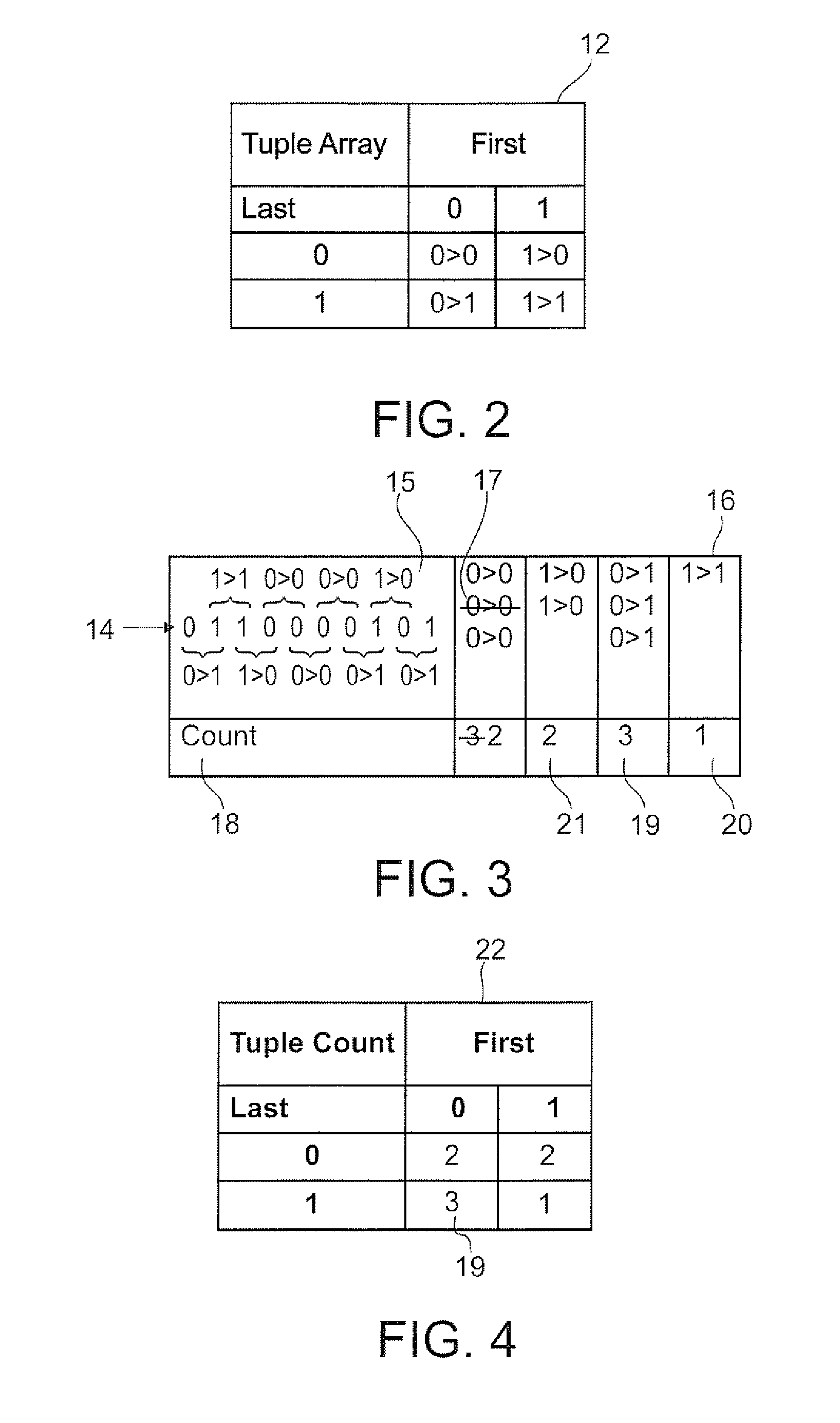
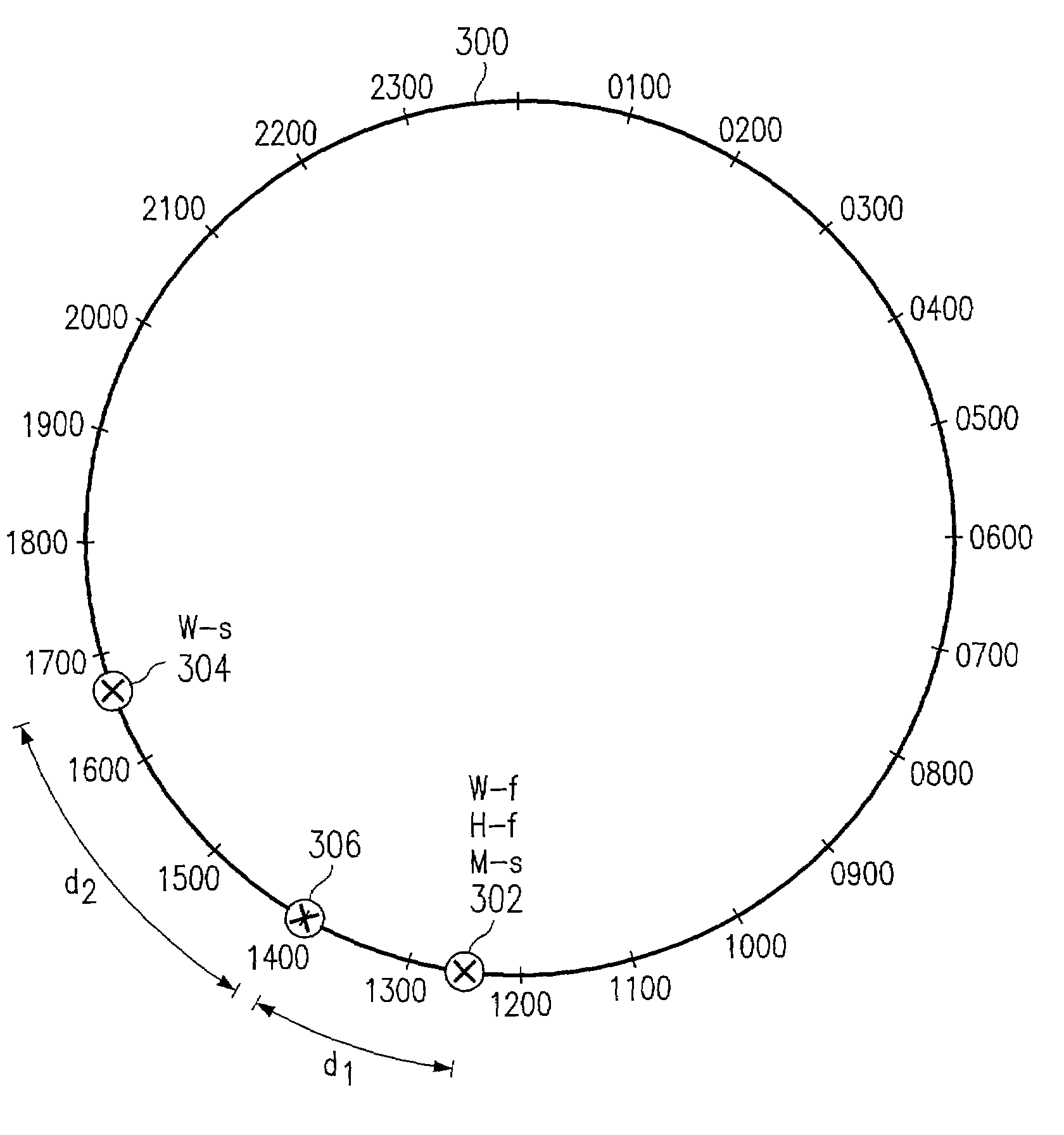
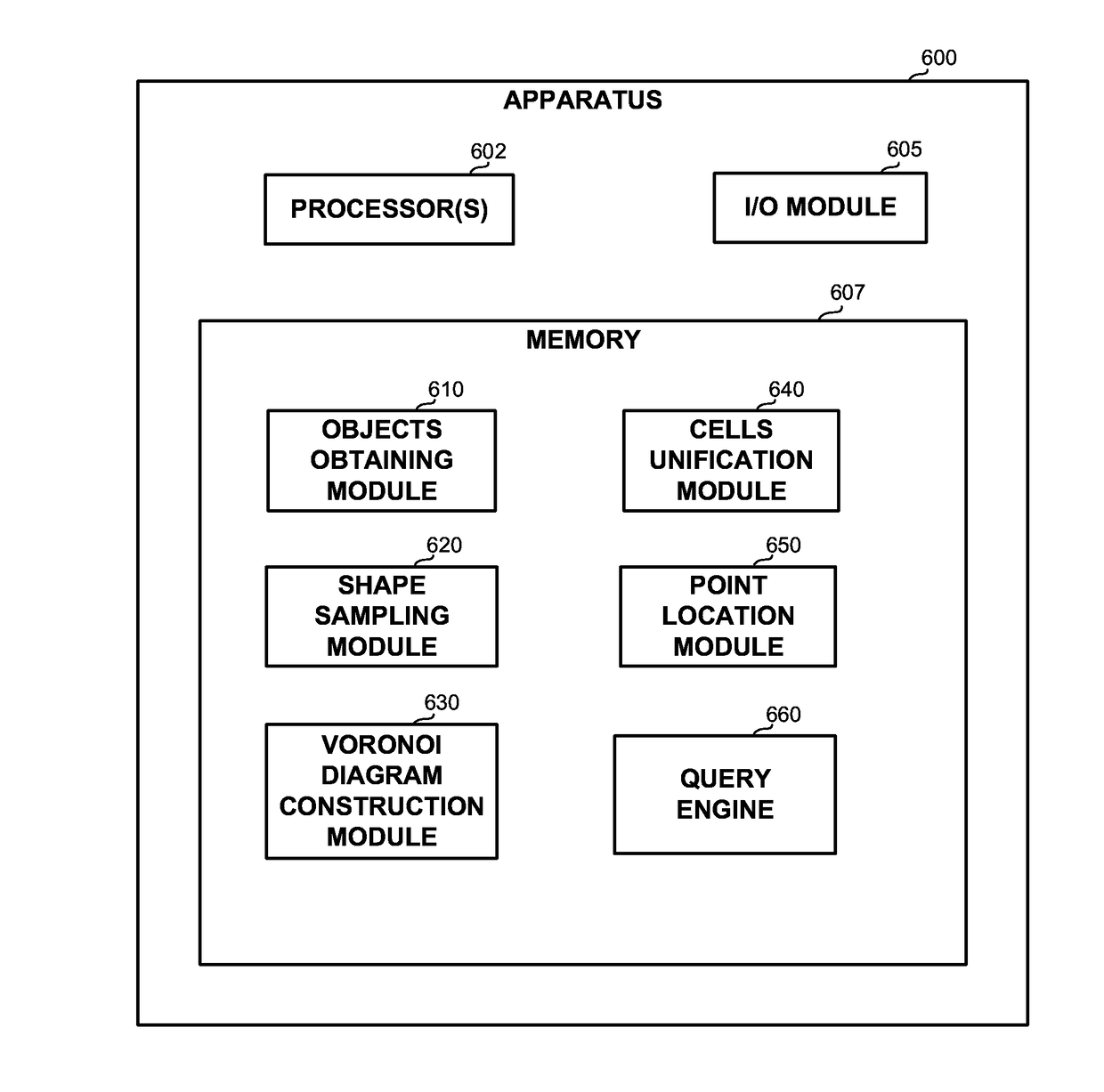
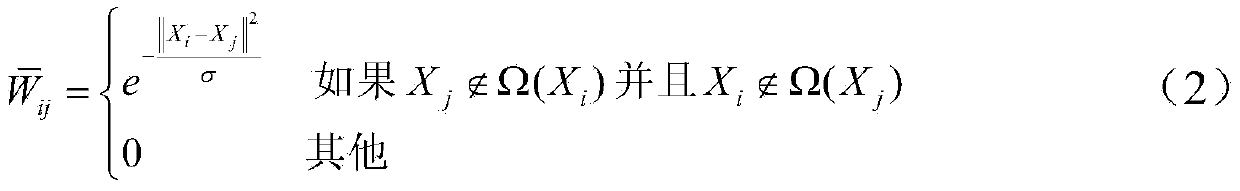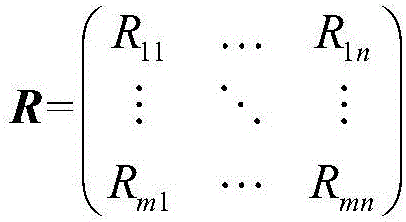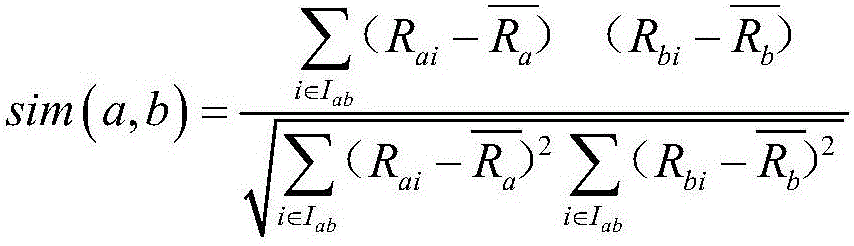Patents
Literature
42 results about "Close neighbor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Distributed network data storage system and method
ActiveUS20020147815A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemClose neighbor
The present invention is a system and method for distributed, highly scalable, wide area peer-to-peer network data storage. The functionally equivalent servers in the system are divided into groups. Each server maintains a dynamic list which is polled to determine the availability of the closest neighbor servers. Each server is switched between the groups of servers to optimize network connectivity parameters. Data and directory files are divided into a plurality of pieces which are stored on different servers. Files are uniformly and independently named, utilizing a tree with a common root, logical pathways, and unique file identifiers. When a server receives a client request for file system access, the plurality of file pieces are collected and sent to the client server from the neighbor servers simultaneously in order to optimize bandwidth. Servers with maximum throughput capacity are utilized for highest transmission speed and reduced processing time.
Owner:VIRTUOZZO INT GMBH +1
Information recommending method based on social network
InactiveCN103995823AIncrease coverageSolve the cold start problemData processing applicationsRelational databasesClose neighborSocial web
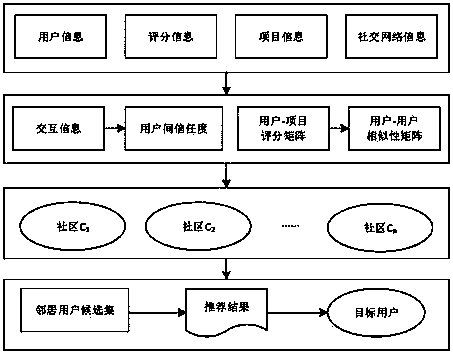
The invention discloses an information recommending method based on a social network. The information recommending method includes the following steps that first, trust degree and similarity between users are calculated, and a user relation matrix is constructed through weighted values; second, the users are clustered through a community discovering algorithm, and then a closest neighbor set of the users is formed; third, scores are predicted, and a recommending list is generated. The information recommending method based on the social network can achieve the following advantages that first, the cold start problem is solved: trust degree is introduced into the method, if enough neighbors cannot be obtained according to the common grading articles in the recommending process, trustable friends can serve as the start point of prediction, and thus the cold start problem can be relieved, and user coverage can be improved; real time performance is improved: community division is performed on the user network through the community discovering algorithm commonly used in social network analysis, in other words, same user interests are clustered, and thus the time for finding the neighbor set of the users is greatly shortened, and the real time performance of the information recommending response is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
User group correlation degree-based personalized recommendation method and system
ActiveCN103077220AResolved Accuracy DecreaseHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsInternet communicationPersonalization
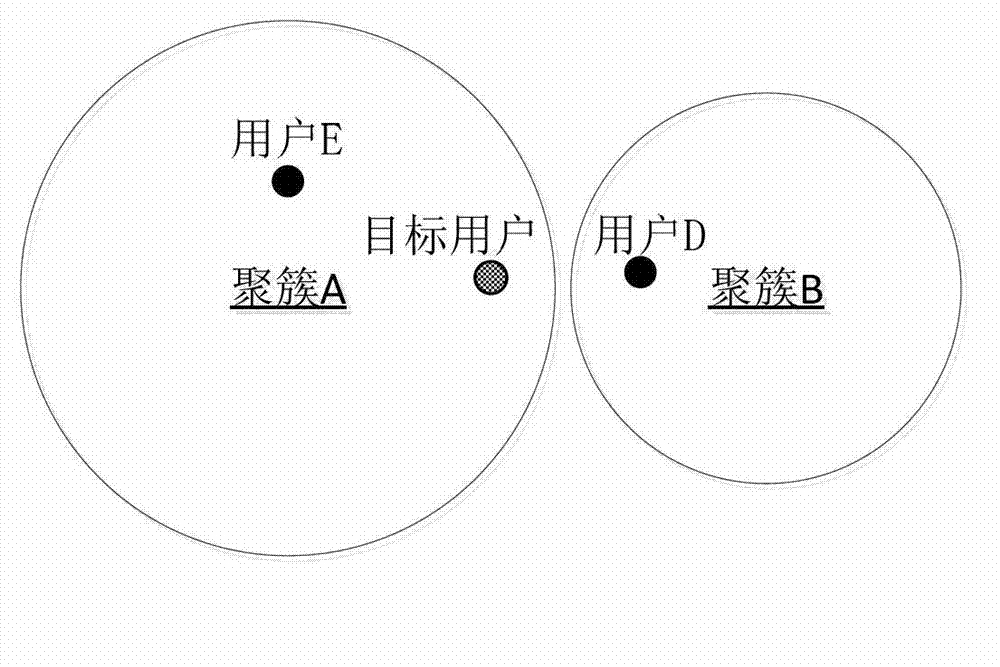
The invention relates to the field of internet communication, and discloses a user group correlation degree-based personalized recommendation method, which comprises the following steps of: A, clustering users by using a clustering algorithm; B, judging distance from a target user to a cluster edge, executing a step C when the distance is greater than a given threshold value, otherwise executing B-1, calculating correlation degree between a cluster of the target user and other clusters, B-2, combining previous r clusters related with the cluster of the user, B-3, searching n closest neighbors in the combined cluster, and further executing a step D; C, searching n closest neighbors in the cluster of the target user; D, predicting a grading value of a related product according to grade of the closest neighbor on the product; and E, selecting the previous m products to be recommended to the user according to the level of a predicted grading value. The invention also discloses a user group correlation degree-based personalized recommendation system. According to the method and the system, the accuracy for personalized recommendation can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distributed network data storage system and method
ActiveUS7209973B2Short response timeConducive to loadDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemClose neighbor
The present invention is a system and method for distributed, highly scalable, wide area peer-to-peer network data storage. The functionally equivalent servers in the system are divided into groups. Each server maintains a dynamic list which is polled to determine the availability of the closest neighbor servers. Each server is switched between the groups of servers to optimize network connectivity parameters. Data and directory files are divided into a plurality of pieces which are stored on different servers. Files are uniformly and independently named, utilizing a tree with a common root, logical pathways, and unique file identifiers. When a server receives a client request for file system access, the plurality of file pieces are collected and sent to the client server from the neighbor servers simultaneously in order to optimize bandwidth. Servers with maximum throughput capacity are utilized for highest transmission speed and reduced processing time.
