Time synchronization system and method with multiple synchronization domains, and cross-domain device
A technology for time synchronization and synchronizing equipment, which is applied in time division multiplexing systems, synchronization devices, transmission systems, etc., and can solve problems such as network maintenance difficulties, link asymmetric errors, and long BMC switching time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
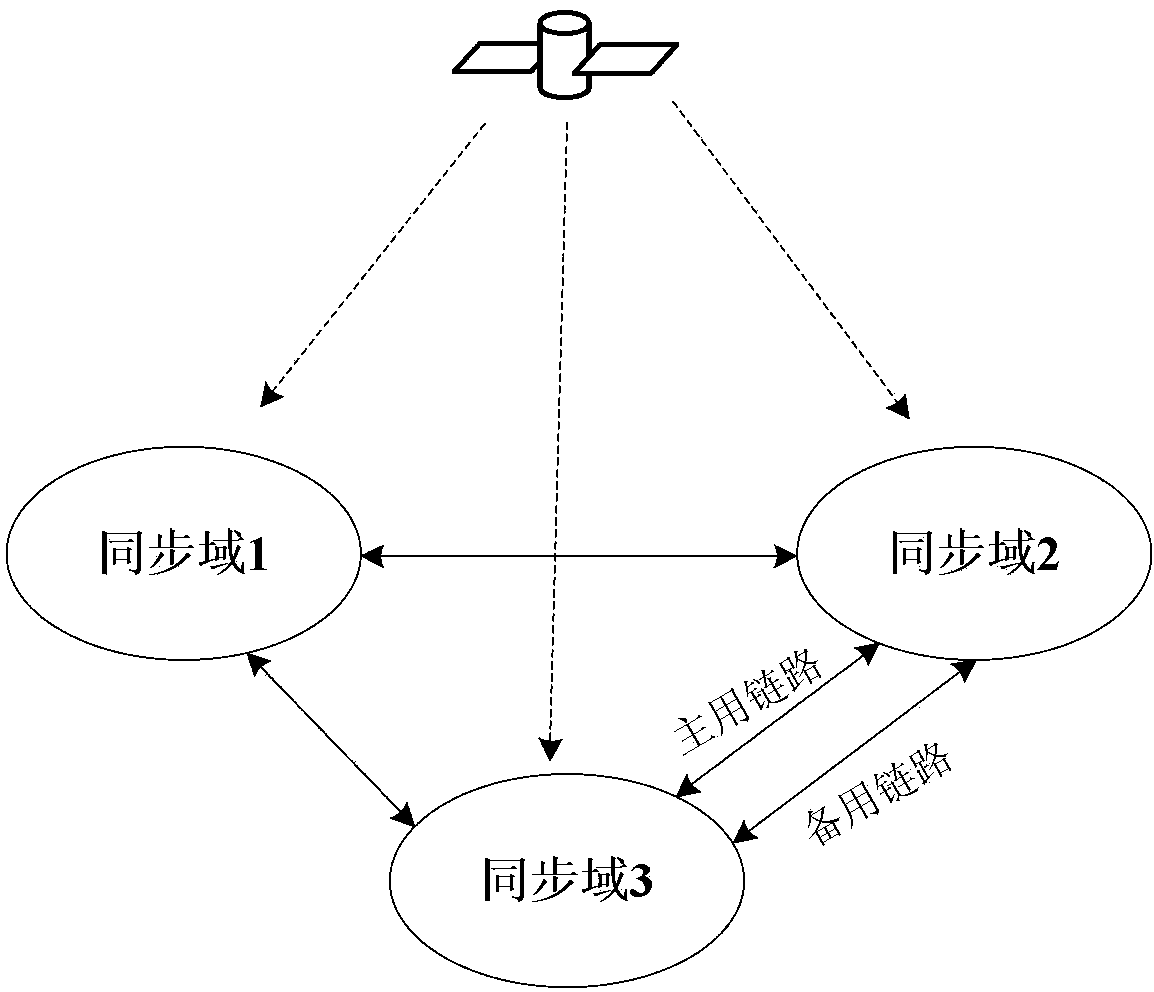
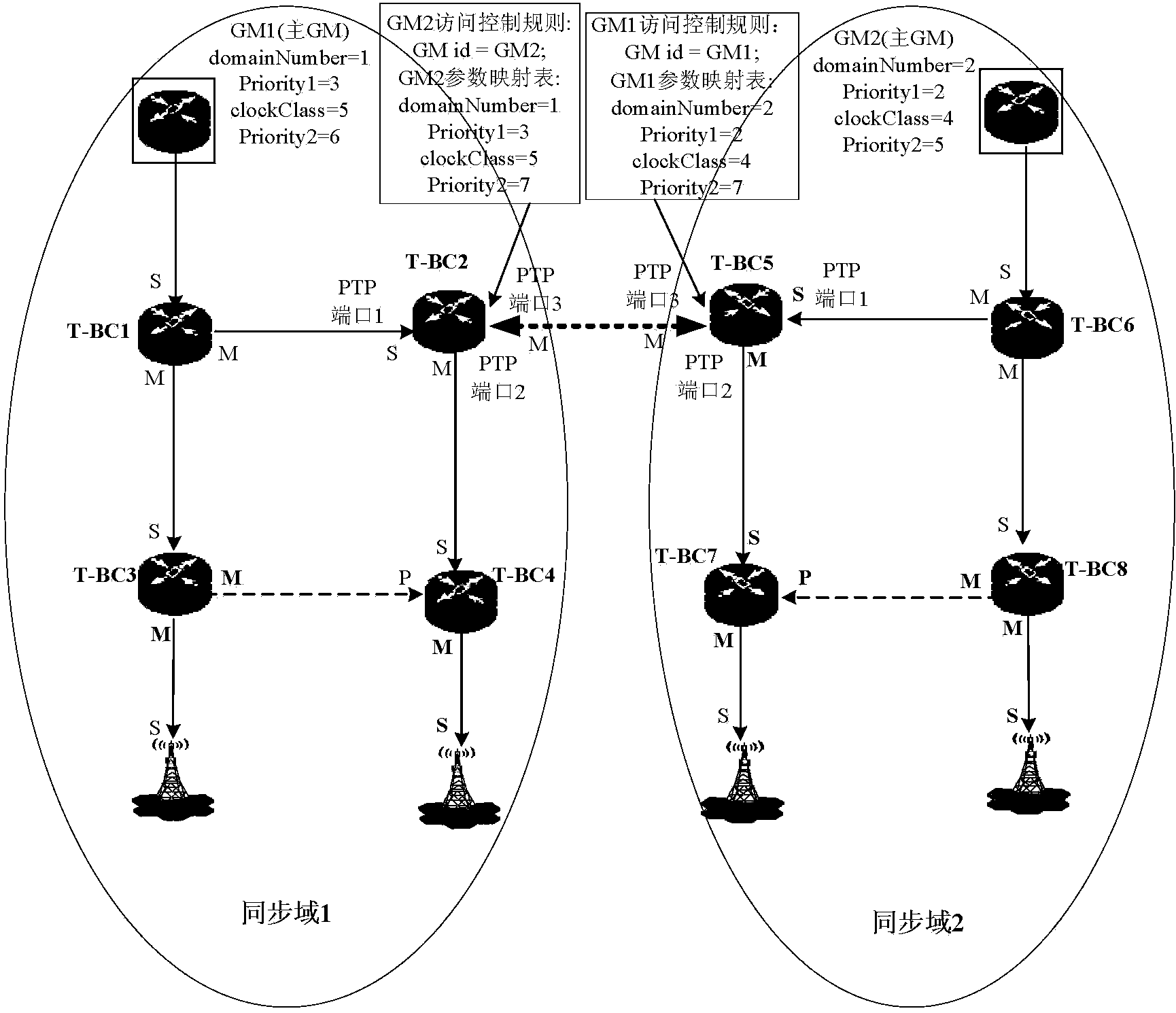
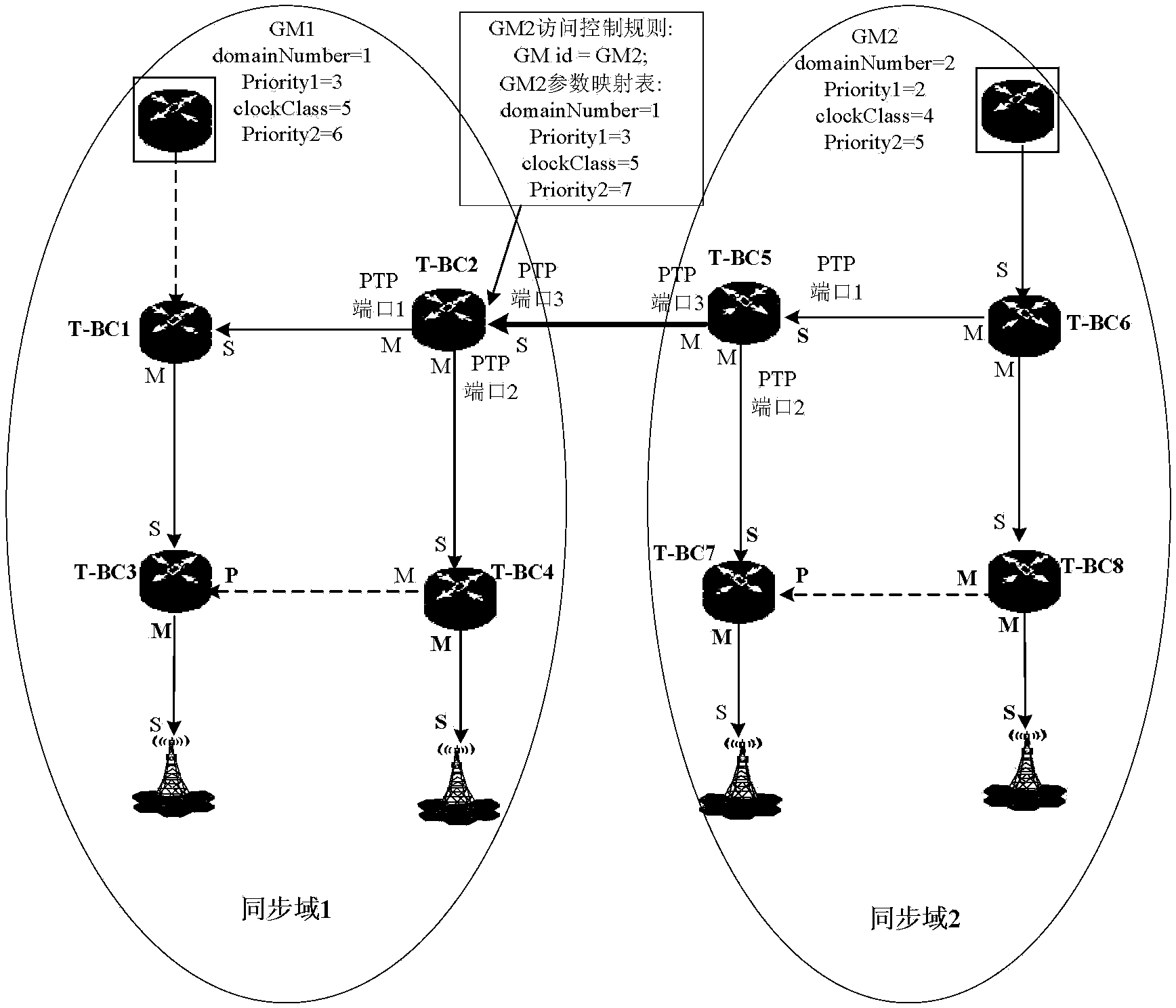
[0127] This embodiment mainly relates to inter-domain GM backup in a peer-to-peer architecture (Master-Master inter-domain relationship).
[0128] In this embodiment, the time synchronization network is divided into multiple synchronization domains, and GM is deployed in each synchronization domain. There is a peer-to-peer relationship between synchronization domains. Inter-domain PTP packets need to be preprocessed during inter-domain intercommunication, including domain Inter-domain access control checks and inter-domain parameter mapping.
