A method for identification of microbial populations by two nucleotide real-time sequencing-by-synthesis profiles
A two-nucleotide, synthetic sequencing technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of unfavorable trace template detection and identification, large demand for PCR product samples, increased sequencing steps and sequencing time, etc., to increase the length of sequencing and reduce the cost of sequencing , the effect of reducing the number of reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
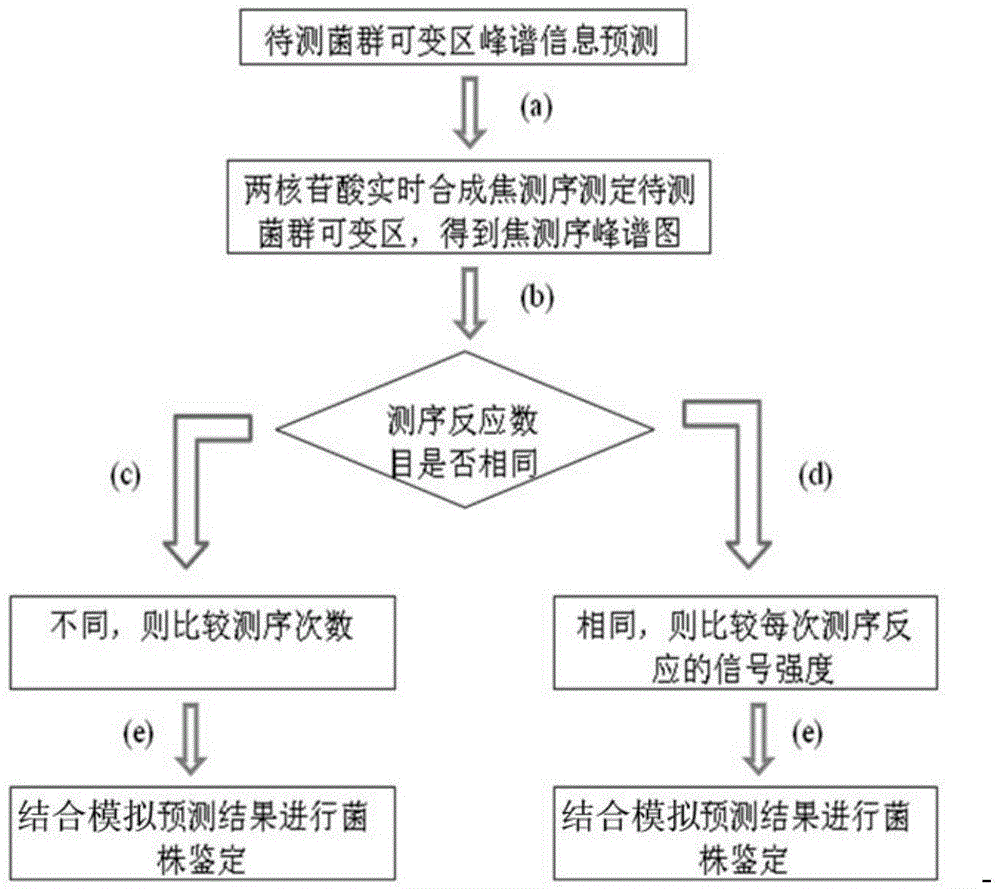
[0025] Example 1: Method for Identifying Microbial Populations Using Two Nucleotide Real-Time Synthesis Sequencing Profiles
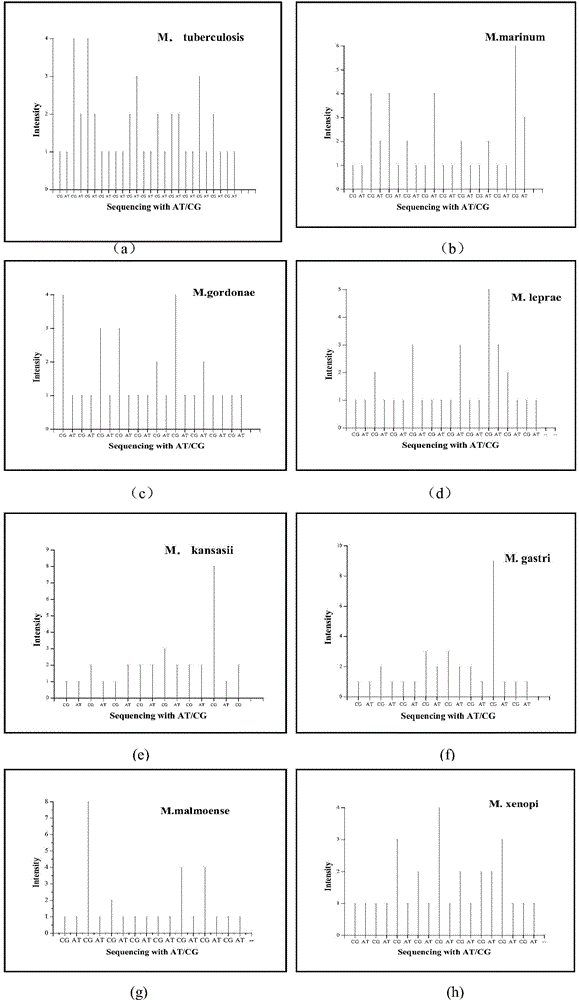
[0026] 1.13 Mycobacterium sp. rnpB gene peak spectrum prediction
[0027] With 13 kinds of mycobacteria (M.paratuberculosis, M.tuberculosis, M.gastri, M.kansasii, M.marinur, M.gordonae, M.malmoense, M.leprae, M.intracellular, M.xenopi, M.celatum, M. fortuitum, M. smegmatis) as an example, to describe the method of two nucleotide real-time sequencing peaks to identify microbial populations. In this example, the rnpB gene was selected as the sequencing target. The sequences of the variable regions of the partial rnpB genes of these 13 mycobacteria are shown in Table 1. First, according to the gene sequences of the strains, the peak spectrum information of the partial rnpB gene variable regions of these 13 mycobacteria genera was predicted in the case of two-nucleotide real-time synthetic sequencing.
