Fabricating method of photo crystalline plastic optical fiber
A technology of crystalline plastic and optical fiber, which is applied in the direction of cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide light guide, cutting, etc., can solve the problems of even closing, difficult to preserve optical crystallized optical fiber, optical fiber loss, etc., and achieve the effect of improving control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
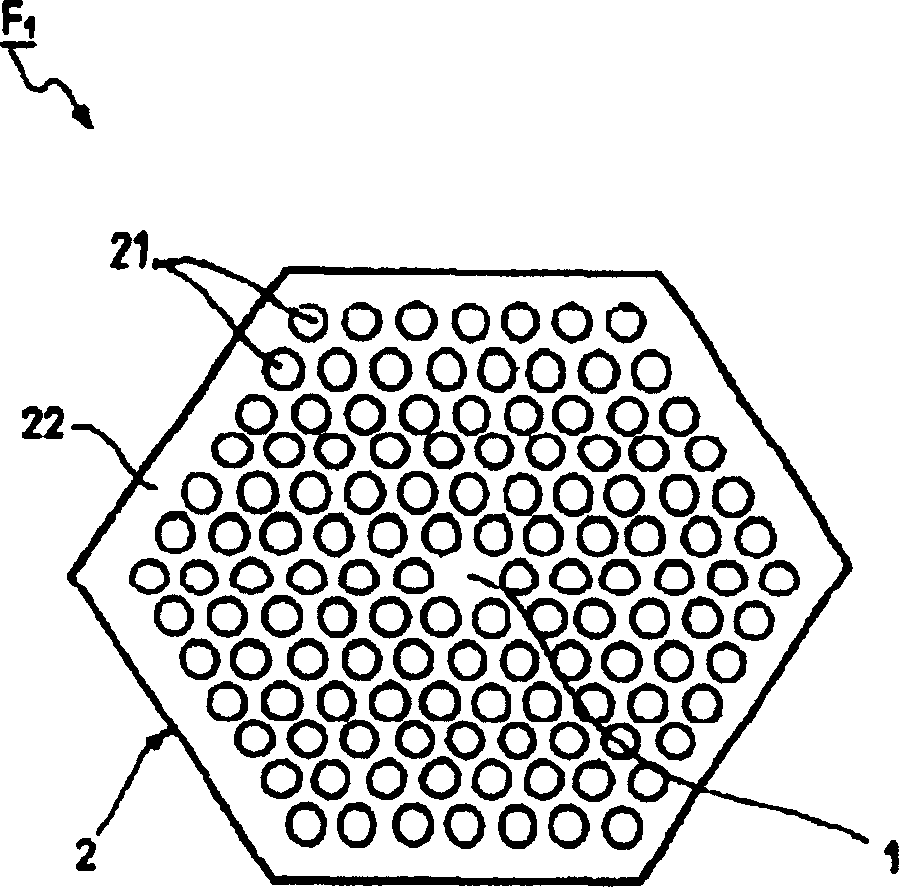
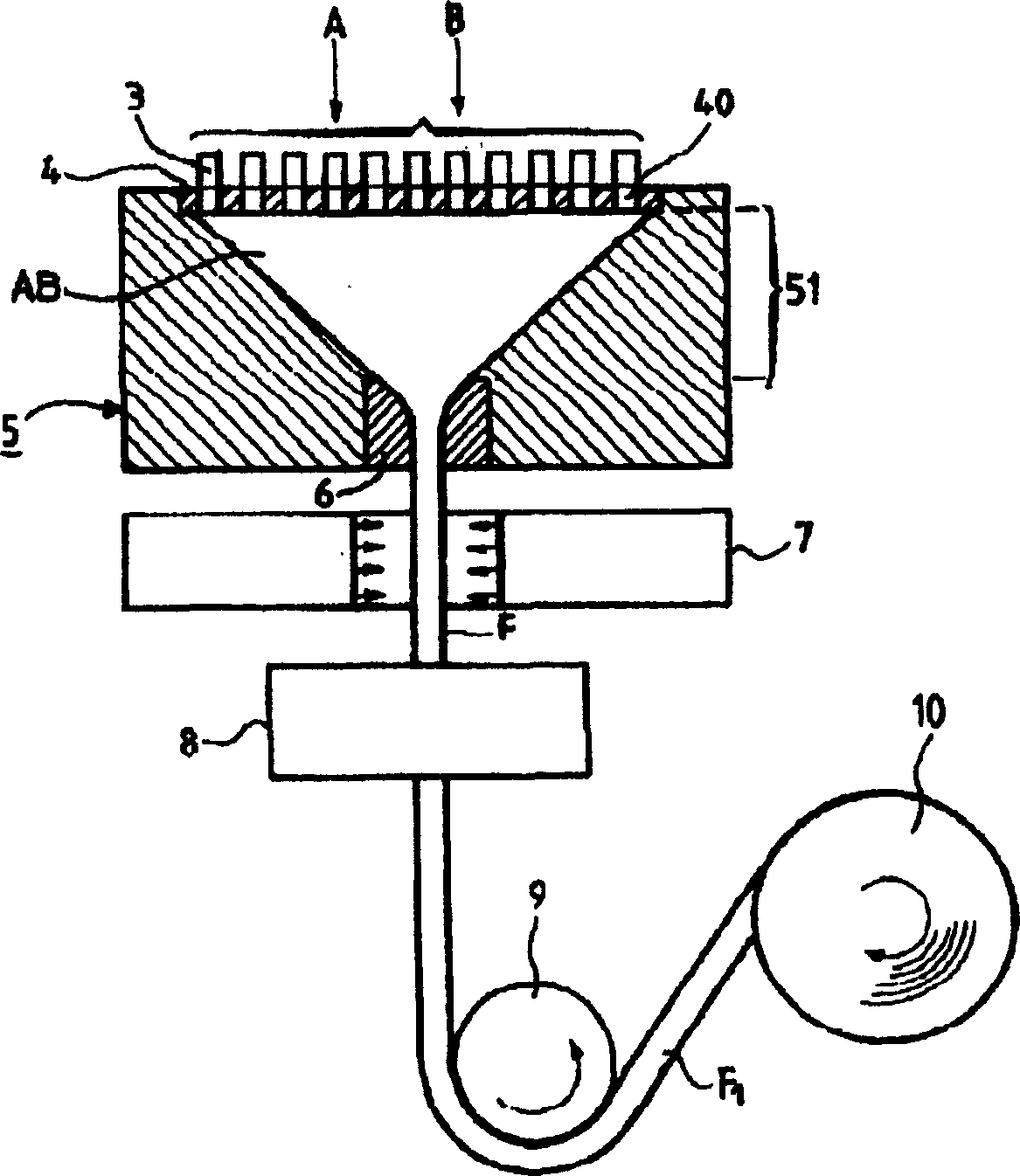