Owner:VIRTUOZZO INT GMBH +1
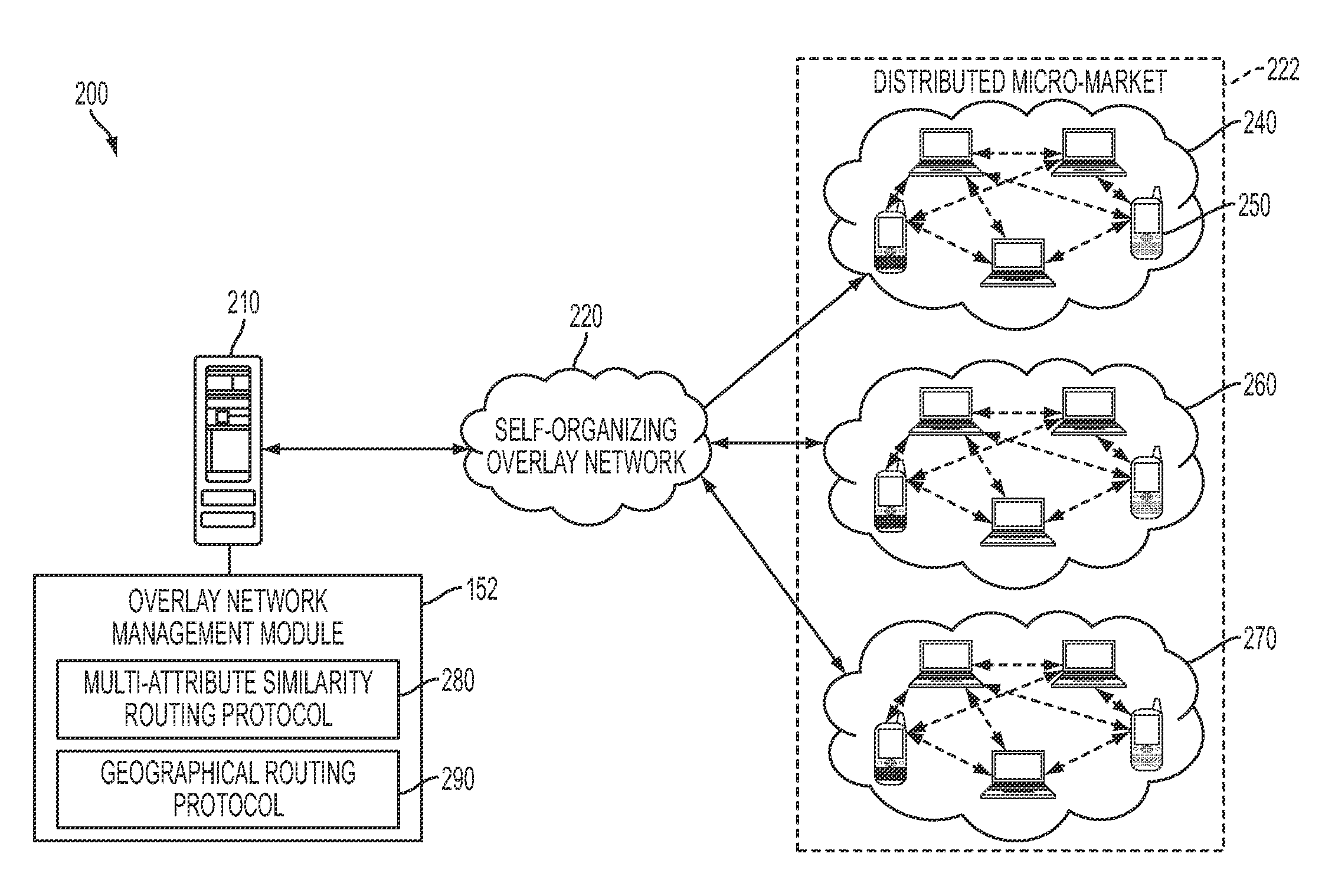
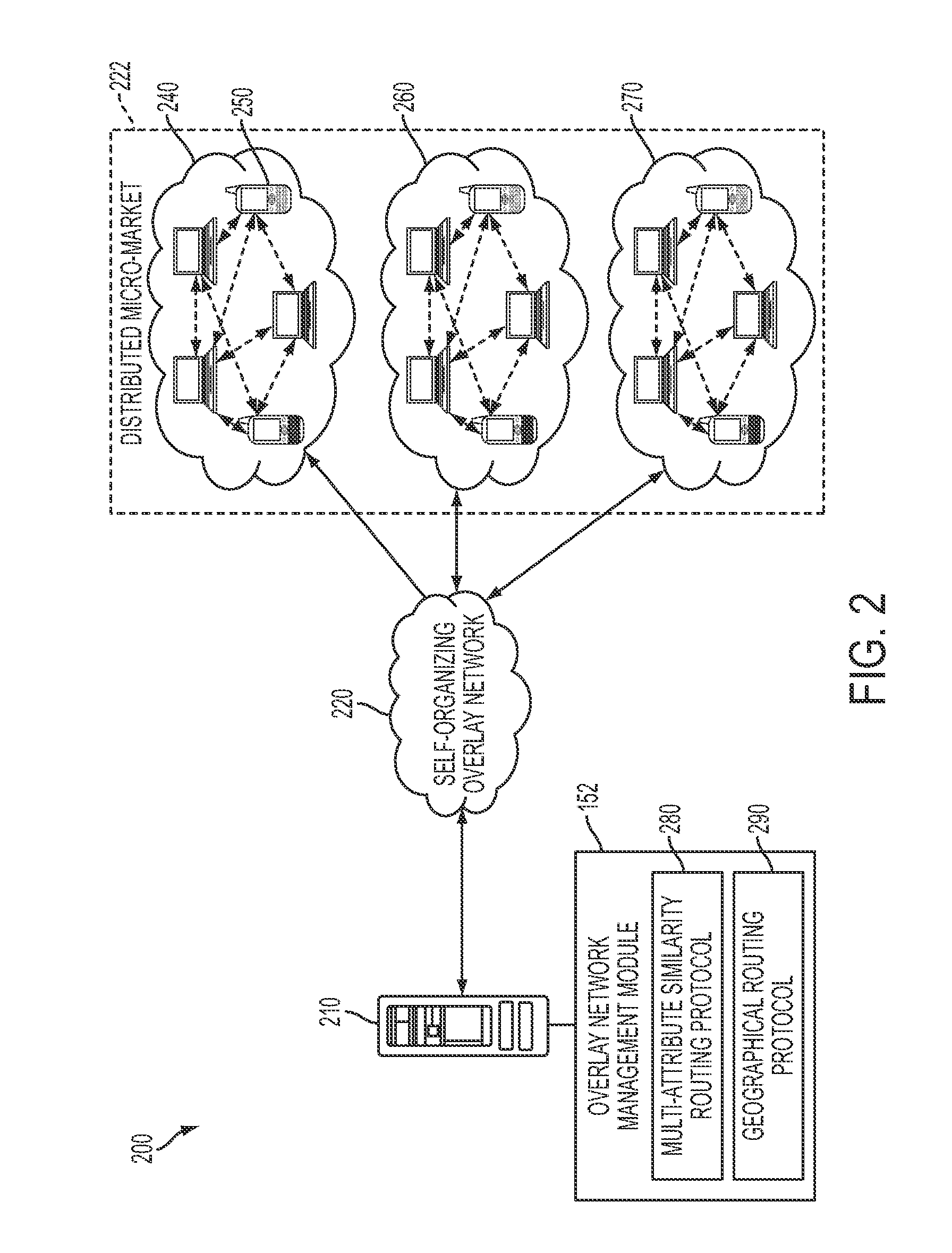
Method and system for creating peer-to-peer geographical routing and multi-attribute similarity routing
InactiveUS20130036236A1Efficient scalabilityData efficientDigital computer detailsLocation information based serviceMessage routingGeolocation
A system and method for creating a peer-to-peer geographical routing overlay network and a multi-attribute similarity routing overlay network. The geographical overlay network can be generated utilizing a geographical routing protocol to organize connections between one or more distributed micro-markets depending on a geographical location of each market and to detect a geographically close neighbor in a decentralized manner. The multi-attribute similarity overlay network can be computed by applying a filtering function based on a multi-attribute routing protocol defined over at least one attribute in order to enable decentralized clustering of the distributed micro-markets. The multi-attribute similarity protocol can be combined with the geographic overlay protocol to route messages to a target set of similarity-based attributes and a target geographic location thereby dynamically evolve a structure of distributed micro-markets over time and optimize a market interaction in the overlay network.
Owner:XEROX CORP
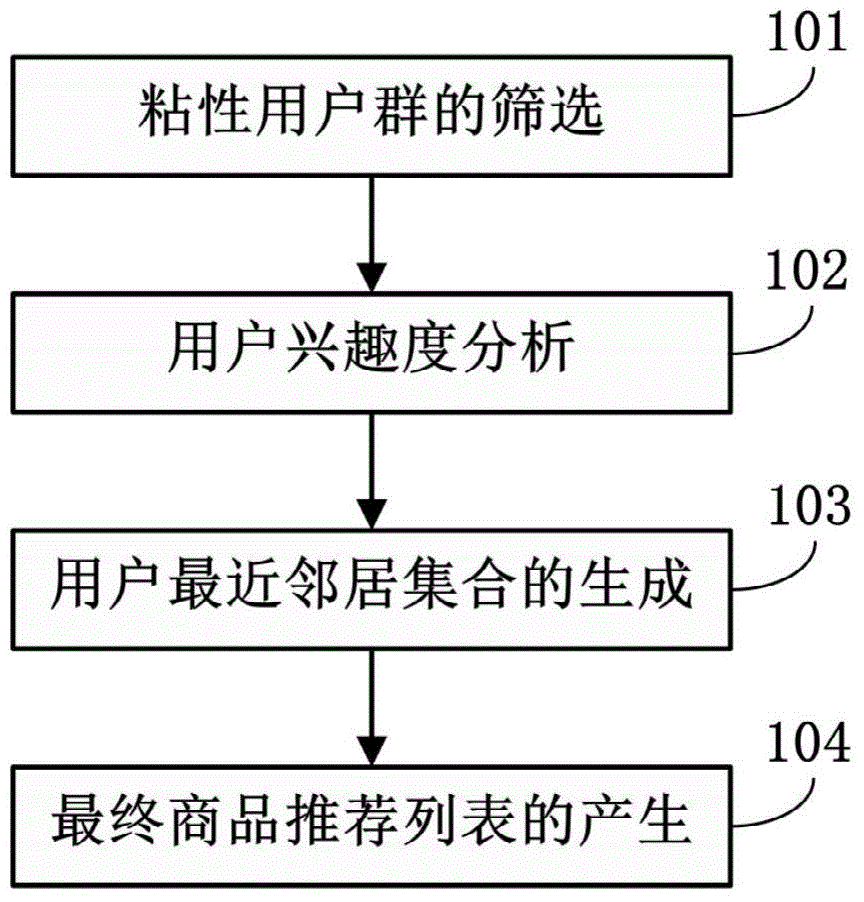
Commodity recommendation method and device based on electronic business platform and server
The invention relates to a commodity recommendation method and device based on an electronic business platform and a server. The commodity recommendation method and device based on the electronic business platform and the server are used for improving the accuracy of individual commodity recommendation. The method comprises the steps that adhesive user groups are screened; user interestingness is acquired; a neighbor set closest to a target user is generated; a commodity recommendation list is generated. According to the technical scheme, the obtained adhesive user groups can be more accurate and efficient; due to the fact that only the interestingness of each user in the adhesive user groups is recorded in an obtained scoring matrix, an evaluation matrix can be filled, and the density of the scoring matrix is improved; the closest neighbor set between the target user and the other users in the adhesive user groups is calculated through the scoring matrix, the similar neighbors of the target user can be searched for more accurately, and then the accuracy of recommending commodities to the target user is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
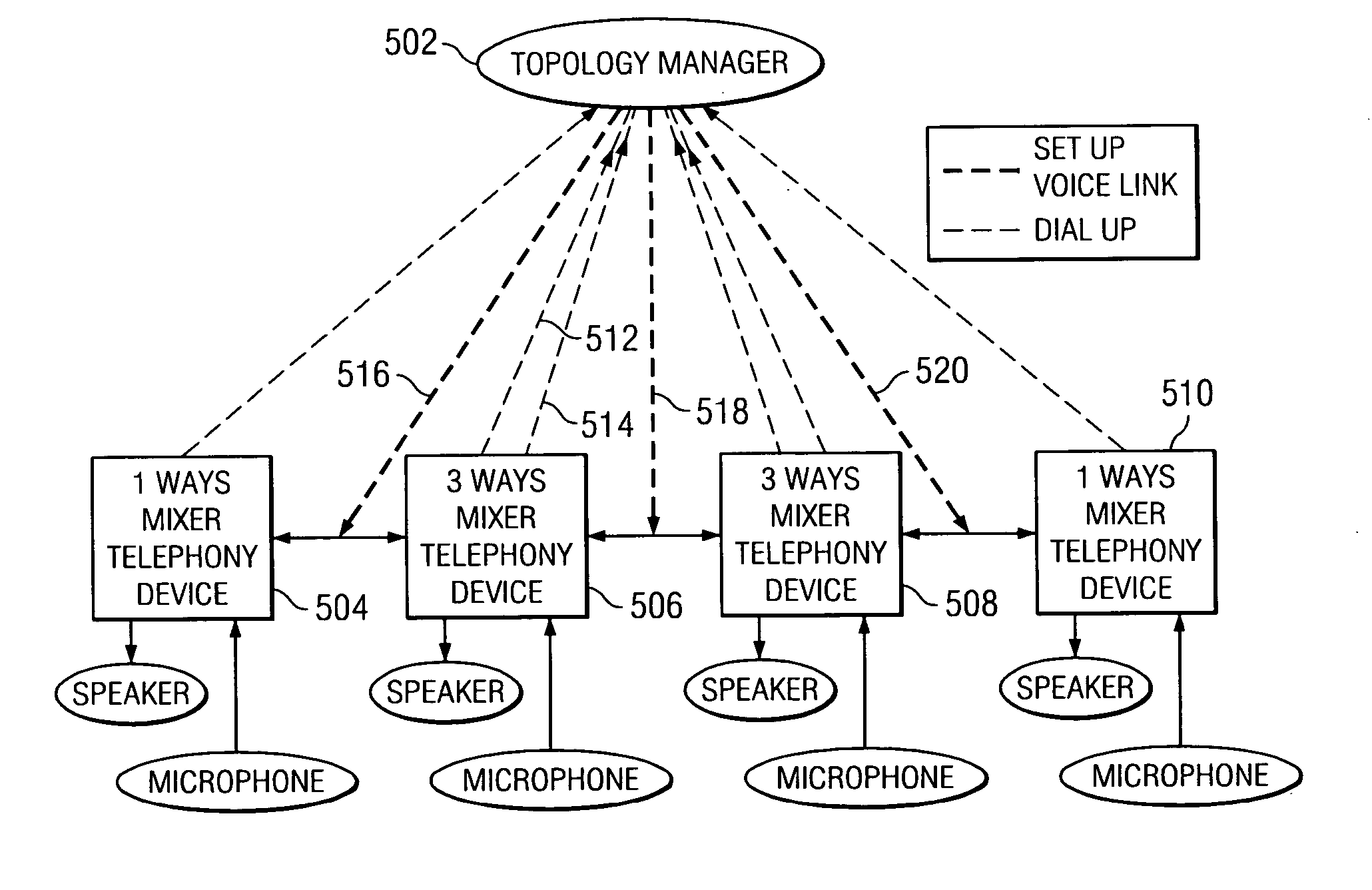
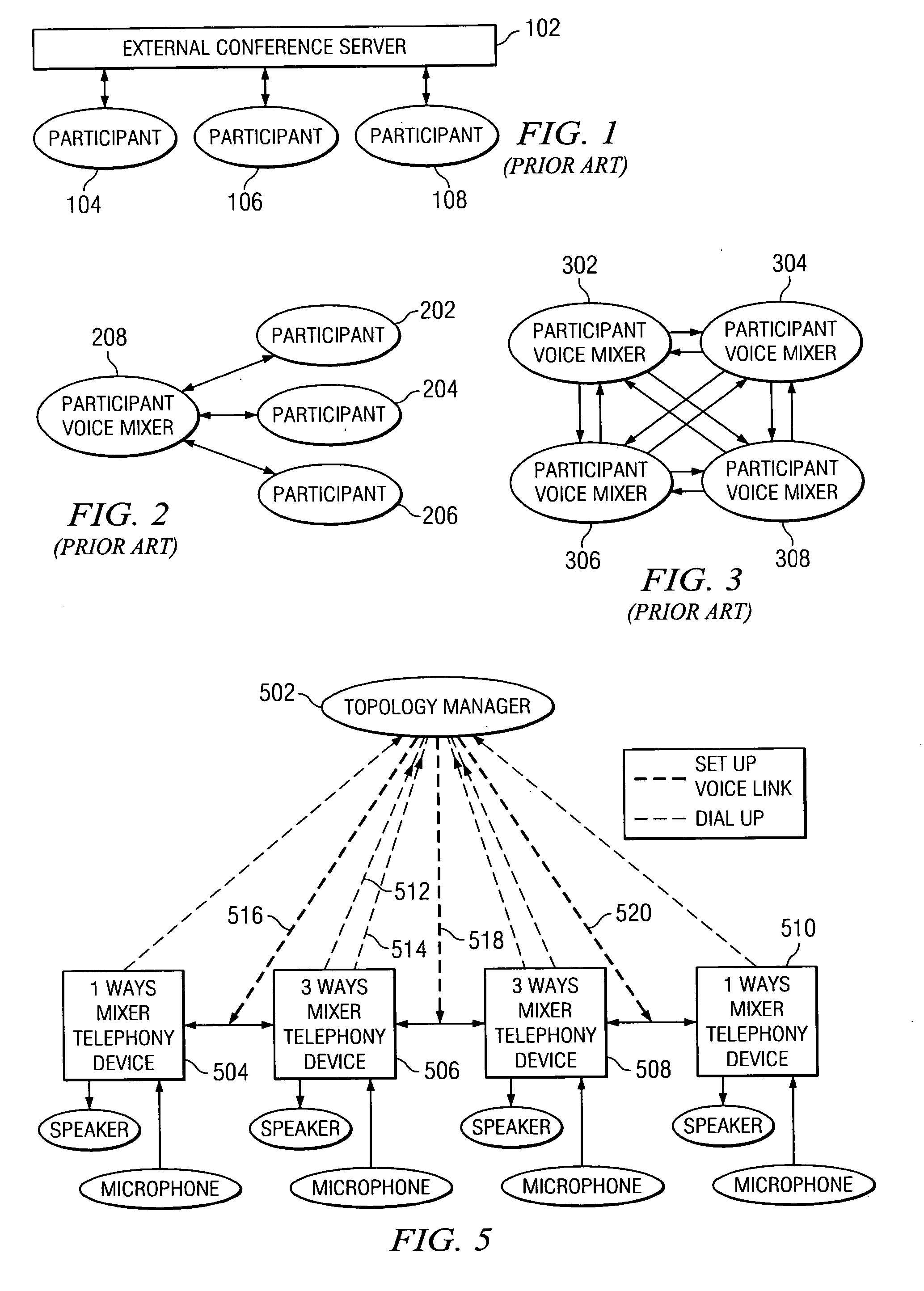
N-ways conference system using only participants' telephony devices without external conference server
InactiveUS20060062368A1Special service for subscribersCircuit fault indicationsTraffic delayNetwork conditions
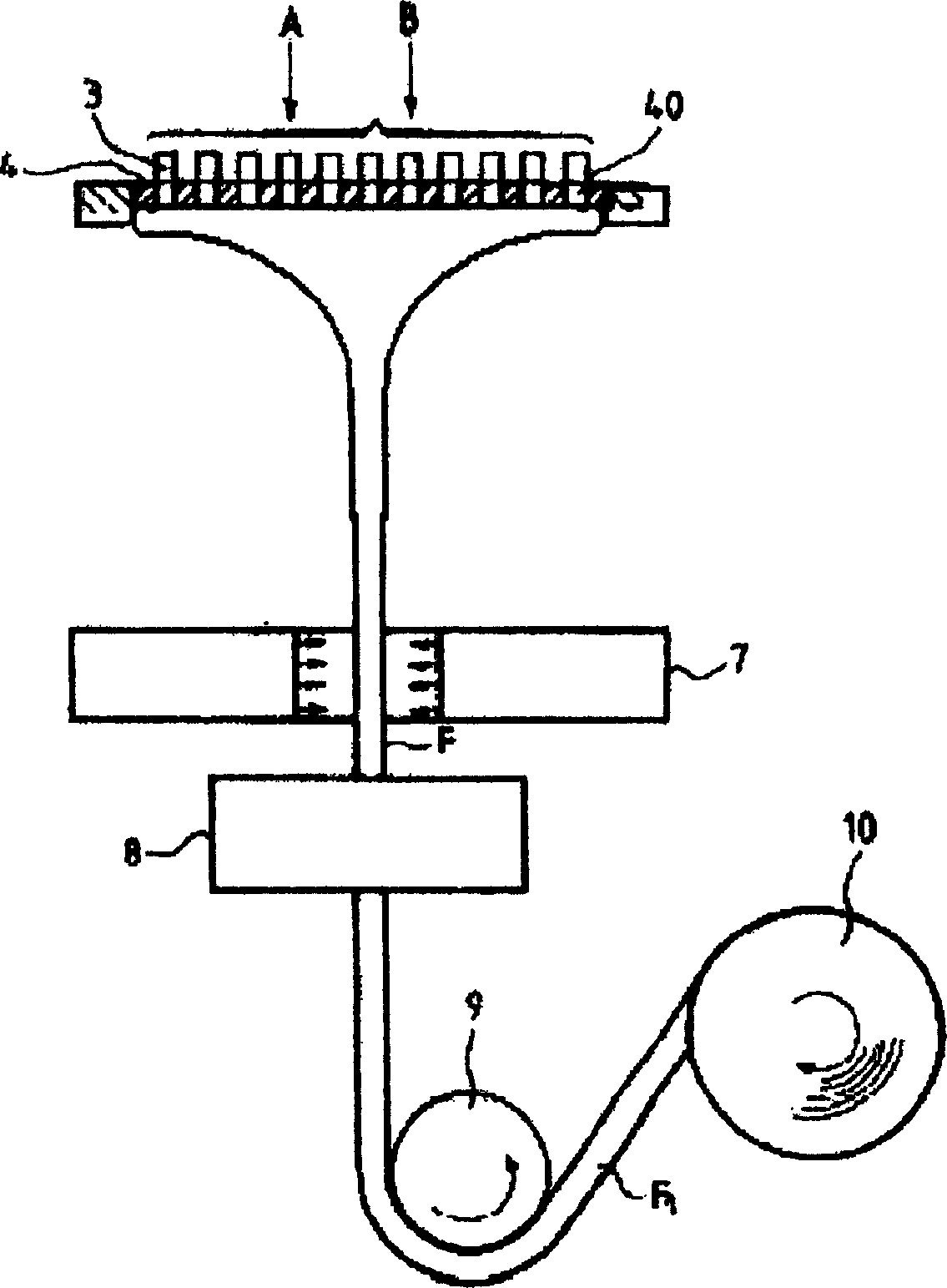
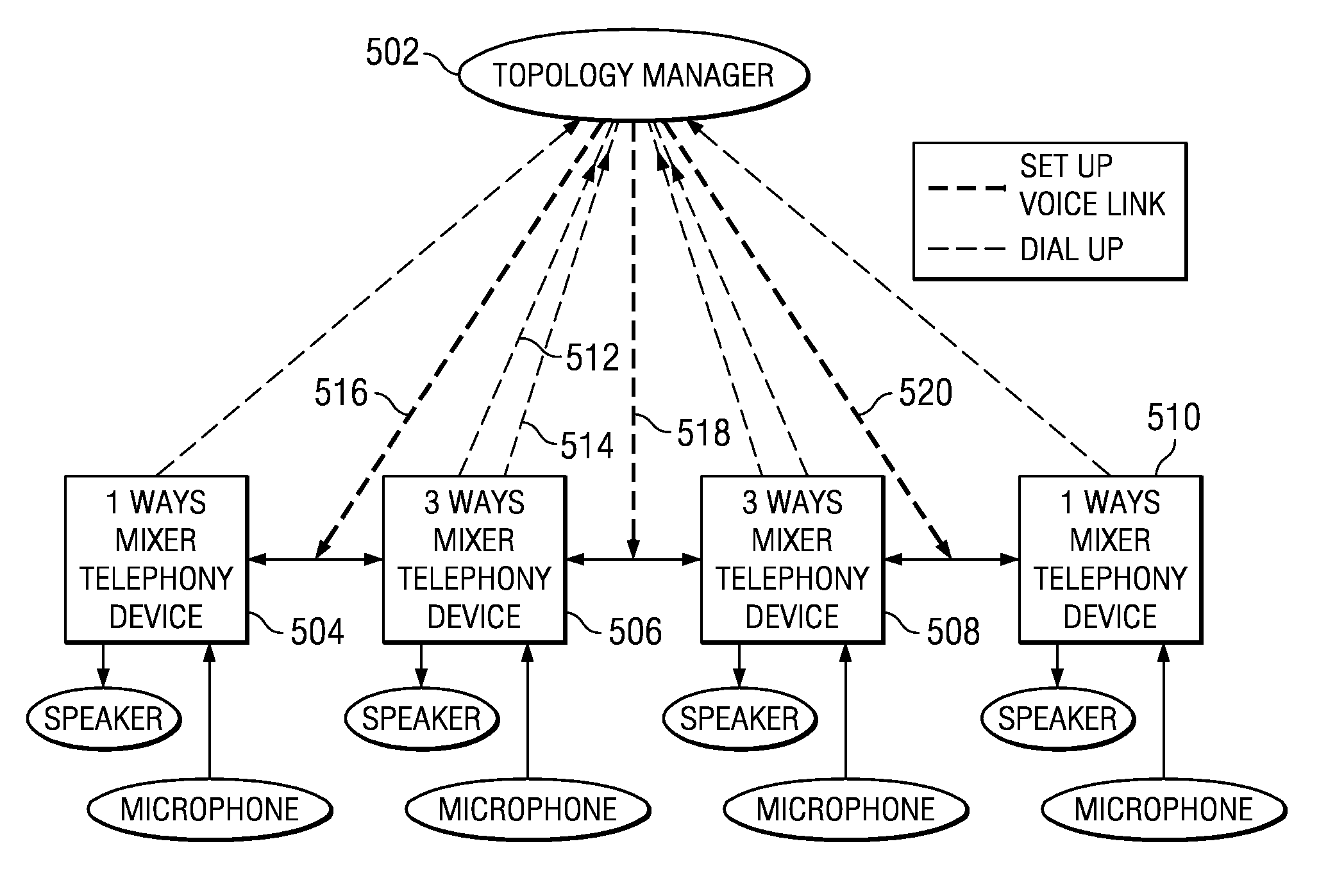
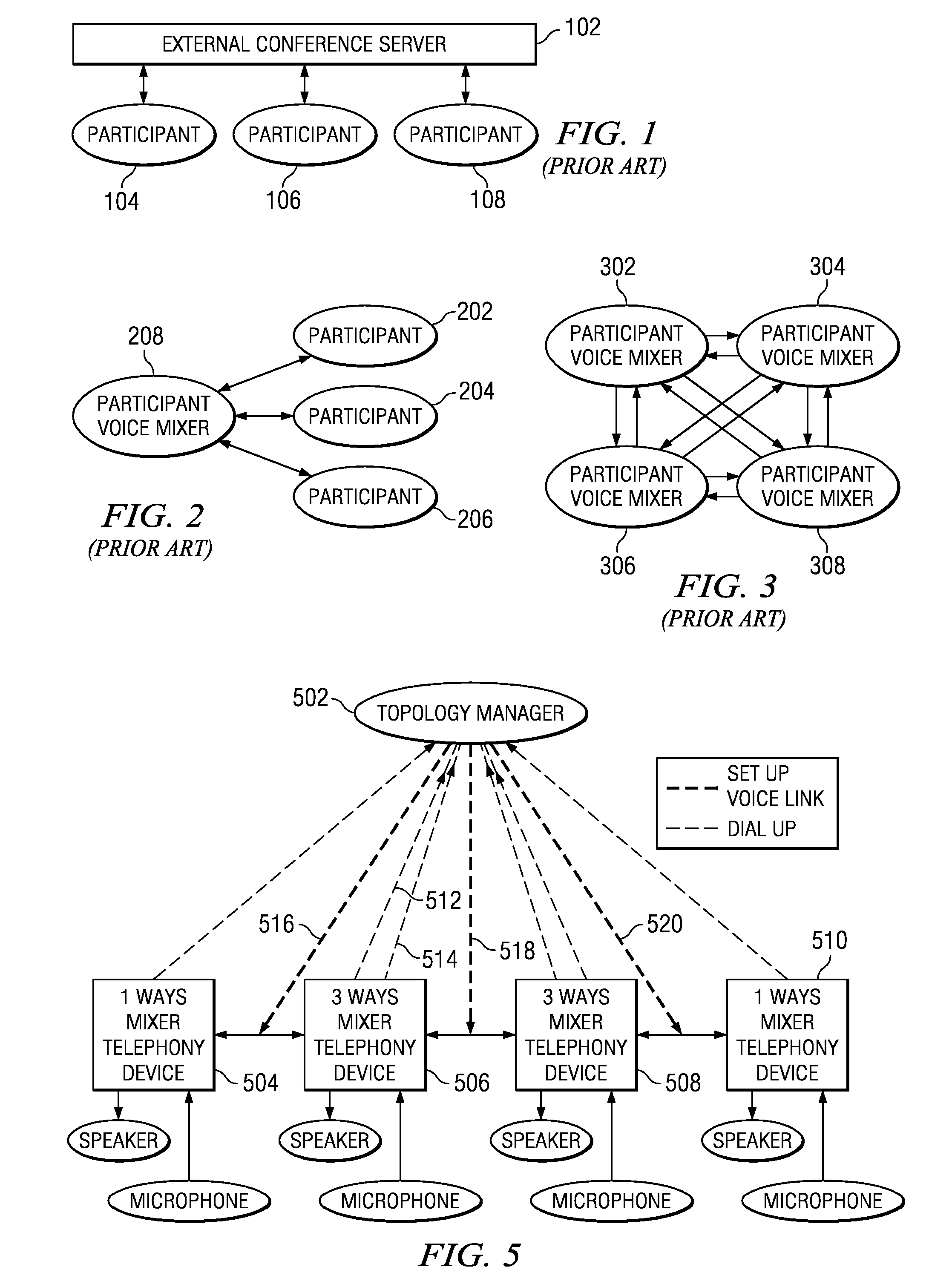