[0028] Table 1 Partial variable region sequences of...
Embodiment 2
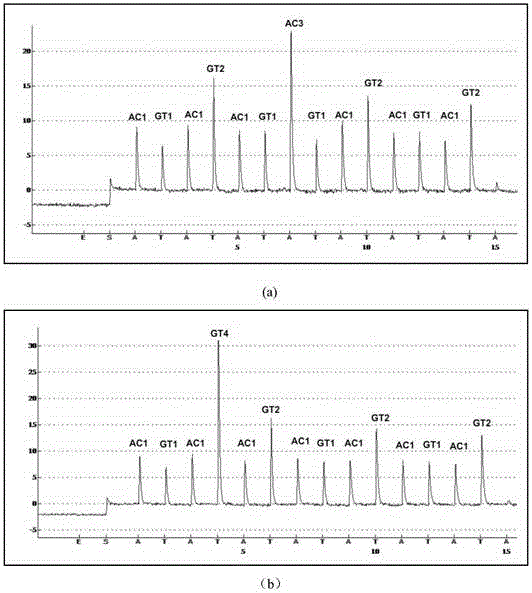
[0037] Example 2: Identification of Two Mycobacteria Based on Pyrosequencing Platform's Two-nucleotide Real-Time Synthesis Sequencing Map
[0038] In order to verify the feasibility of this method in the identification of actual samples, two strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis (M.paratuberculosis) and Mycobacterium celaturn (M.celaturn) were identified using two-nucleotide real-time sequencing-by-synthesis. In this example, a pyrosequencing platform based on real-time sequencing-by-synthesis is used.
[0039] (1) DNA sample preparation
[0040]First, the genomic DNA of M. paratuberculosis and M. celaturn strains was extracted and stored at -20°C until use. Part of the rnpB gene (RNasePRNAgene) variable region of the strain was amplified by PCR under the action of polymerase. Amplification primers are: F: 5'-CGGATGAGTTGGCTGGGCGG-3'; R: 5'-GGGTGAAACGGTGCGGTAAGAGC-3'. Among them, the 5' end of the reverse primer was labeled with biotin to obtain the PCR samples required ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com