[0129] Specifically, configure the access control list on the cross-domain device, and configure the GM parameter mapping table (equivalent to the local priority function based on the synchronization domain), namely: (1) inter-domain access control, (2) inter-domain parameter mapping- Domain local precedence, specifically:
[0130] 1. If the GM in the synchronization domain is normal, the synchronization device in the domain will prefer...
Embodiment 2
[0169] This embodiment mainly involves the realization of inter-domain link backup and loop avoidance.
[0170] In the present invention, other synchronization domains are abstracted as virtual GM, and the synchronization equipment in this domain is abstracted as virtual BC; that is, the virtual BC is connected to a GM in this domain and a plurality of virtual GMs; as Image 6 shown. Its specific implementation plans include:
[0171] 1. Multiple synchronous links between domains are configured with different priorities to realize inter-domain link protection;
[0172] Among them, the inter-domain link priority is for a certain domain. For example, there are link A and link B in domain 1 and domain 2. For domain 1, the priority of link A is higher than that of link B; but for domain 2 Say, link B priority can be higher than link A;
[0173] For example, you can distinguish the priority of links by configuring different priority 2; you can switch between multiple synchronous...
Embodiment 3
[0186] This embodiment mainly involves cross-domain transfer of time source information.
[0187] The cross-domain transmission of GM information can be adopted but not limited to the following two methods:
[0188] Mode 1, domain-by-field synchronization mode (logic BC)
[0189] The Announce message carries GM parameters, including domain number, source port ID, timestamp, P1, CC, P2, GMid, hop count, and time source type; when passing across domains, the domain number needs to be modified every time a synchronization domain passes through It is the domain number of the synchronization domain currently passed; other parameters remain unchanged; note that the number of hops needs to be increased.
[0190] It should be noted that the prior art believes that the PTP domain is similar to the nature of a VPN, and the domains are isolated from each other; in fact, for the synchronization network, the concept of the PTP domain as an "area synchronization area" is more suitable.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com