An n-ways conferencing system using only the participants' telephony devices and without an external conference server. A plurality of telephony devices dial in to and report their mixing capability to a connection topology manager. The connection topology manager also determines the location of each telephony device and neighboring telephony device pairs in the conference service, as each telephony device is used for mixing voice signals of its closest neighbors, and calculates a minimum conference traffic delay for each telephony device. The connection topology manager then builds a topology for the conference service based on the mixing capability, location, and minimum conference traffic delay, wherein the connection topology manager distributes a mixing computation in a substantially uniform manner across the plurality of telephony devices. When a change in the network condition is detected, the connection topology manager rebuilds the topology to bypass the change in the network condition.
Owner:IBM CORP
Regression prediction method and device
InactiveCN102385719ARich relevant informationImprove predictive performanceForecastingData setAlgorithm
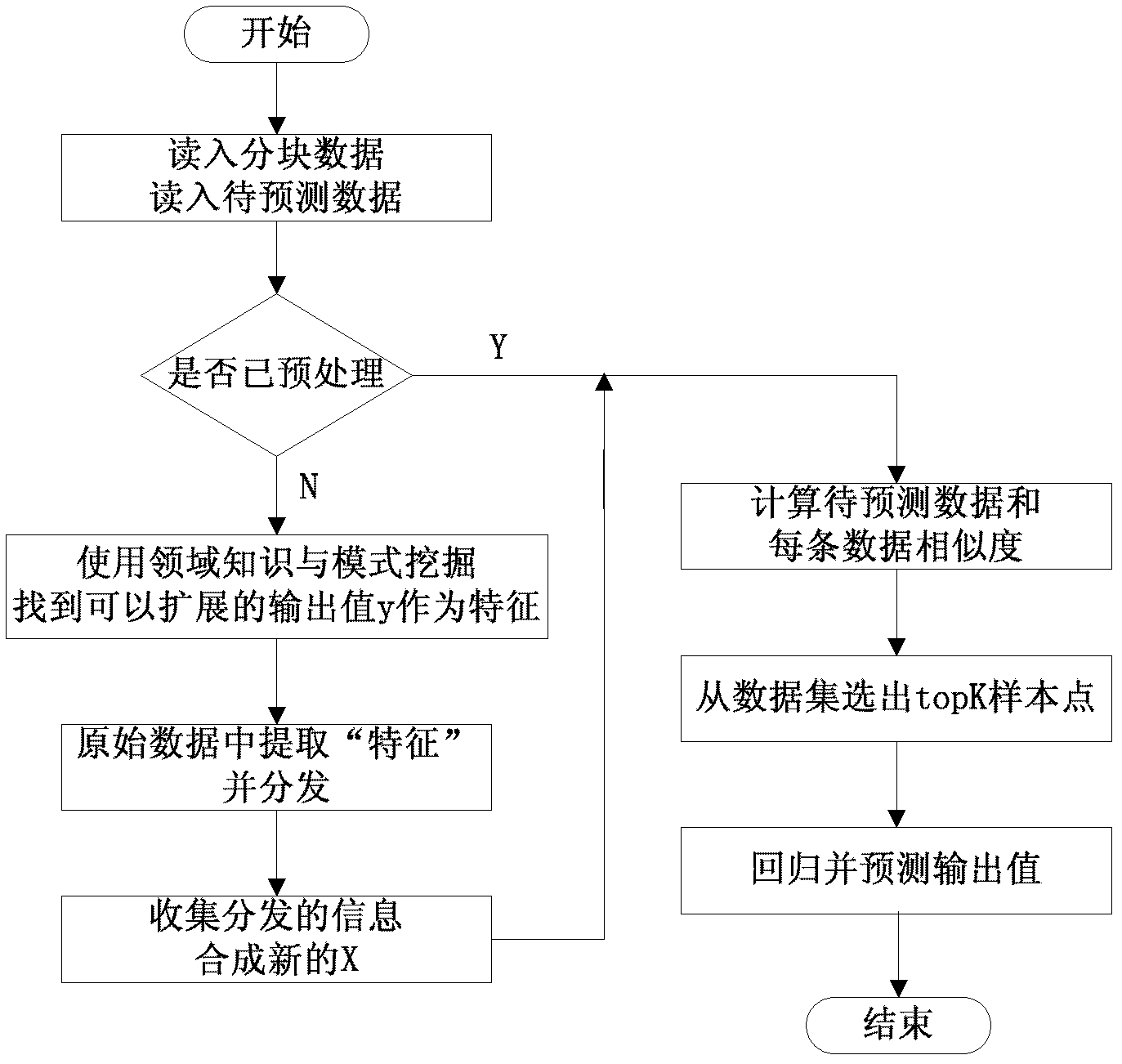
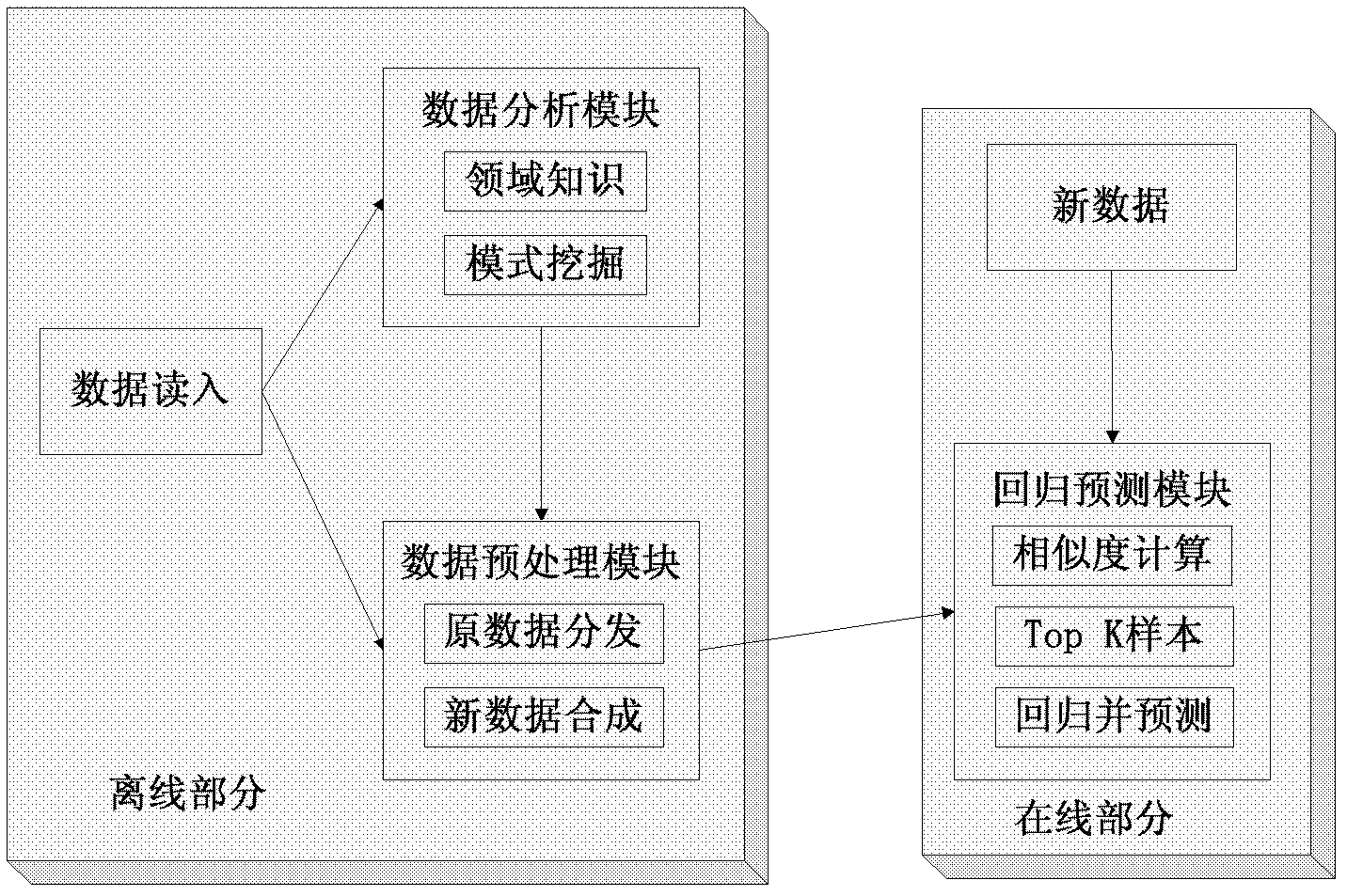
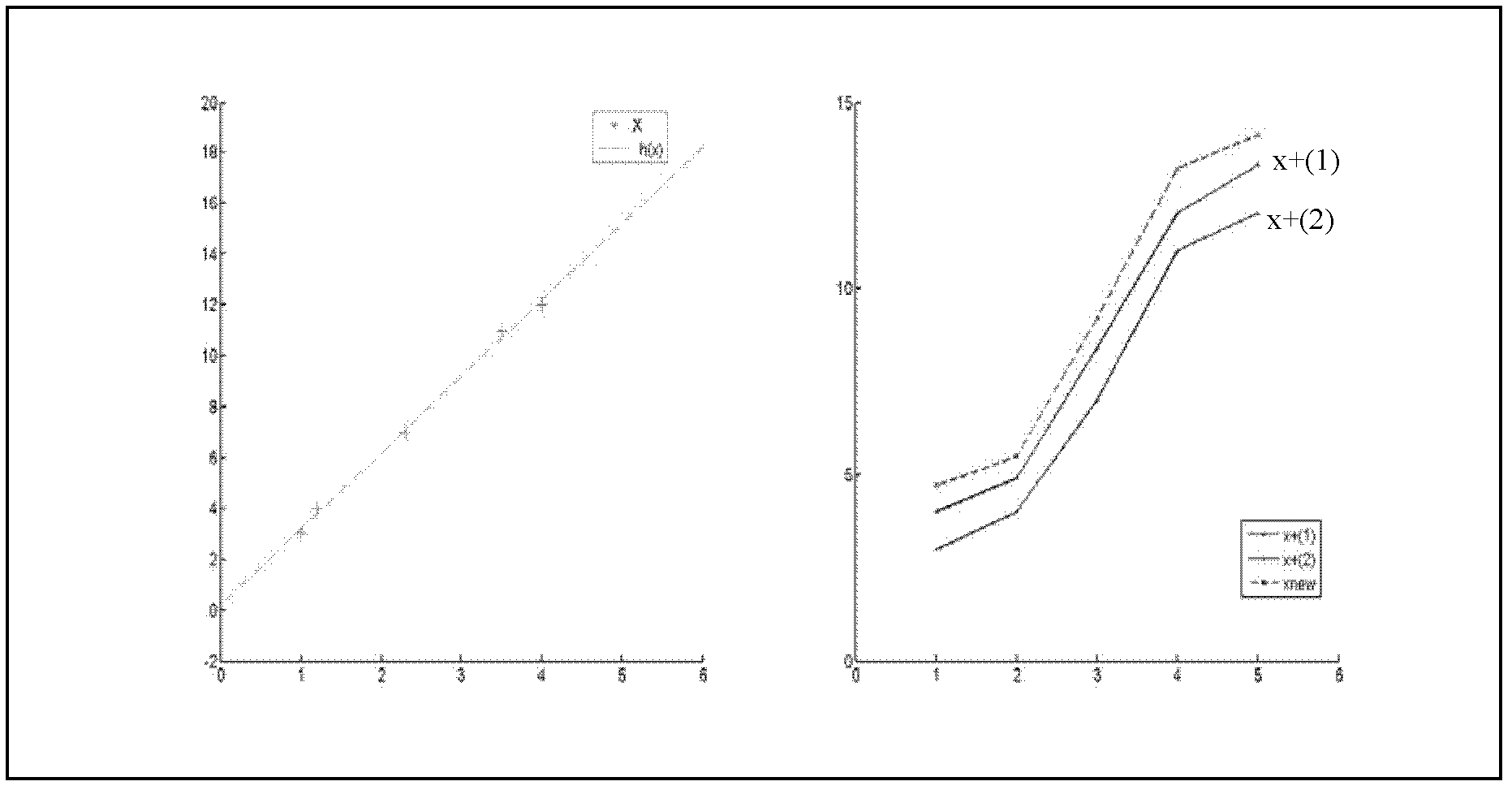
The invention provides a regression prediction method, wherein not only similarity between independent variables X is taken into consideration, but also similarity between dependent variables Y of raw data is taken into consideration, and the model of output value y development based on the historical angle of close neighbors. Compared with the conventional model without taking data development mode into consideration, only one preprocessing section is added to a data set, and the information of the data point can be diversified without the need of extra resource; and the information of the raw data point X is diversified, and finally the prediction effect is improved. Furthermore, the regression prediction method can be realized on a MapReduce frame, and the execution speed can be improved by utilizing the parallelism of the device.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optimized Partitions For Grouping And Differentiating Files Of Data
InactiveUS20110016124A1Reduce the numberData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFrequency spectrumData file
Methods and apparatus teach a digital spectrum of a data file. The digital spectrum is used to map a file's position in multi-dimensional space. This position relative to another file's position reveals closest neighbors. Certain of the closest neighbors are grouped together to define a set. Overlapping members in the groups may be further differentiated from one another by partitioning. An optimized partition of set S of N overlapping groups yields a maximum strength for groups and members in that partition. Among other things, the optimized partition includes relative strengths of every individual member in every possible partition and weighting functions applied to the relative strengths and to subgroups of files within the partitions.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Relevancy filter for new data based on underlying files
