A method for remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated farmland soil by strengthening ryegrass and rhizosphere microorganisms with anionic-non-mixed surfactants
A technology of surfactants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, applied in the field of contaminated soil remediation, can solve the problems of low bioavailability and limited bioremediation efficiency, and achieve the effects of promoting the absorption and accumulation of PAHs, improving remediation efficiency, and simple technical processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
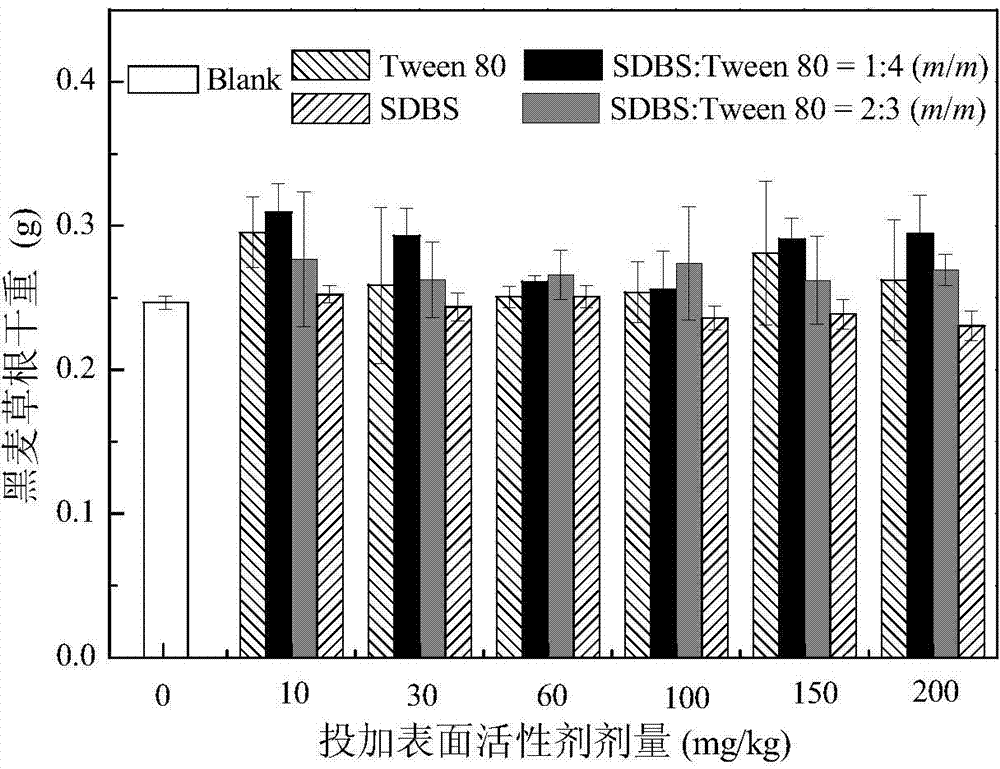
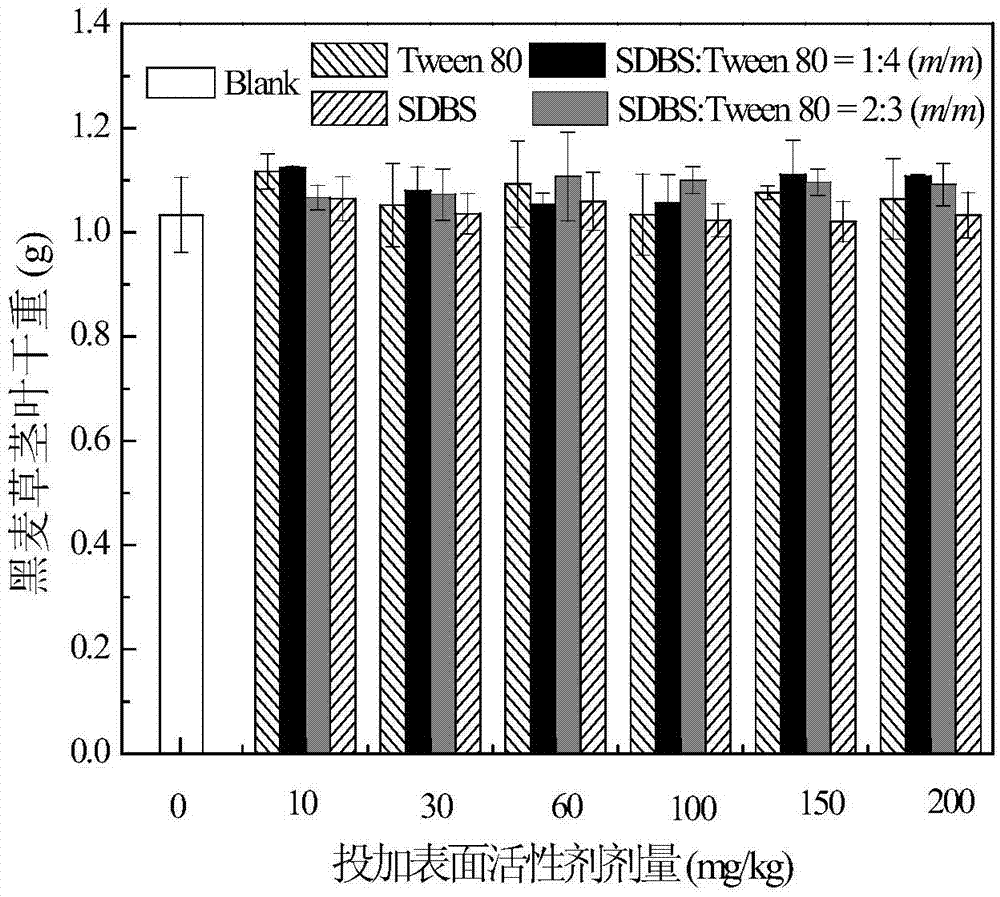
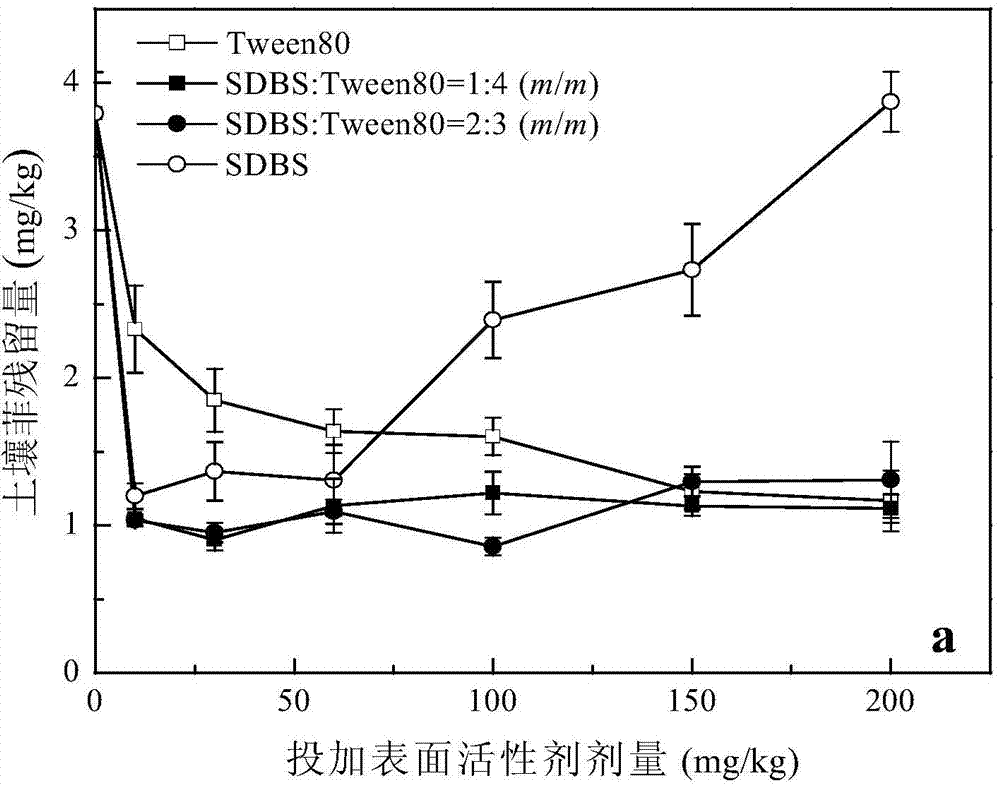
[0031] Weigh about 500 g (dry weight) of contaminated soil onto a clean plastic film (40 cm in length and width). Further, 60 mL of SDBS-Tween 80 anion-nonionic mixed surfactant with a mass concentration of 10 mg / kg (concentration × volume) was added to the soil, wherein, SDBS: Tween 80 = 0:5 (mass ratio). Mix the soil and surfactant thoroughly, then put it on a clean non-woven fabric, adjust the field water holding capacity with a soil moisture content of about 60%, and finally, fully pulverize the soil and put it into a series of pots (diameter 12 cm× 10 cm high).
[0032] After the ryegrass seeds are screened and induced to become white, 8 clusters are planted in each pot, with 5 plants in each cluster. Pots are placed randomly on long shelves in the greenhouse. During the potting period, the temperature in the greenhouse is 28-32°C during the day and 20-25°C at night. Pots were watered as needed to maintain field capacity at a soil moisture content of 60%. After 40...