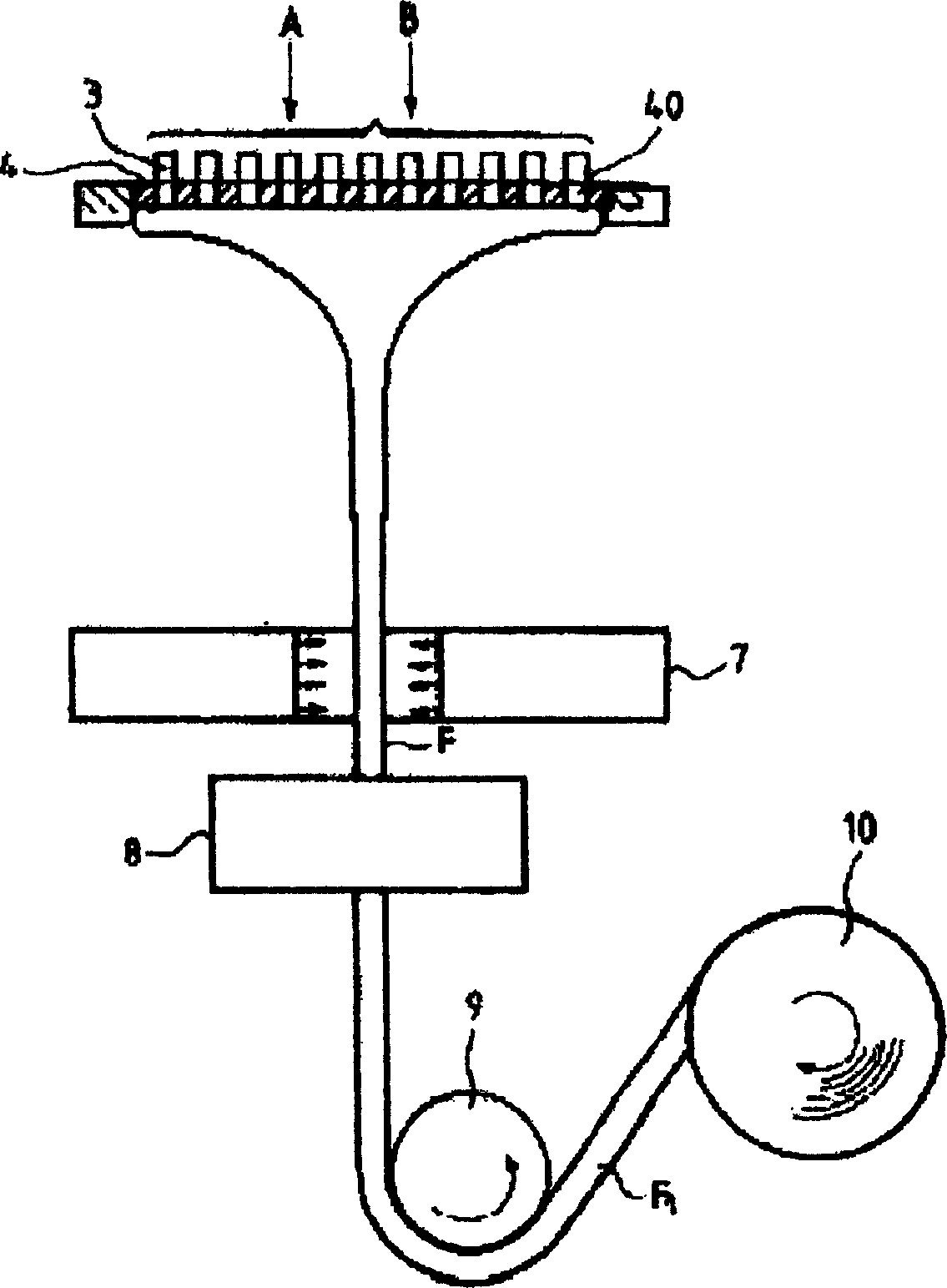
[0035] figure 1 A schematic cross-sectional view of an optical crystallized plastic optical fiber obtained by employing a manufacturing method of a preferred embodiment of the present invention is depicted.
[0036] For example, the optical crystallized plastic optical fiber F1 has a diameter of 100-1000μm and has a hexagonal structure.
[0037] The cladding 2 is formed with a periodic arrangement, for example hexagonal in this embodiment, of cavities 21 which are substantially circular and have a microscopic diameter. The term "microscopic diameter" refers to an average cavity diameter of less than 1 micron, on the order of 1 micron or on the order of 10 microns. For example, in this embodiment, the diameter is 1-30 microns.
[0038] These hollow cavities (without solid or liquid material), for example containing air, are distributed longitudinally in the cladding polymer matrix 22 obtained by UV curing. In this embodiment, the shortest distance between two cavities is sma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com