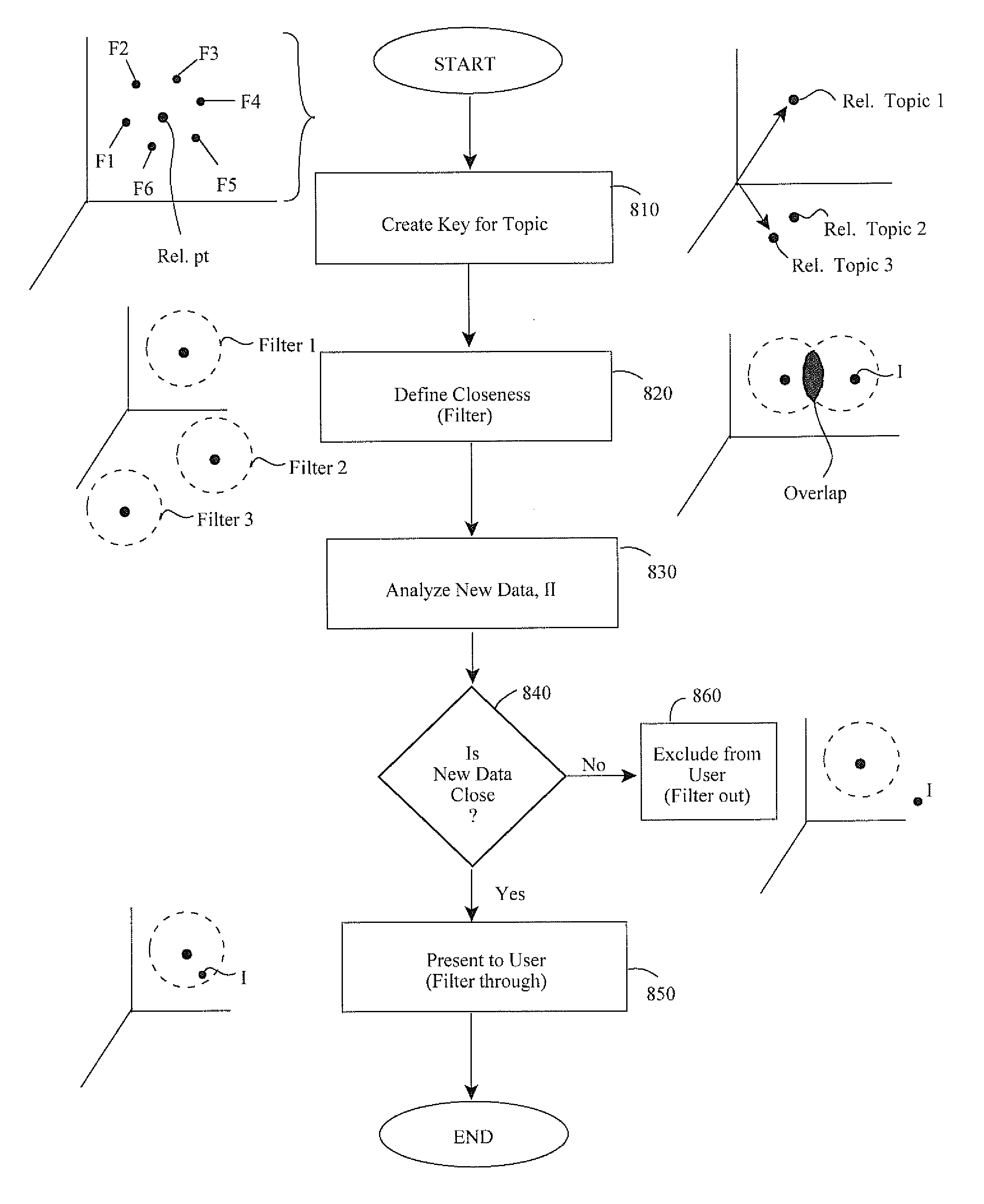
InactiveUS20110252063A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFrequency spectrumSubject matter
Methods and apparatus teach a digital spectrum of a file representing underlying original data. The digital spectrum is used to map a file's position. This position relative to another file's position reveals closest neighbors. When multiple such neighbors are grouped together they can be used to indicate relevance in current data under consideration on a same or different computing device. Also, relevance can be found without traditional notions of needing structured data or users initiating searching for relevance or by examining metadata / administrative information associated with the files. A plurality of original files represent underlying original bits of data from which a key is created in a mapping space for a relevancy topic. If new data is sufficiently close to this, it is related to the topic and presented to users. Various closeness measures are defined as are methods for key creation. Still other features contemplate computing arrangements and program products.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Grouping and Differentiating Files Based on Underlying Grouped and Differentiated Files
InactiveUS20110016136A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDifferentiated servicesData stream
Methods and apparatus teach a digital spectrum of a file. The digital spectrum is used to map a file's position. This position relative to another file's position reveals closest neighbors. When multiple such neighbors are arranged, first “patterns” of data are created that further define digital spectrums of new files. It is within this sorted new data that emergent relationships or second “patterns” are examined, according to the techniques for its underlying files, or “patterns of patterns.” Representatively, original files are stored on computing devices. If encoded, they have pluralities of symbols representing an underlying data stream of original bits of data. The original files are examined for relationships between each of the files. The original relationships are converted to new files. The new files are representatively encoded and examined for other relationships. The new files are then grouped or differentiated from one another based these new relationships yielding insight into how the original files can be grouped or differentiated.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
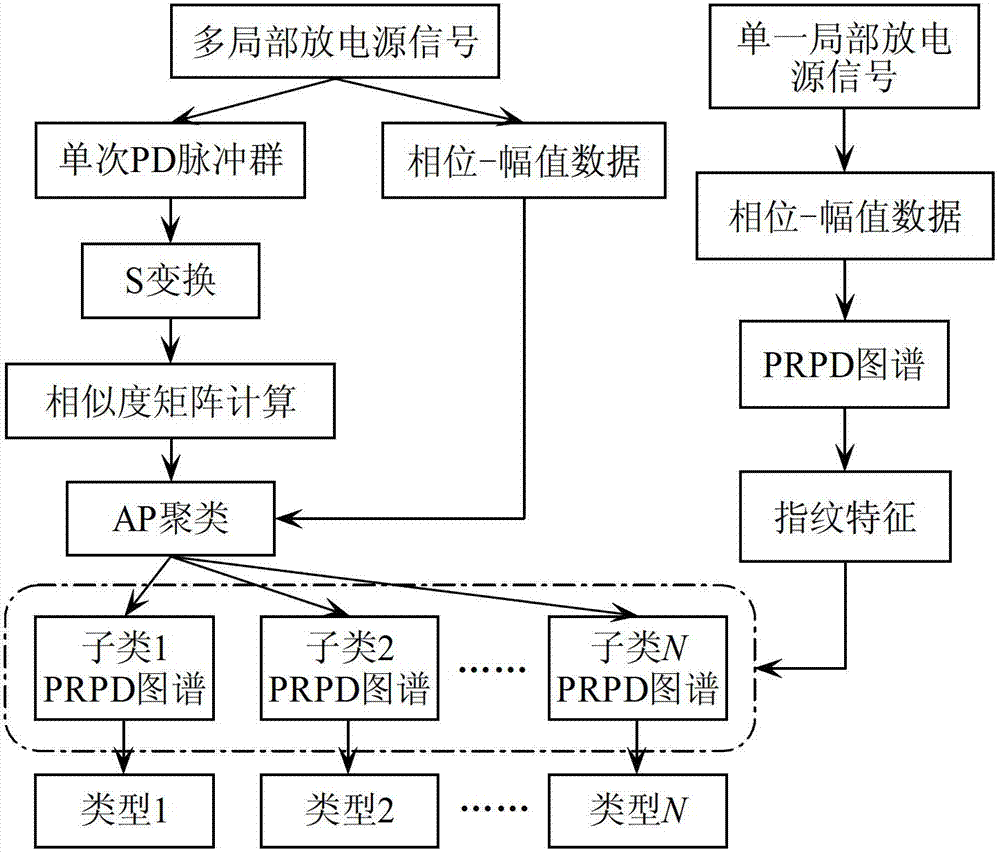
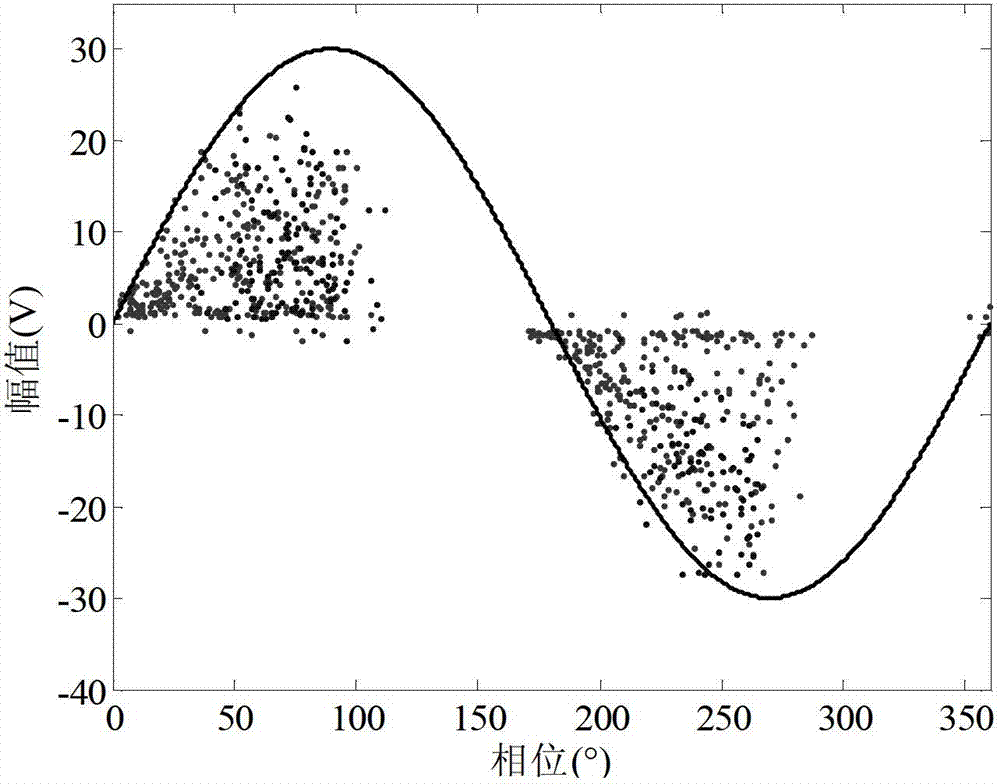
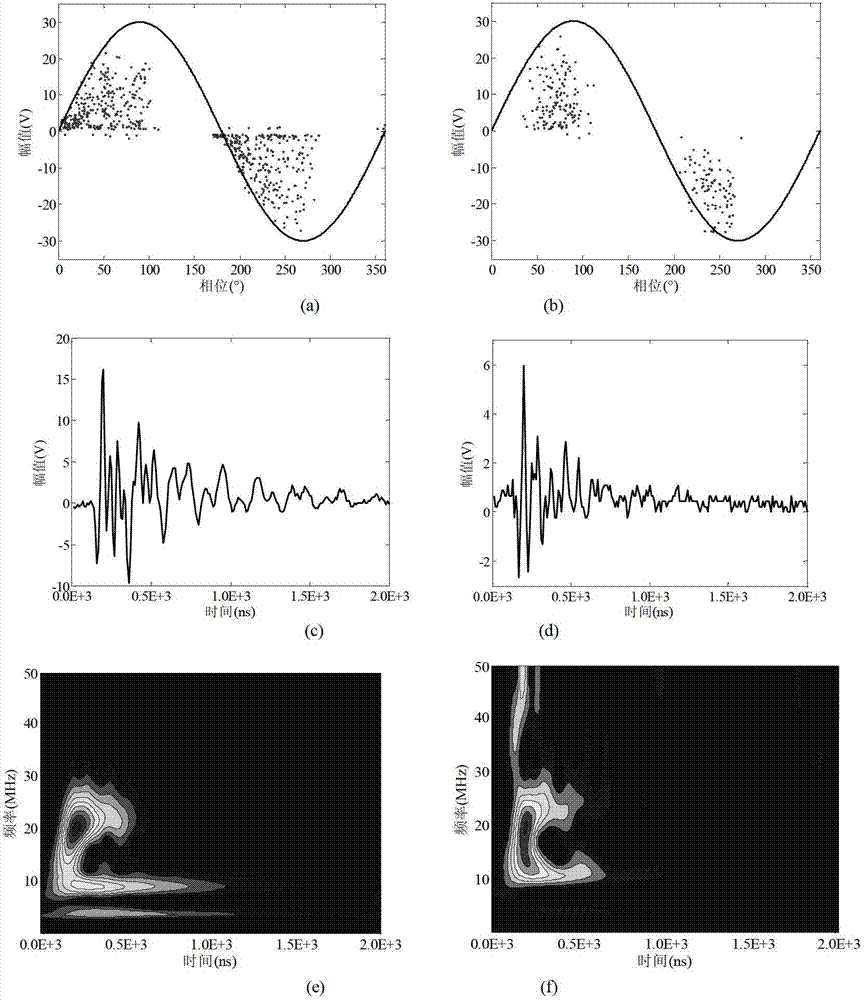
Separation and recognition algorithm for transformer oiled paper insulation multiple partial discharging source signals
ActiveCN103091612ARealize automatic separationAchieve separationTesting dielectric strengthOriginal dataTime–frequency analysis