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Weigh about 500 g (dry weight) of contaminated soil onto a clean plastic film (40 cm in length and width). Further, 60 mL of SDBS-Tween 80 anion-nonionic mixed surfactant with a mass concentration of 10 mg / kg (concentration × volume) was added to the soil, wherein, SDBS: Tween 80 = 1:4 (mass ratio). Mix the soil and surfactant thoroughly, then put it on a clean non-woven fabric, adjust the field water holding capacity with a soil moisture content of about 60%, and finally, fully pulverize the soil and put it into a series of pots (diameter 12 cm× 10 cm high).
[0035] After the ryegrass seeds are screened and induced to become white, 8 clusters are planted in each pot, with 5 plants in each cluster. Pots are placed randomly on long shelves in the greenhouse. During the potting period, the temperature in the greenhouse is 28-32°C during the day and 20-25°C at night. Pots were watered as needed to maintain field capacity at a soil moisture content of 60%. Afte...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Weigh about 500 g (dry weight) of contaminated soil onto a clean plastic film (40 cm in length and width). Further, 60 mL of SDBS-Tween 80 anion-nonionic mixed surfactant with a mass concentration of 10 mg / kg (concentration × volume) was added to the soil, wherein, SDBS: Tween 80 = 2:3 (mass ratio). Mix the soil and surfactant thoroughly, then put it on a clean non-woven fabric, adjust the field water holding capacity with a soil moisture content of about 60%, and finally, fully pulverize the soil and put it into a series of pots (diameter 12 cm× 10 cm high).
[0038] After the ryegrass seeds are screened and induced to become white, 8 clusters are planted in each pot, with 5 plants in each cluster. Pots are placed randomly on long shelves in the greenhouse. During the potting period, the temperature in the greenhouse is 28-32°C during the day and 20-25°C at night. Pots were watered as needed to maintain field capacity at a soil moisture content of 60%. Afte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com