The invention discloses a separation and recognition algorithm for transformer oiled paper insulation multiple partial discharging source signals. According to the separation and recognition algorithm, time-frequency analysis and close-neighbor similar transmission clusters are adopted to conduct separation and recognition of the multiple partial discharging source signals. The separation and recognition algorithm comprises the steps of firstly, using S transformation to conduct the time-frequency analysis for partial discharging pulses, obtaining an S transformation amplitude (STA) matrix, calculating similarity of the pulses, secondly, using the similarity matrix to conduct the close-neighbor transmission cluster, achieving automatic separation of the discharging pulses, finally, extracting fingerprint feature recognition discharging source modes of a pulse phase partial distribution (PRPD) pattern map of subclass pulses, and using the multiple discharging source signals which are collected through tests and combined by manual work for verification of effectiveness of the separation and recognition algorithm. According to the separation and recognition algorithm for the transformer oiled paper insulation multiple partial discharging source signals, the number of the clusters and corresponding pulse groups can be provided according to the similarity among the pulses and free of influence of the pulse width. When certain pulse width is used for extracting a single pulse wave form for collected PD original data, separation of the multiple discharging sources can be well achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
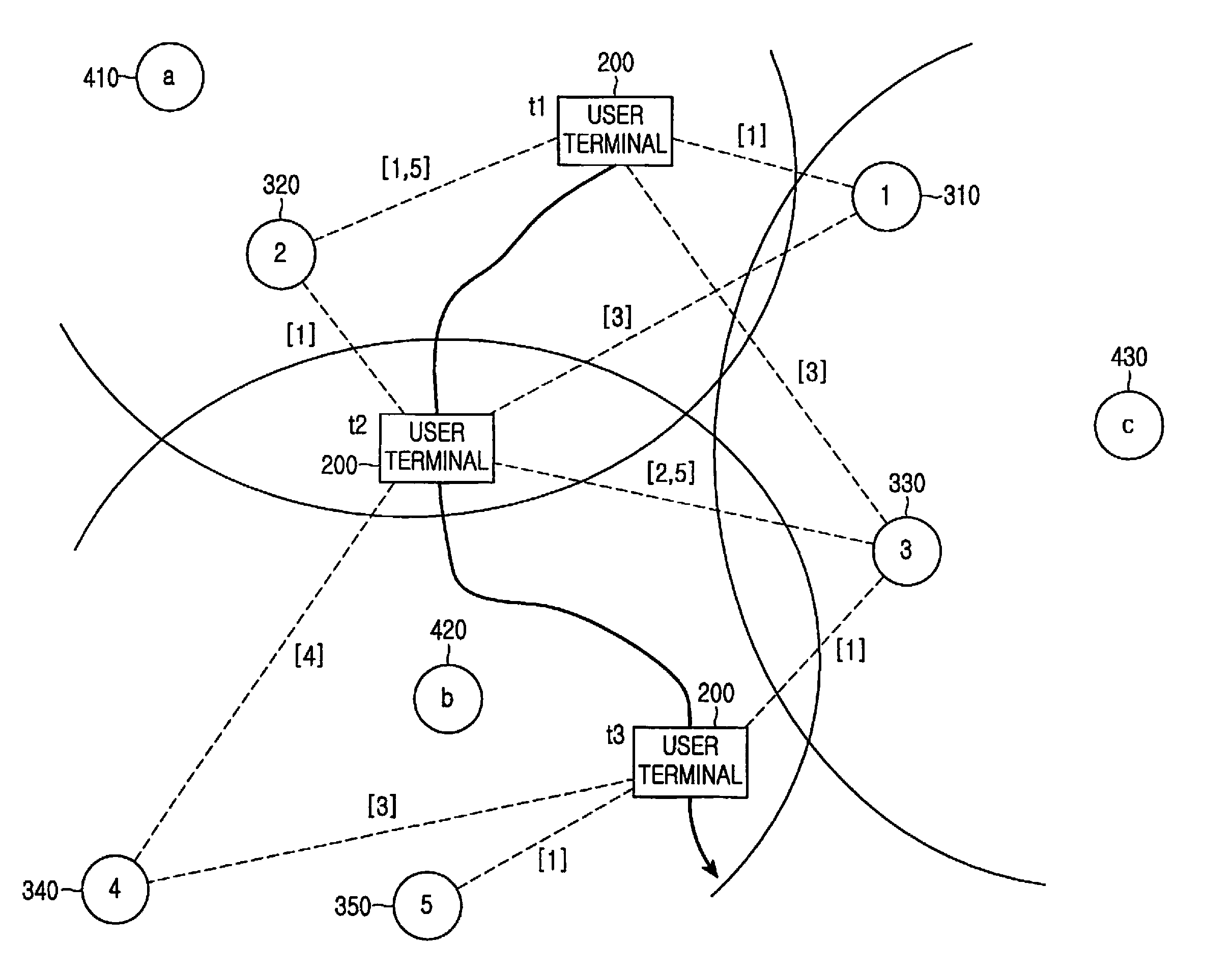
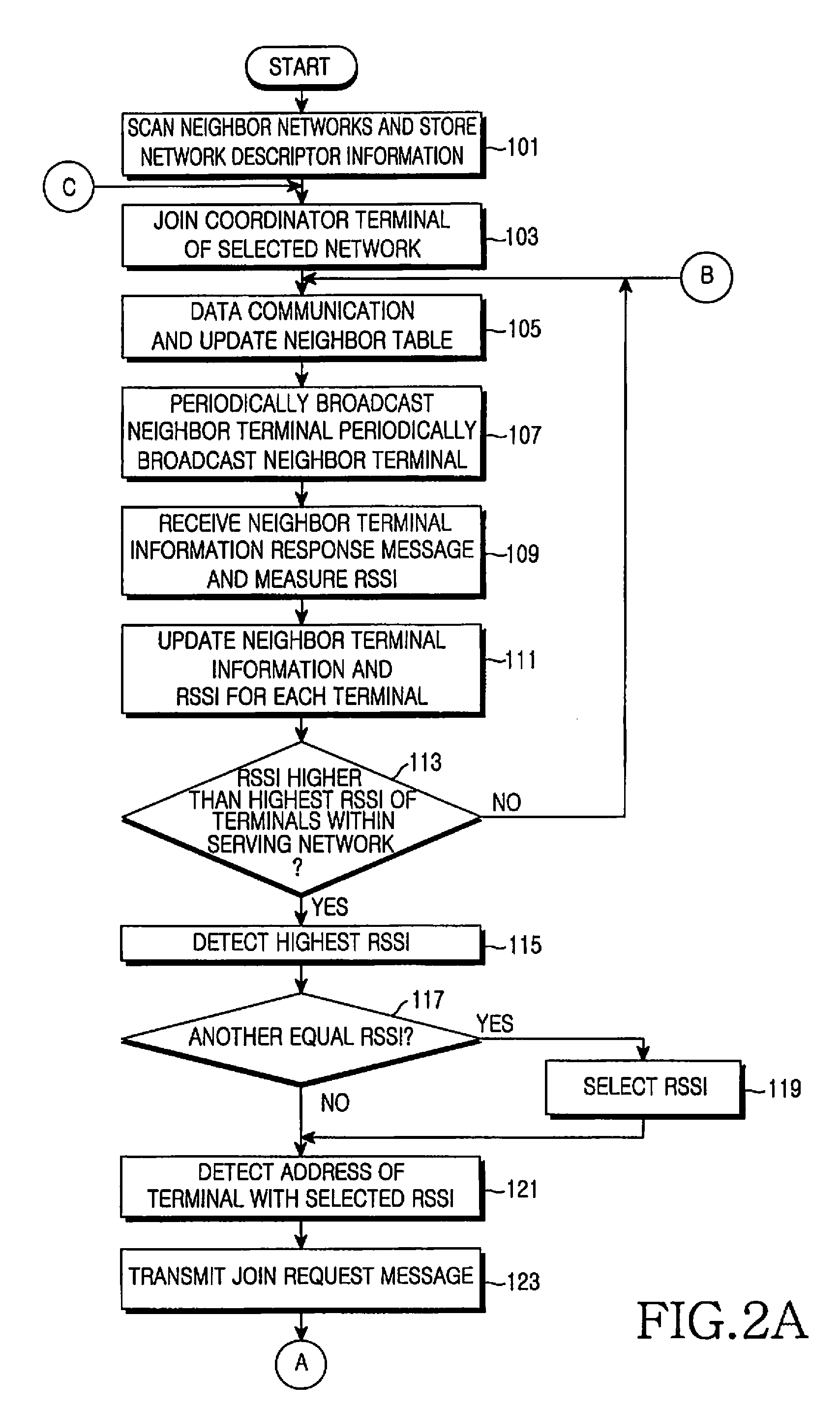
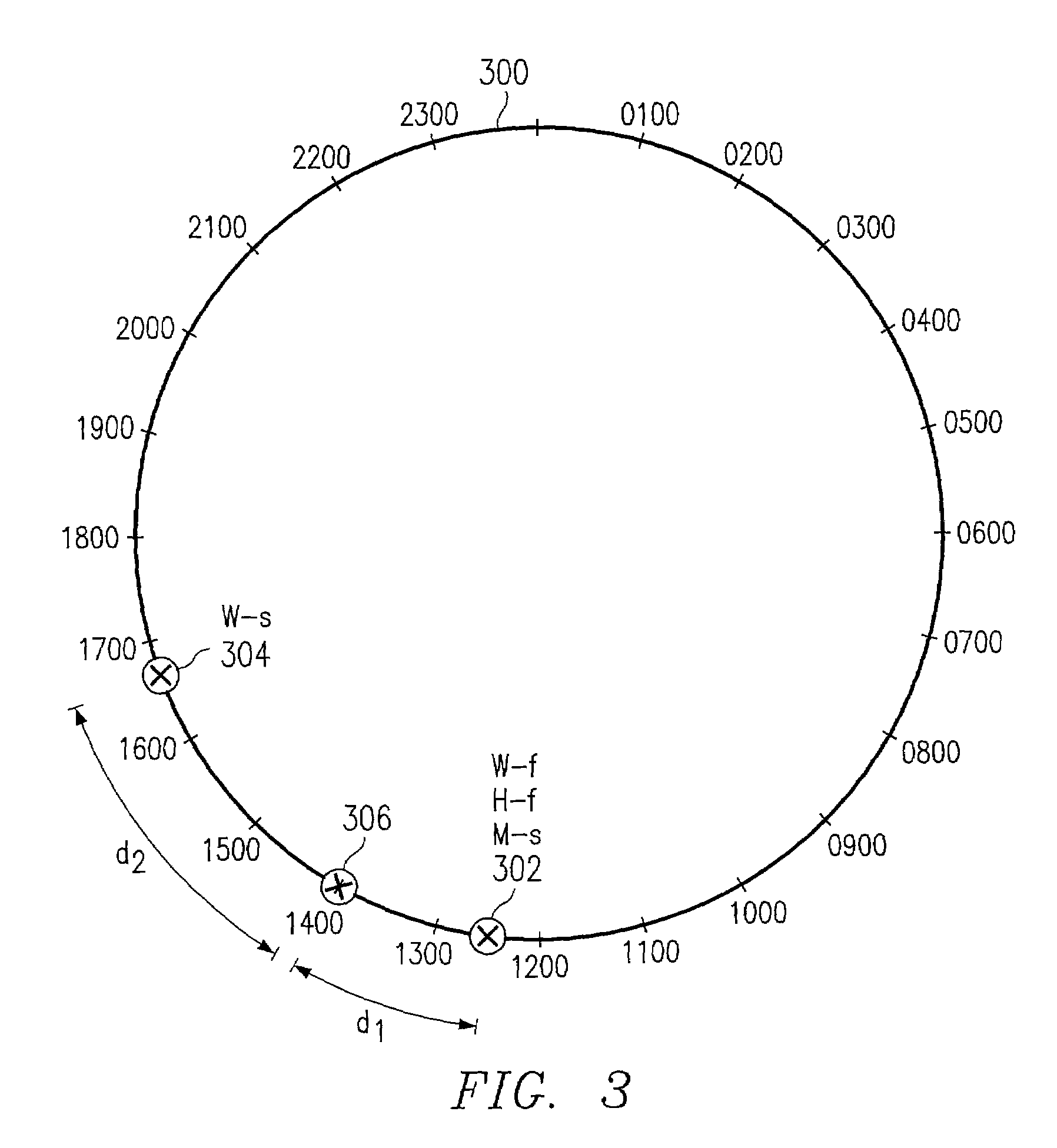
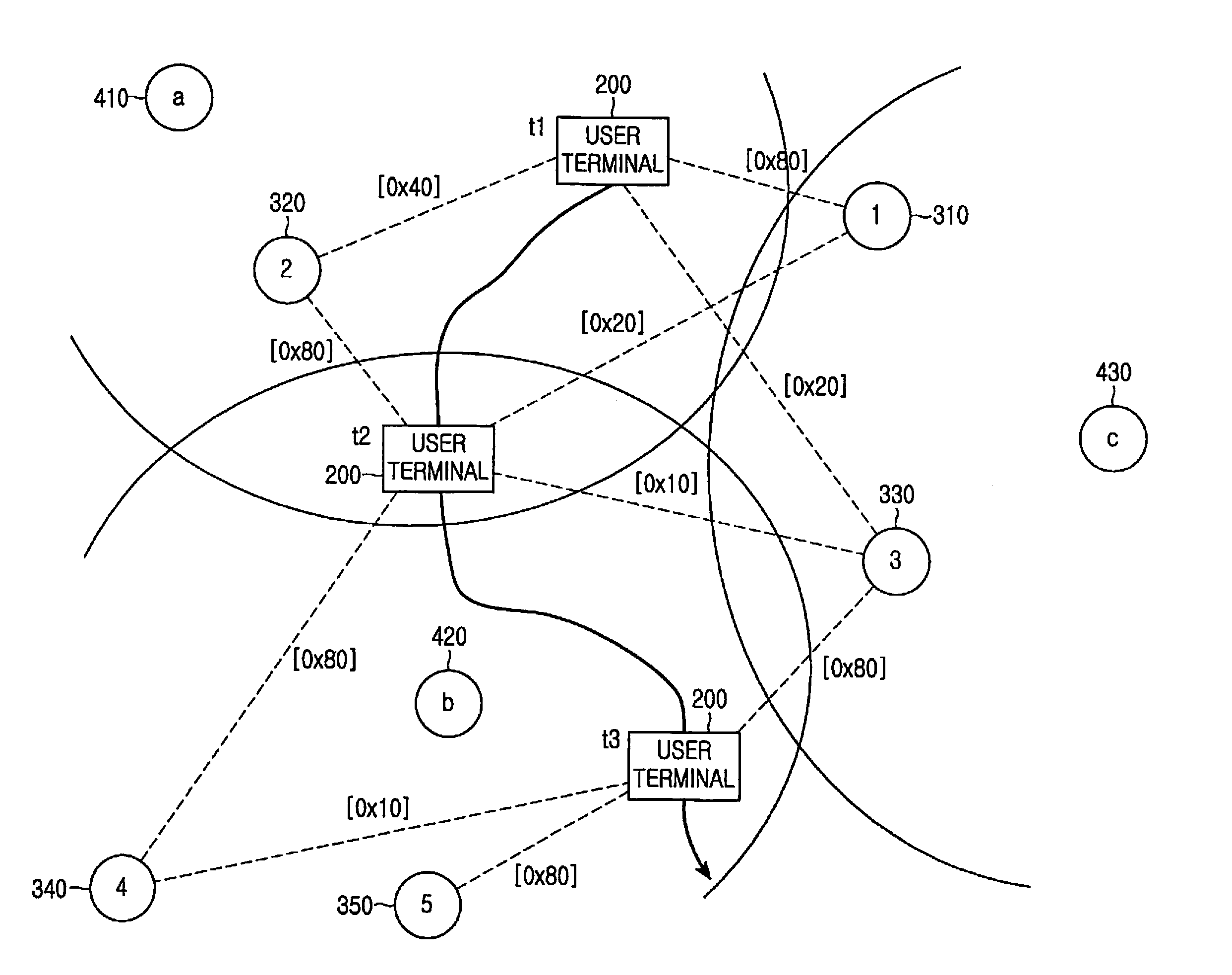
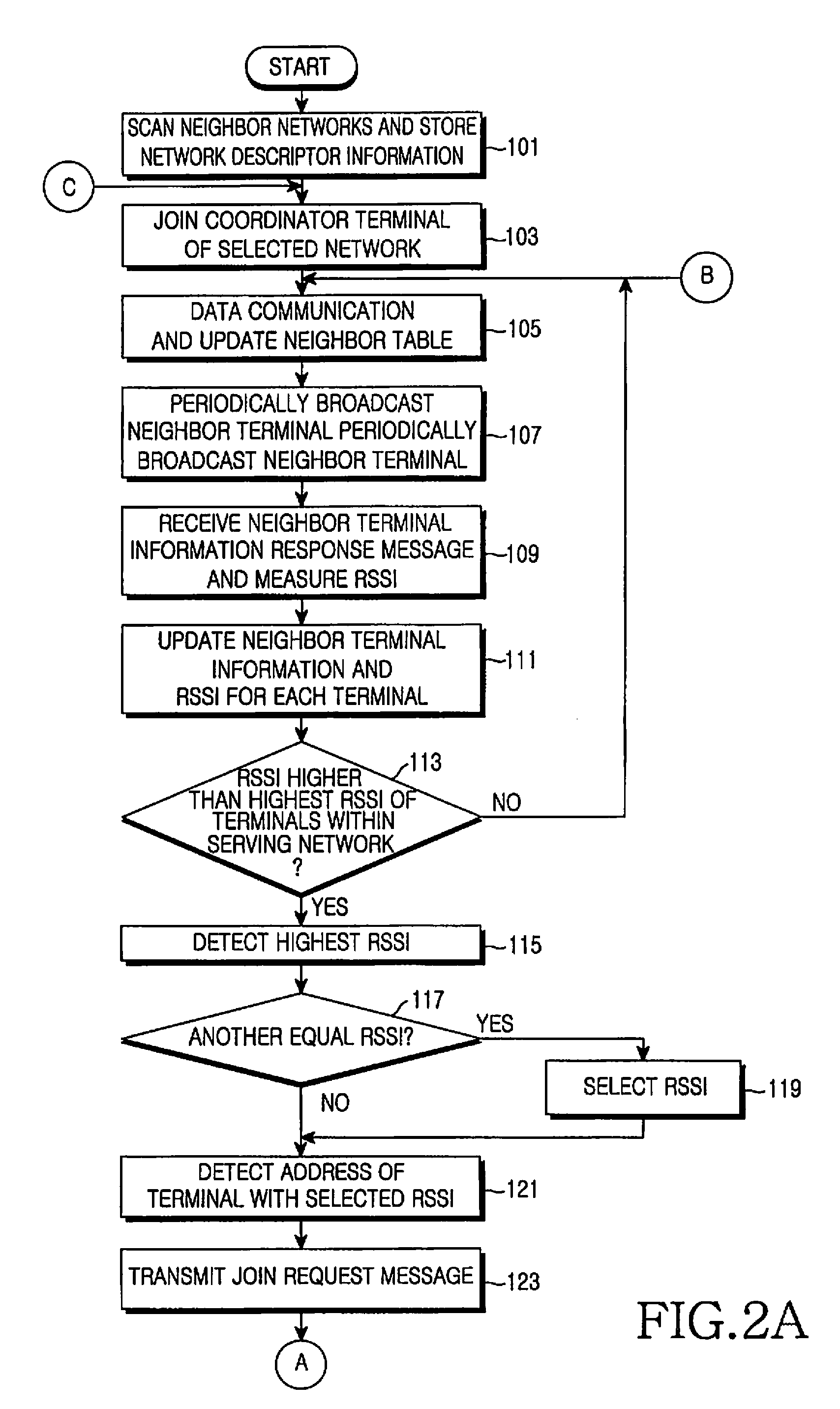
Method and apparatus for connecting to network in a short-range mobile communication terminal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Large-scale intelligent group independent collaborative modeling method for imitation of starling group flight
ActiveCN108830373ASolve the problem of finding the optimal valueAdaptableSustainable transportationArtificial lifeDiseaseCrowds
The invention provides a large-scale intelligent group independent collaborative modeling method for imitation of starling group flight. The method comprises the steps of initializing a population andparameters thereof, setting as follows: in the initial state, all Agents use initial positions as optimal positions, and all Agents use optimal values of six or seven most closest neighbors as localoptimal values; calculating a fitness function, and setting distribution anisotropy of neighbors around each Agent, wherein six or seven most closest neighbors are isotropic, and interaction between the Agents depends on a topological distance; selecting an updating company, comprising the step of selecting one of the six or seven most closest neighbors as an updating company for a certain Agent;defining an interaction relationship of Agents; and updating Agent speed and position. The method has a broad application prospect in military, emergency, industrial and medical care fields like dronecluster intensive formation, group emergency evacuation in a large collection place, large-scale robot group collaborative operation, and disease spread control.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for a distributed fault tolerant network configuration repository
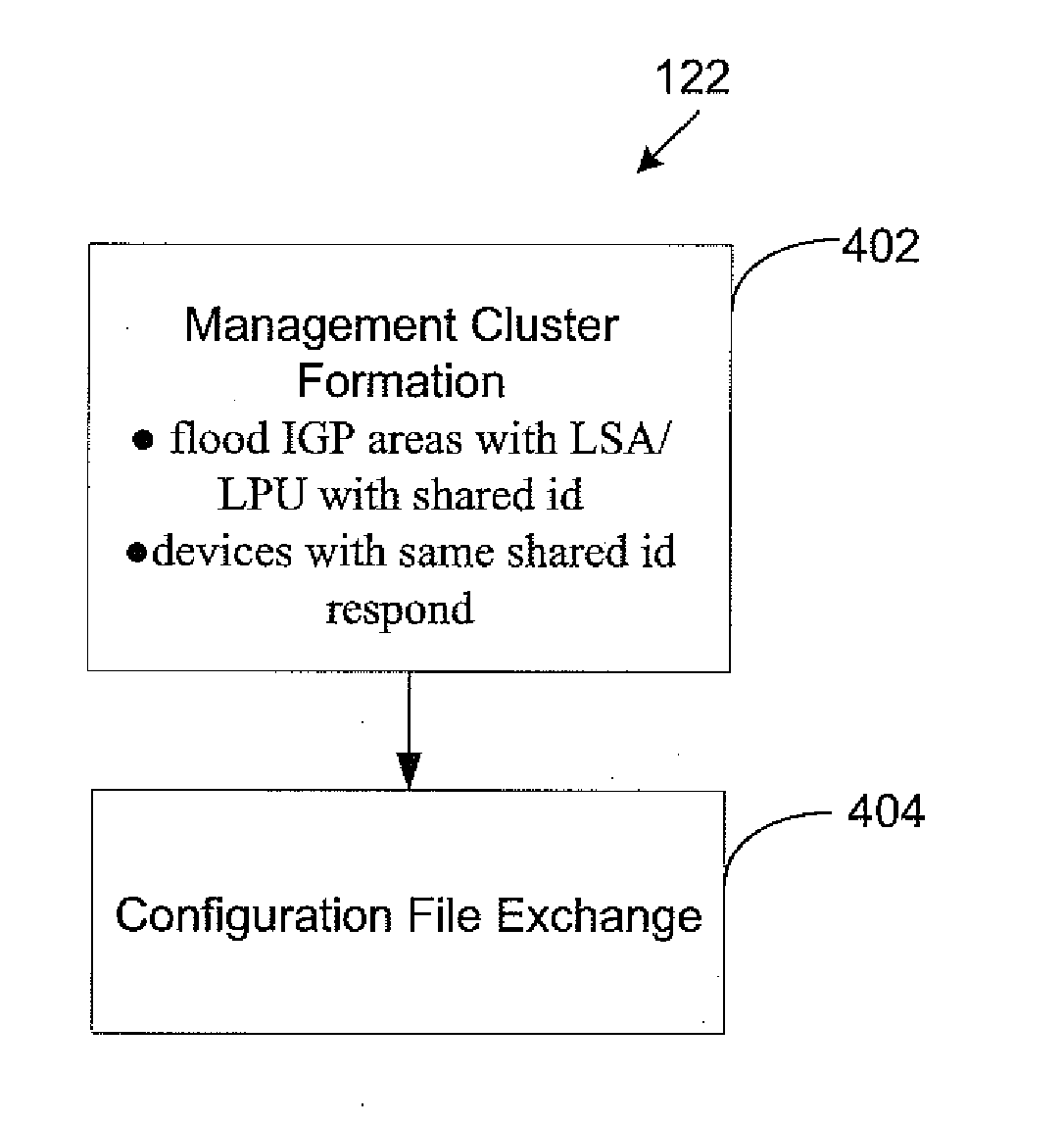
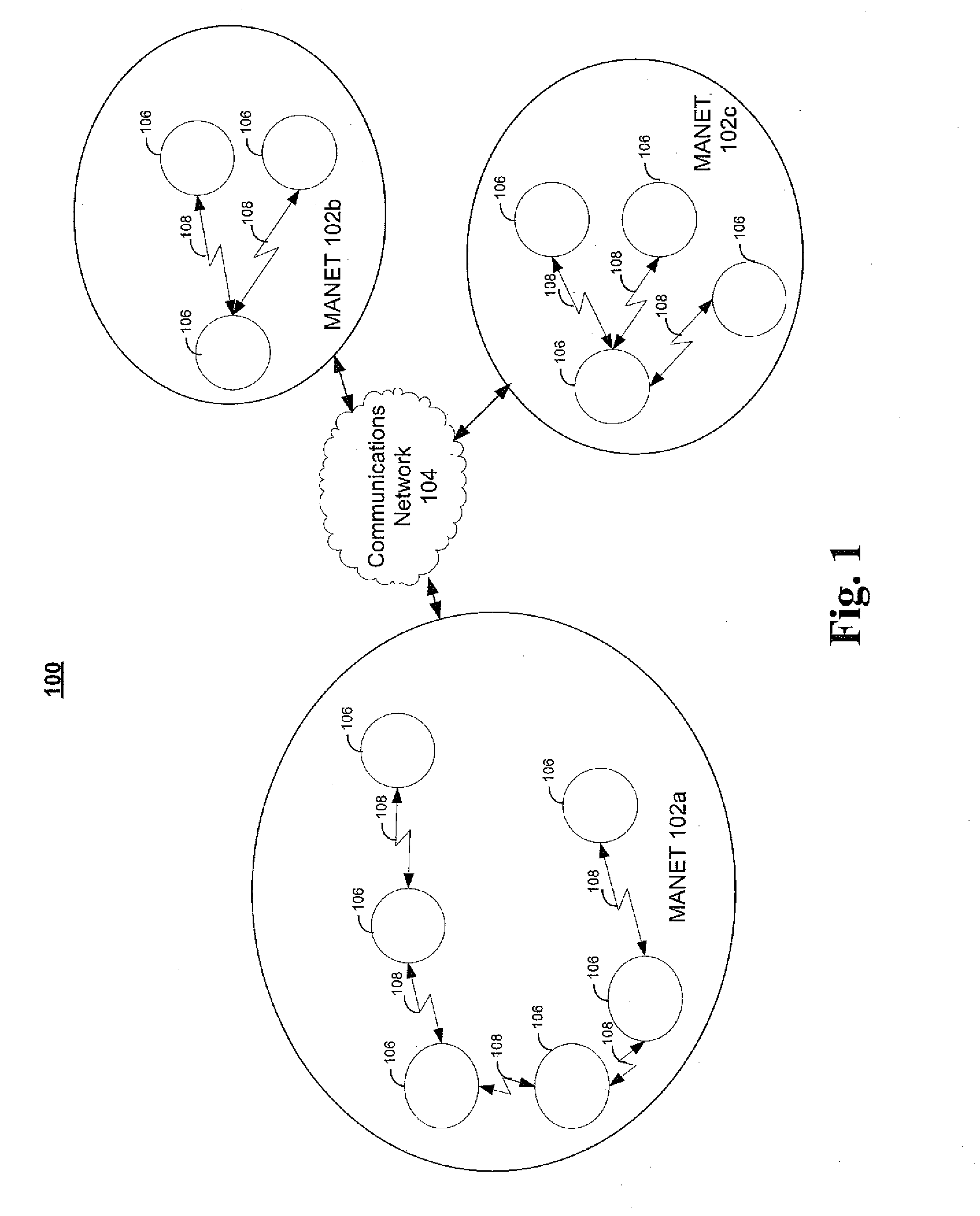
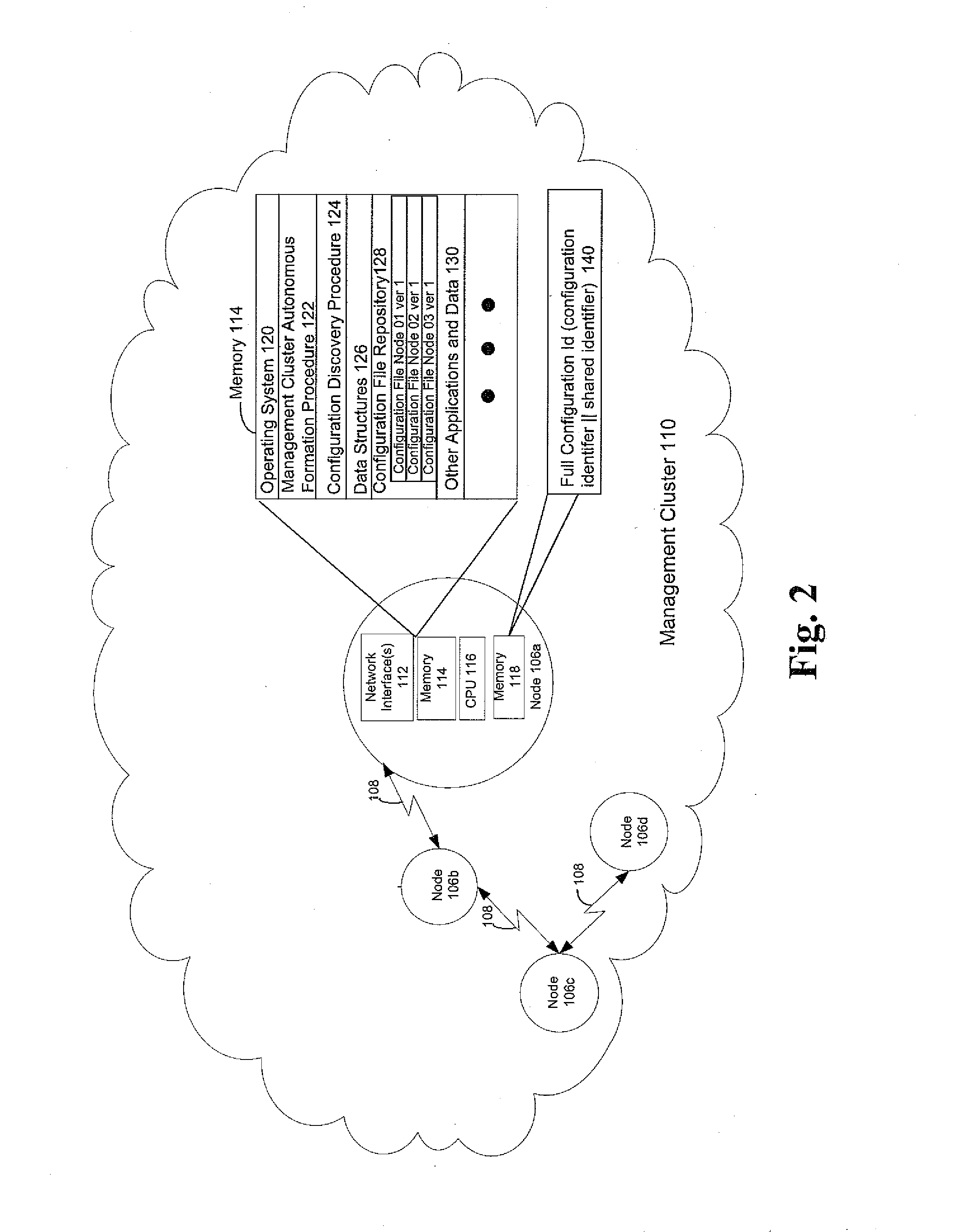
InactiveUS20110185047A1Well formedChanges to configurationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsClose neighborDistributed computing
An autonomous management cluster of network elements serves as a distributed configuration repository. Network elements sharing a common pre-determined shared identifier autonomously form themselves as a management cluster. The network elements in the cluster exchange configuration files. In the event of a loss, destruction, or corruption of one of the network element's configuration file, the network element recovers its configuration file from its closest neighbor in its management cluster. The management cluster can also be used to efficiently disseminate configuration changes by simply communicating the changes to one or more elements in the cluster, and allowing the other nodes in the cluster to discover and retrieve their updated configuration files.
Owner:TT GOVERNMENT SOLUTIONS
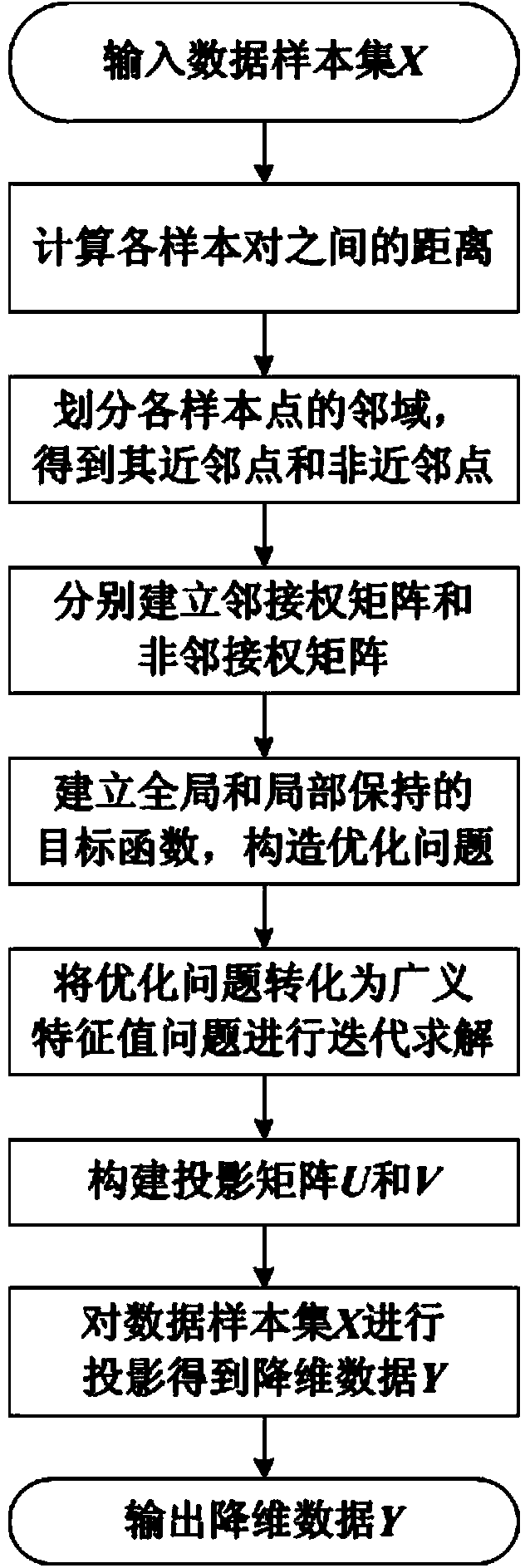
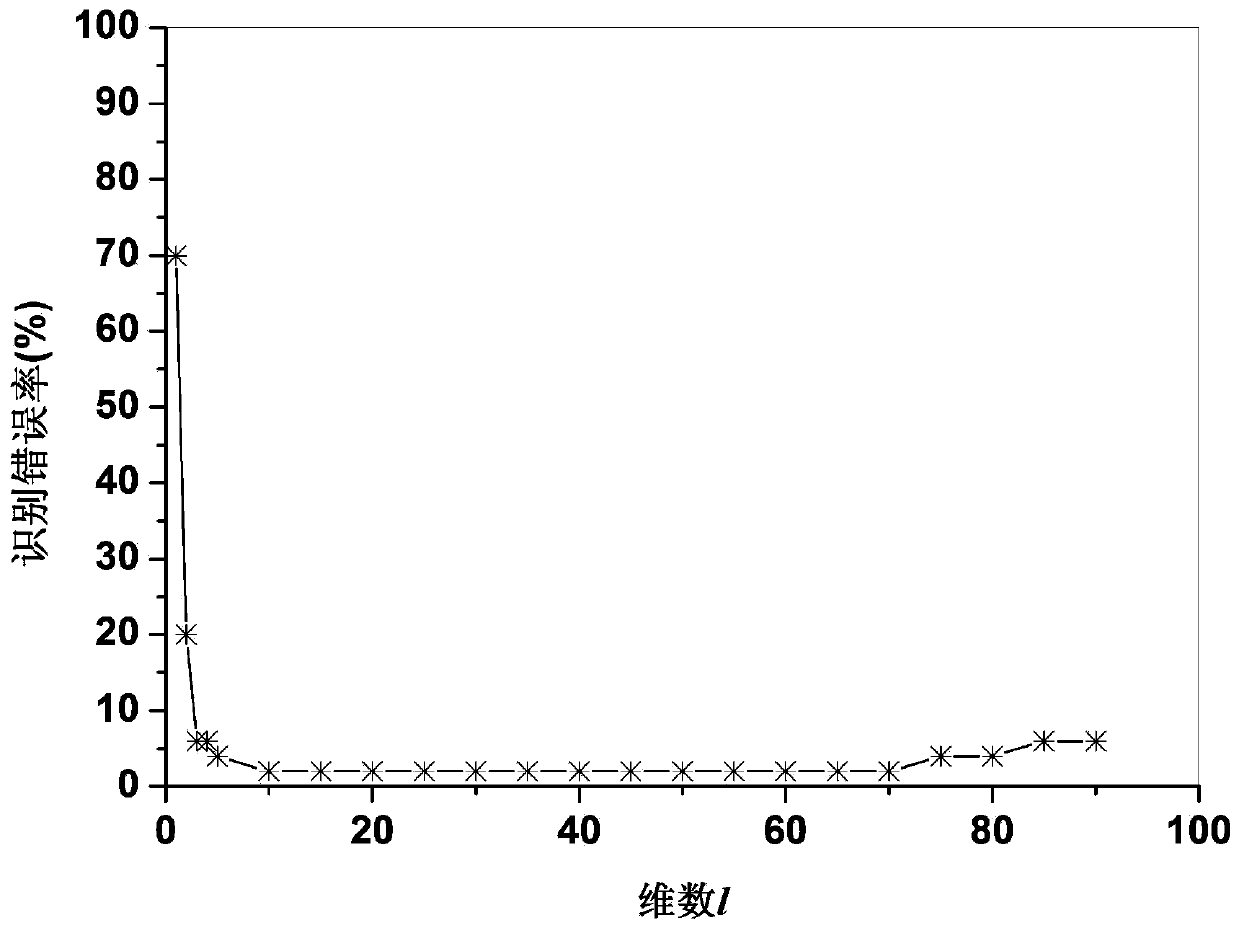
A data dimension reduction method based on a tensor global-local preserving projection
ActiveCN103605985AGood dimensionality reduction effectCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixDimensionality reduction
A data dimension reduction method based on a tensor global-local preserving projection comprises the following steps: (1) data samples are selected to form a sample set which is to be subjected to dimension reduction; (2) distances between sample pairs are calculated; (3) neighborhoods of sample points are divided to obtain close neighbor points and non-close-neighbor points; (4) neighboring right matrixes and non-neighboring right matrixes are established according to close neighbor relations and not-close-neighbor relations among the samples; (5) An object function corresponding to data global and local structure preserving is established, and an optimization problem is constructed; (6) the optimization problem is converted to a generalized eigenvalue problem, and a projection matrix is obtained through solving the problem; and (7) projection is carried out on the sample set to obtain dimension reduction data. Targeting at a dimension reduction problem of second order tensor data, the invention provides the data dimension reduction method which can simultaneously carry out excavation on the global and local structures of the data, which is good in dimension reduction effects and which are based on the tensor global-local preserving projection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
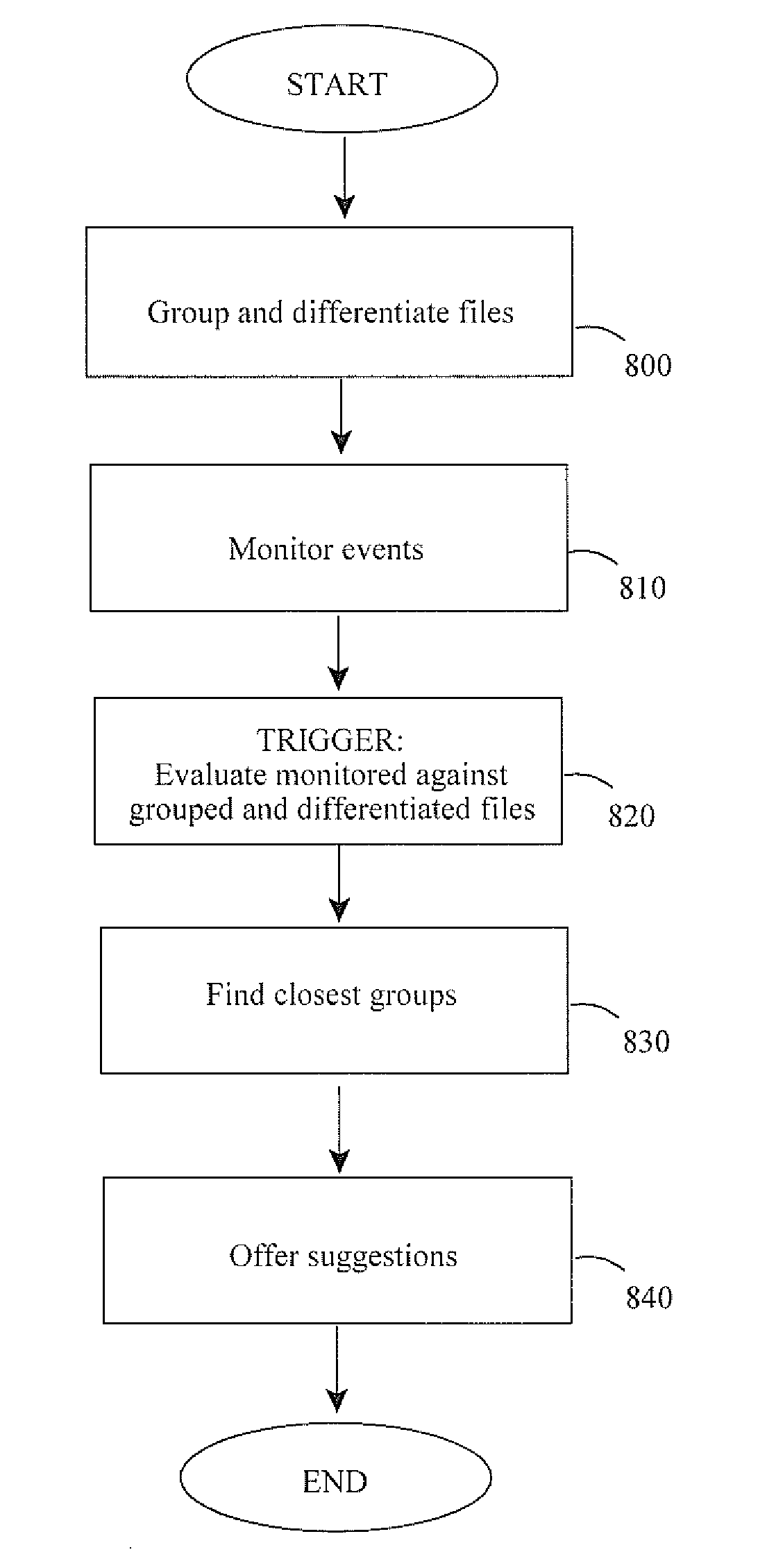
Harvesting relevancy data, including dynamic relevancy agent based on underlying grouped and differentiated files
InactiveUS20110225154A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesDifferentiated servicesFrequency spectrum
Methods and apparatus teach a digital spectrum of a file representing underlying original data. The digital spectrum is used to map a file's position. This position relative to another file's position reveals closest neighbors. When multiple such neighbors are grouped together they can be used to indicate relevance in current data under consideration on a same or different computing device. Also, relevance can be found without traditional notions of needing structured data or users initiating searching for relevance or by examining metadata / administrative information associated with the files. A dynamic relevancy agent is configured for installation on the same or different computing device to monitor events regarding the current data and to initiate the examination of relevancy. It also presents to a user suggestions of data closest to the current data. Various triggering events to undertake a relevancy examination are also described as are predetermined criteria to define relative closeness.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Self-learning intelligent call routing gatekeeper
InactiveUS7113775B2Special service for subscribersSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsClose neighborCall routing
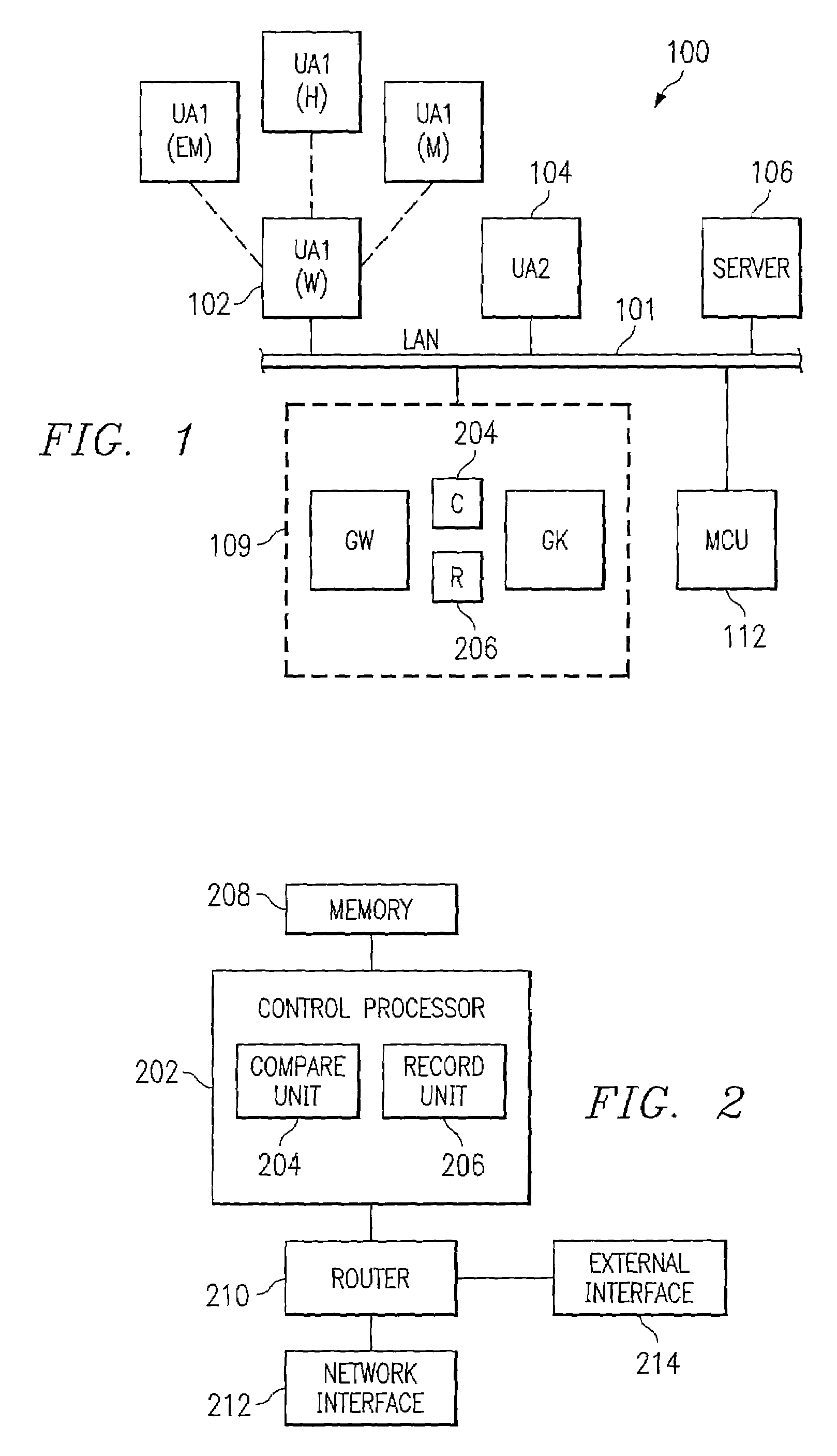
A gatekeeper (109) including a compare unit (204) and a record unit (206). The compare unit (204) receives call requests and accesses a database which is a record of where a called party picked up the call, e.g., at home, at the office, via a mobile phone, or via an emergency number. The compare unit (204) performs an analysis such as a “closest neighbor” analysis to determine the location of the user at the time of day closest to that of the present call. The call is then routed to the user at that location. The record unit (206) then makes the appropriate notation in the database for the latest call.
Owner:UNIFY INC
Method and apparatus for connecting to network in a short-range mobile communication terminal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method, apparatus and product for efficient solution of nearest object problems
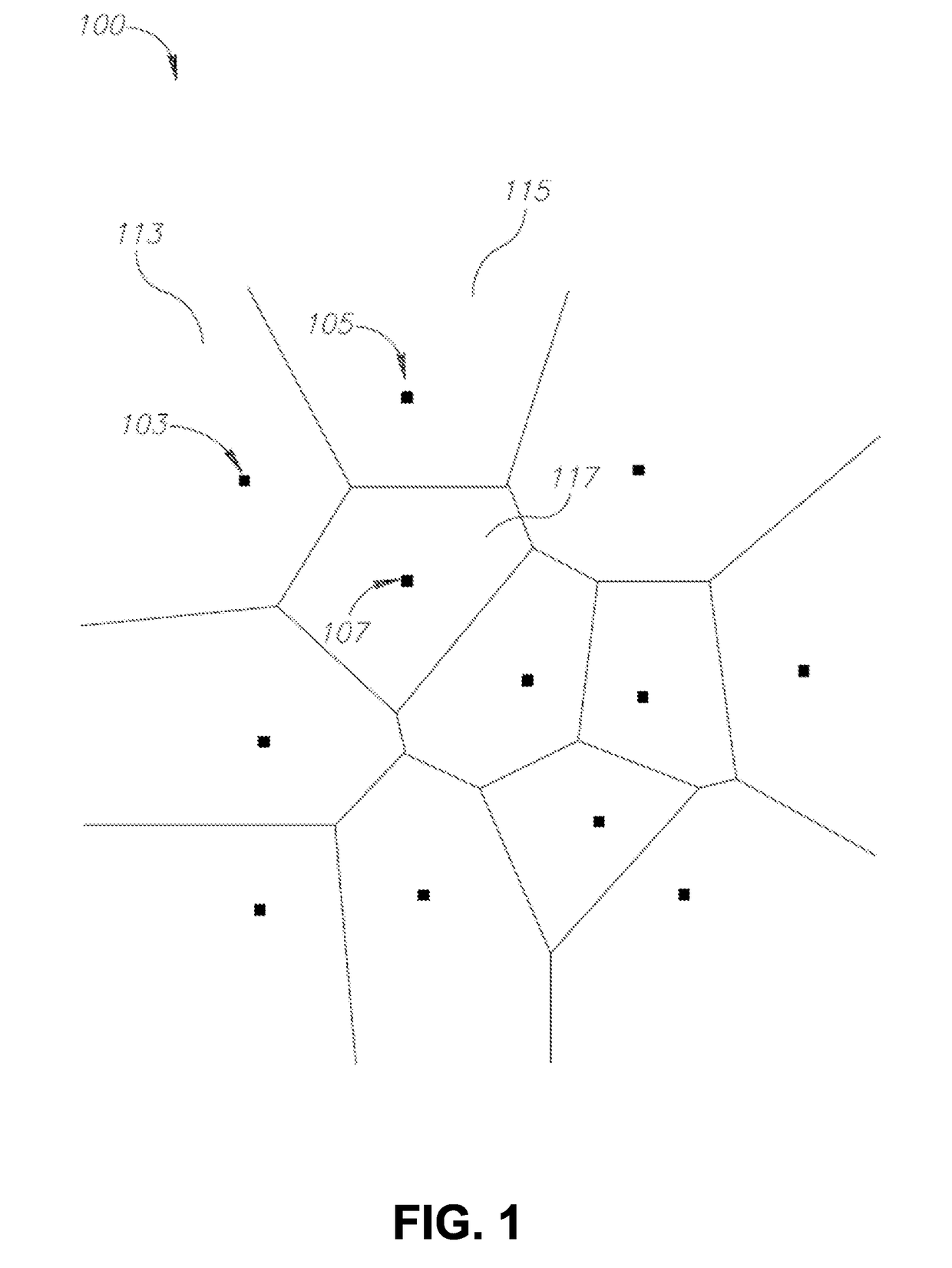
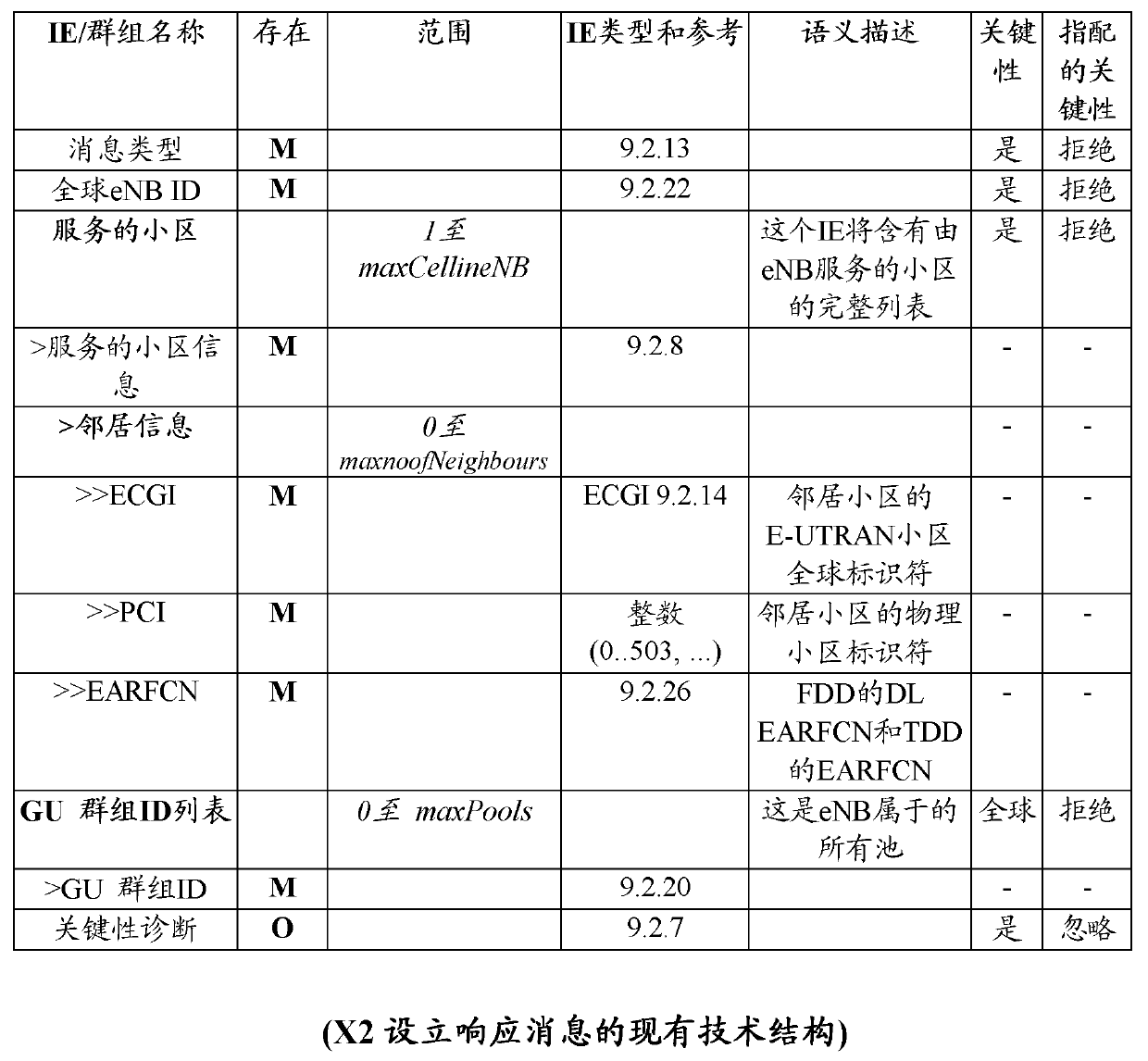
InactiveUS20170234693A1Instruments for road network navigationGeographical information databasesAlgorithmClose neighbor
A computer-implemented method, computerized apparatus and computer program product for efficient solution of nearest object problems. A set of objects having non-point shapes representable by one or more geometric elements are obtained. For each object in the set the one or more geometric elements are sampled to obtain a set of points representing the set of objects. A Voronoi diagram is constructed for the set of points, whereby a subdivision of a space accommodating the set of objects into a plurality of cells, each cell containing a single point of the set of points and defining a region of closest neighbors of the point, is obtained. Cells containing points representing the same object are aggregated into a unified cell defining an estimated region of closest neighbors of the object.
Owner:IBM CORP
Clustering method for performing matrix decomposition by taking subset grouping as auxiliary information
InactiveCN107330443AClustering quicklyImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
The invention relates to a clustering method for performing matrix decomposition by taking subset grouping as auxiliary information, which is characterized in that grouping information of a certain number of subsets is obtained through collecting grouping results of a user for different subset to act as guidance for clustering, a close neighbor set and a far neighbor set of objects in the subset are obtained based on the results, and the category of each object in the subset is enabled to be close to the category of objects in the close neighbor set but be different from the category of objects in the far neighbor set through a mode of adding regular items to an objective function for matrix decomposition so as to complete clustering. The clustering method not only considers the decomposition error, but also reduces the difference between grouping of objects in the subset and grouping of objects in the close neighbor set and increases the difference between grouping of objects in the subset and grouping of objects in the far neighbor set at the same time in matrix decomposition based on a grouping result of the subset in the previous step, thereby achieving satisfactory results without the need of excessive number of constraints, and is fast in clustering, high in efficiency and low in labor cost in practical application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A method and a network node for sharing information over an interface in a telecommunications system
InactiveCN103202092AImprove visualizationOptimize topologyConnection managementNetwork data managementClose neighborRadio Base Station
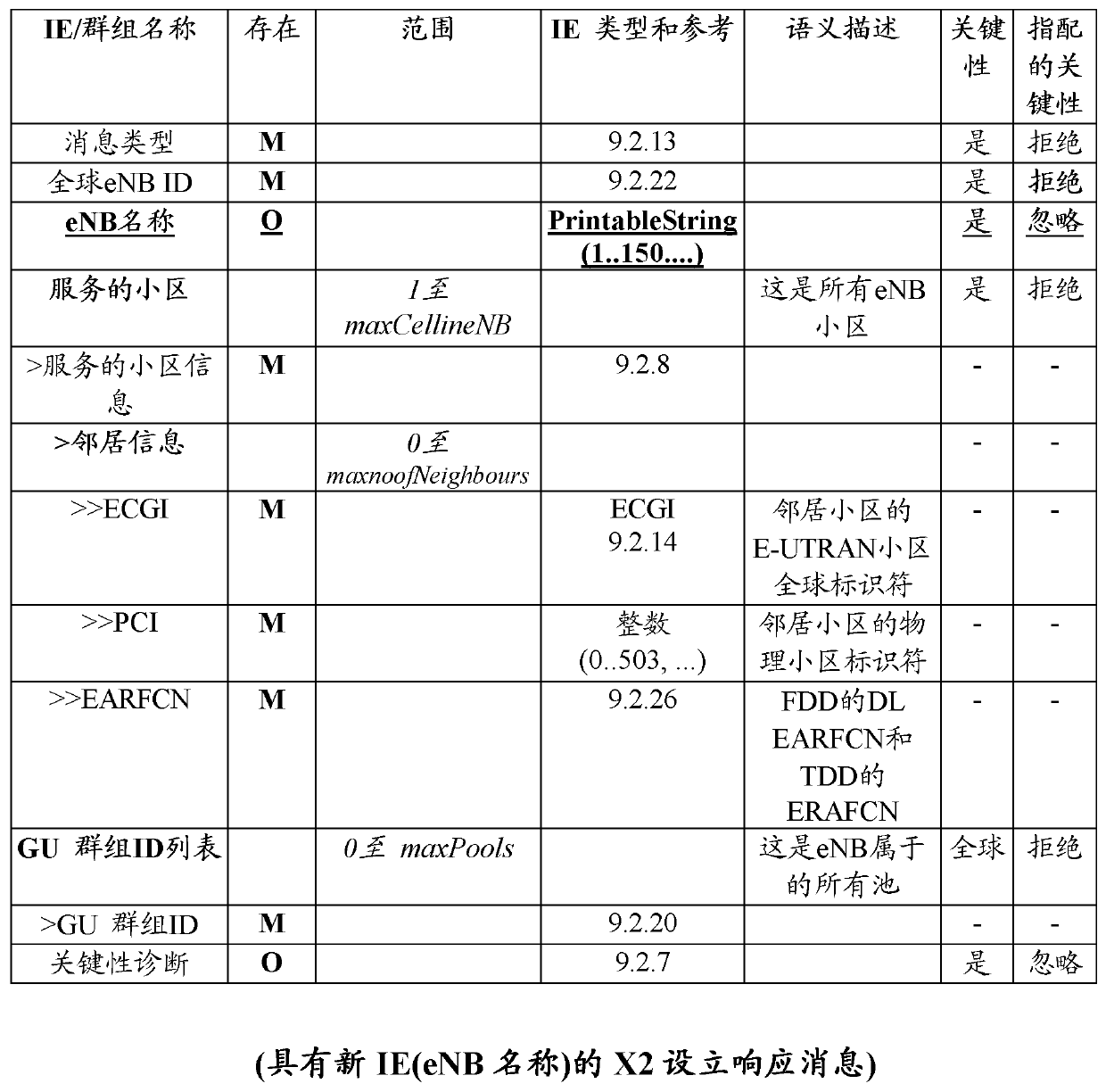
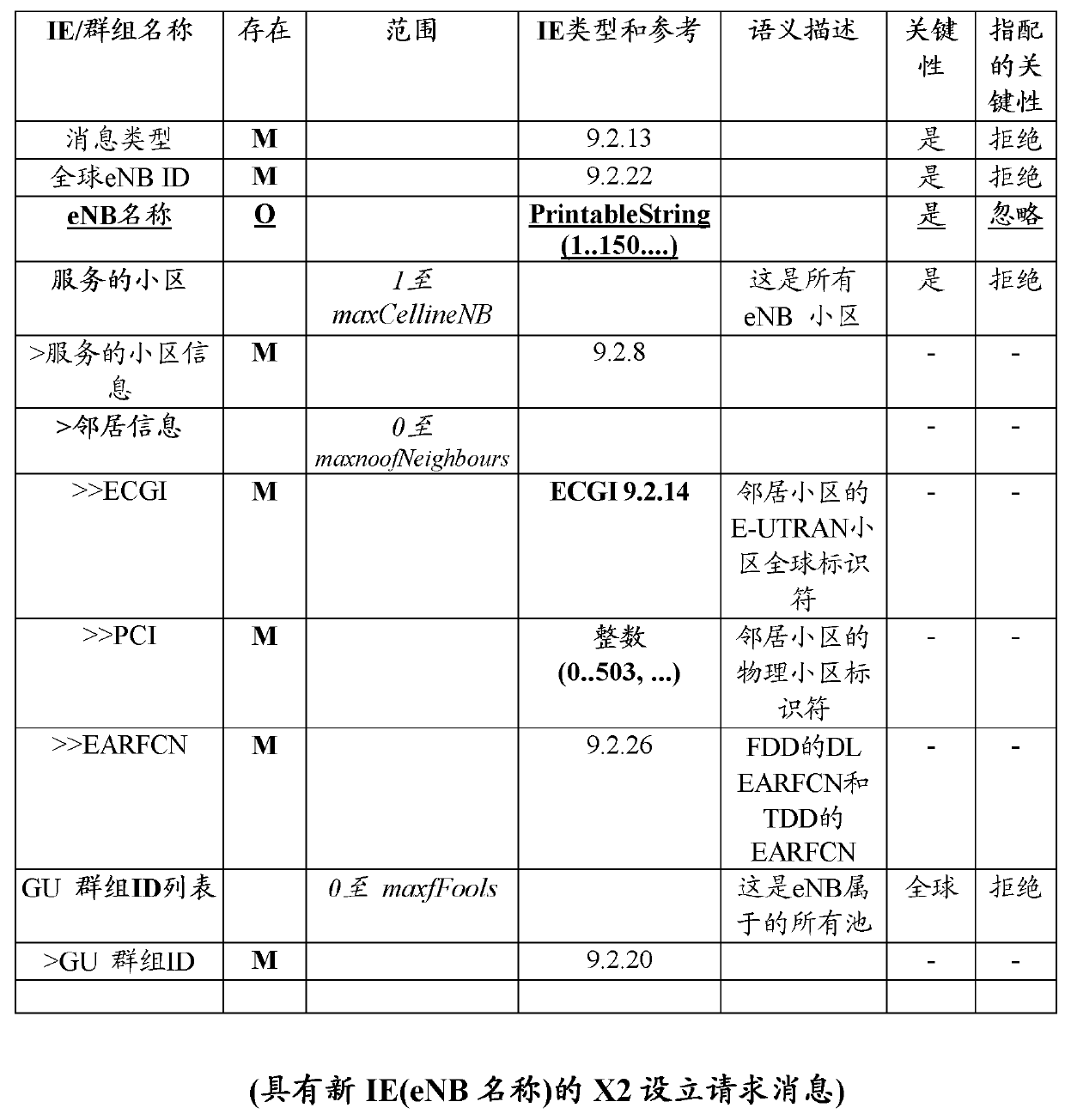
The exemplary embodiments of the presently claimed invention relate to a method and a radio base station (600) for identifying candidate or neighbor base stations. The radio base station (600) is configured to include in a first message an information element (IE) including the name of the radio base station (600) and to transmit this message, via the X2 interface, to a candidate or target radio base station. In response, the target base station includes its name in an IE of a response message and send it to the first (initiating) radio base station (600). The name sharing improves visualization and topology since the closest neighbor radio base station is easily identifiable when building radio base station's relations.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method, apparatus and product for efficient solution of nearest object problems
ActiveUS20190120653A1Instruments for road network navigationGeographical information databasesAlgorithmClose neighbor
A computer-implemented method, computerized apparatus and computer program product for efficient solution of nearest object problems. A set of objects having non-point shapes representable by one or more geometric elements are obtained. For each object in the set the one or more geometric elements are sampled to obtain a set of points representing the set of objects. A Voronoi diagram is constructed for the set of points, whereby a subdivision of a space accommodating the set of objects into a plurality of cells, each cell containing a single point of the set of points and defining a region of closest neighbors of the point, is obtained. Cells containing points representing the same object are aggregated into a unified cell defining an estimated region of closest neighbors of the object.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
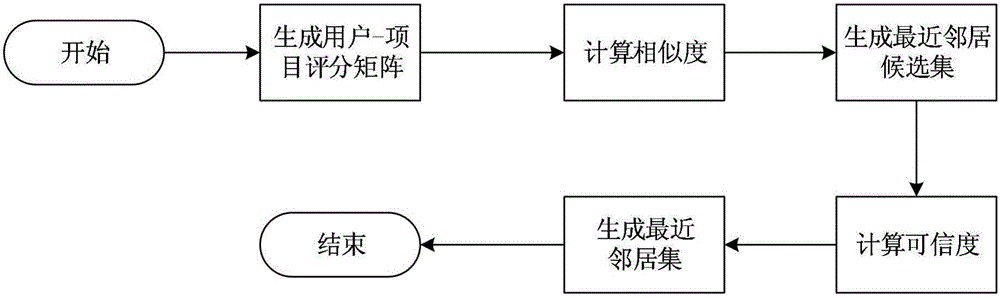
Optimized selection method of user closest neighbor set of electronic commerce recommendation system
InactiveCN106022838AImprove accuracyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMarketingRating matrixClose neighbor
The invention relates to an optimized selection method of a user closest neighbor set of an electronic commerce recommendation system. The optimized selection method comprises the steps that user-project scoring data of a historical record is acquired, and a user-project scoring matrix is established; similarity between a target user and other users is calculated by adopting the Pearson similarity calculating method; for the users in a closest neighbor candidate set, an average error between the score of the user and the scores of the users in the set is calculated according to data of a common scoring item set shared by the user and the users in the above mentioned set, and then confidence level is calculated, when the average error is greater, the confidence level between the target user and the users in the set is smaller; K users having the high confidence levels are used to form the closest neighbor set of the target user, and in addition, 1<K<0. Accuracy of recommendation is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
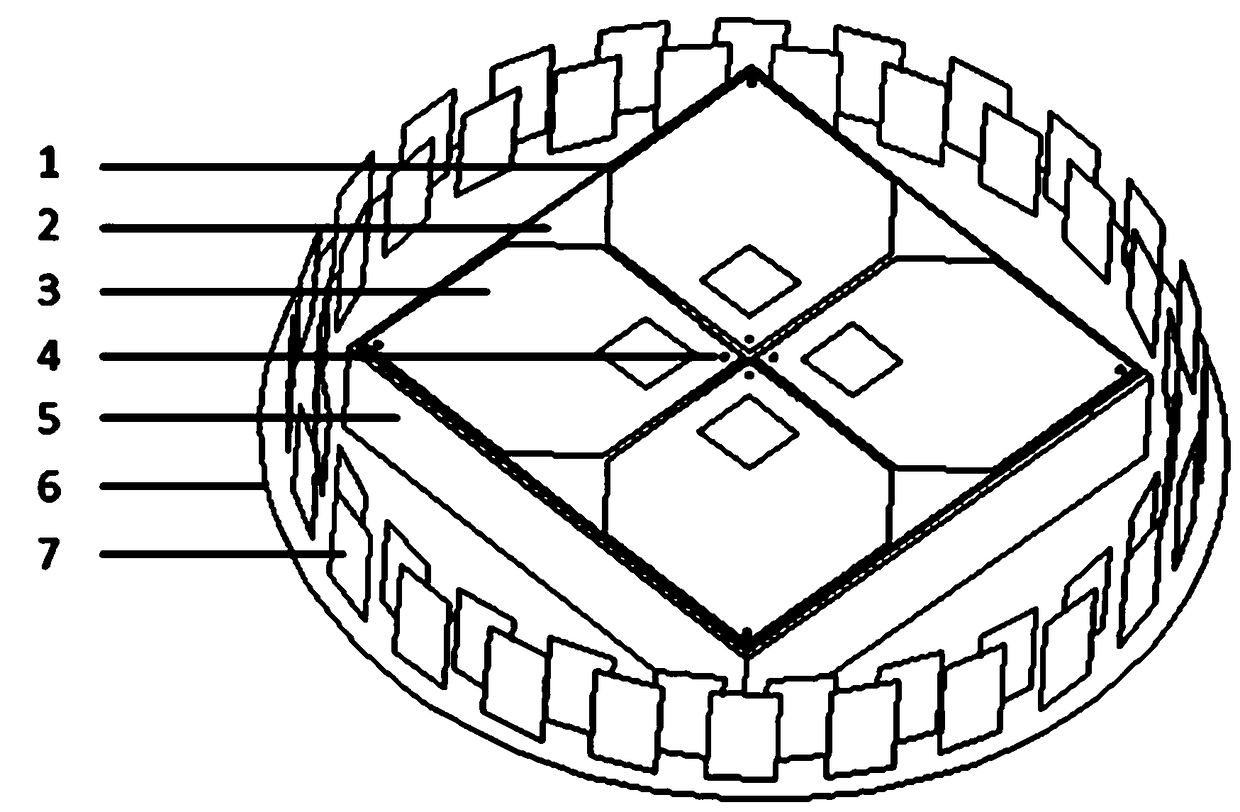
Broadband zero phase center high-precision antenna of butterfly oscillator structure
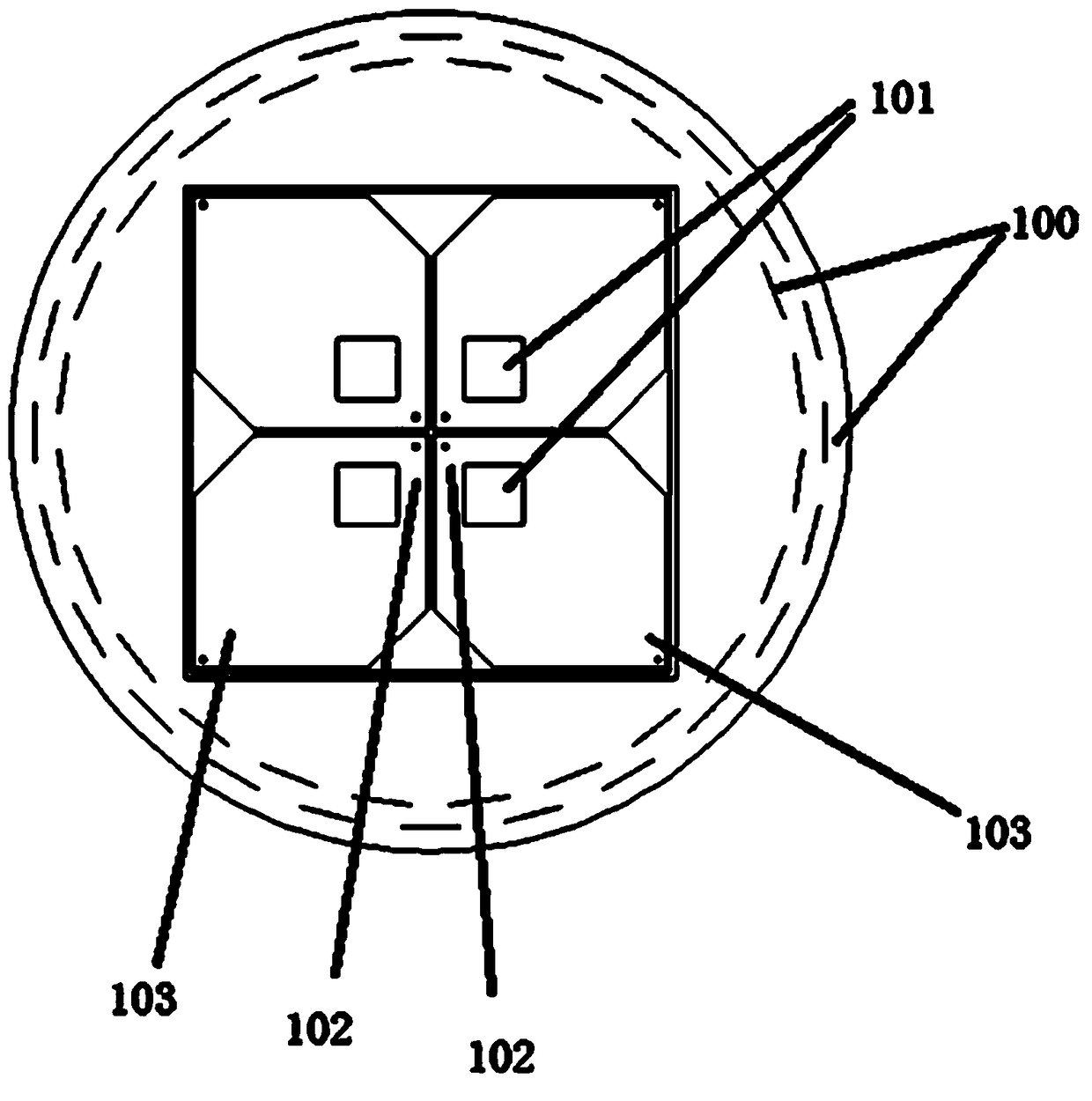
PendingCN109119753AHigh gainHigh beamRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationResonant cavityMultipath effect
The present invention provides a broadband zero phase center high-precision antenna of a butterfly oscillator structure. The broadband zero phase center high-precision antenna comprises an antenna main radiation unit, a resonant cavity, a feed structure and a parasitic radiation structure. The antenna main radiation unit comprises a square PCB, an oscillator structure, a main radiation unit grounding plate and a regulation branchknot; the regulation branchknot is connected with the oscillator structure; the oscillator structure comprises four hexagonal radiation paster oscillators with hollowstructures and with dimensions; the corner of each hexagonal radiation paster oscillator comprises one feed angle and one wing tip angle opposite to the feed angle; the feed angles of the oscillatorsare integrally arranged at the centers of the square PCB and are connected with the feed structure; the side boundary of the feed angles of the adjustable oscillators are close neighbor and in parallel to each other; the wing tip angles of the oscillators are respectively arranged at the four corners of the square PCB to allow the oscillator structure to be a butterfly wing shape; and the parasitic radiation structure is round the antenna main radiation unit, and the lower portion of the main radiation unit grounding plate is connected with the resonant cavity. The broadband zero phase centerhigh-precision antenna of a butterfly oscillator structure has a high gain, a wide beam and a wide band, and is stable in phase center and high in anti-multipath effect capacity.
Owner:国网思极位置服务有限公司 +1
Simplified method of detection by spheres when there is a low signal to noise ratio
InactiveUS6987818B2The detection method is simpleLow signal noiseTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Algorithm
Method of detecting a plurality of symbols transmitted by or to a plurality of users from a received signal, each symbol of a user belonging to a modulation constellation, the detection method using a lattice of points generated by the said modulation constellations, the said plurality of symbols of the different users being represented by a point amongst a subset of points in the said lattice, the said constellation and the received signal being represented by a point characteristic of this signal, referred to as the received point, translated from a point in the said constellation by a noise vector, the method including a step of orthogonal projection of the received point onto an affine subspace, referred to as a projection subspace, parallel to or merged with an affine subspace delimiting the constellation, and a step of seeking the closest neighbor to the point thus projected amongst the points in the constellation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Graph-Based Classification of Elements Such as Files Using a Tool Such as VirusTotal
ActiveUS20210314332A1Good flexibilityImprove balanceWeb data indexingComputer security arrangementsIp addressEngineering
A method of determining the level of maliciousness of an element using a directed hypergraph to classify the element based on information aggregated from its locally identified close neighbors, queried in a data base such as VirusTotal (VT). A crawling procedure is used starting from elements needing classification and collecting a set of their neighbors forming neighborhoods. These neighbors are then used to classify the elements. The neural network classifier is able to obtain as input an entire neighborhood. The input includes several feature vectors, one for each element in the neighborhood. In addition, a mapping of interconnections can be provided for each group of elements. Finally, a maliciousness level is provided for the elements in question. For an incriminated file one or more actions can be taken, such as isolating a machine that received the file, killing processes started by the file, removing persistence of the file on the network or affected computer, cleaning infected samples, modifying risk assessment for computer or network, generating a report, collecting additional artifacts, triggering a search for related elements, blocking a user from taking actions and sending information to other IT or security systems. For other element types, some of the above actions are applicable as well. In addition, there are other actions specific to particular element types, e.g. blocking an IP address or a web domain from network access, restricting user authorization, blocking access to an external device, shutting down computers, erasing memory devices, filtering e-mail messages, and many more.
Owner:CYBEREASON
Compensated linear interpolation of capacitive sensors of capacitive touch screens
An apparatus includes a capacitive touch screen (CTS); a touch screen interpolator (TSI) coupled to the CTS; a touch screen capacitive memory (TSCM) coupled to the touch screen interpolator, wherein the interpolator is configured to: interpolates a value based on data points correlated to at least three nodes: a magnitude change of capacitance of a node having the largest magnitude change; a position of the largest magnitude of change node; a change of magnitude of capacitance of a first closest neighbor node; and a change of magnitude of capacitance of a second closest neighbor node.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Fabricating method of photo crystalline plastic optical fiber
InactiveCN1598631ASimple structureEasy to controlCladded optical fibreCoastlines protectionUV curingGas composition
A method of fabricating a photocrystalline plastic optical fiber comprises, for fabricating the cladding, a step of forming a flow by simultaneously injecting a liquid first composition that is a precursor of the cladding polymer and curable by ultraviolet radiation into a first series of holes in an injection plate, and a second composition that is unreactive to the ultraviolet radiation and is selected from a liquid composition and a gas composition into a second series of holes in the plate. The second series of holes have a substantially periodic distribution and each of the holes of the second series has as its closest neighbors holes of the first series. The method further includes a step of irradiating the flow with ultraviolet radiation to form the photocrystalline plastic optical fiber.
Owner:NEXANS
N-ways conference system using only participants' telephony devices without external conference server
InactiveUS20080198770A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationTraffic capacityTraffic delay
An n-ways conferencing system using only the participants' telephony devices and without an external conference server. A plurality of telephony devices dial in to and report their mixing capability to a connection topology manager. The connection topology manager also determines the location of each telephony device and neighboring telephony device pairs in the conference service, as each telephony device is used for mixing voice signals of its closest neighbors, and calculates a minimum conference traffic delay for each telephony device. The connection topology manager then builds a topology for the conference service based on the mixing capability, location, and minimum conference traffic delay, wherein the connection topology manager distributes a mixing computation in a substantially uniform manner across the plurality of telephony devices. When a change in the network condition is detected, the connection topology manager rebuilds the topology to bypass the change in the network condition.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com