Construction method of magnetic resonance imaging sensor for measuring lead ions
A magnetic resonance imaging and construction method technology, applied in the field of nano-biotechnology detection, can solve the problems of high analysis cost, complicated sample pretreatment process, expensive instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
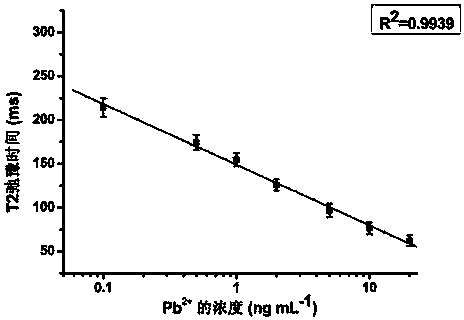
[0024] A method for constructing a magnetic resonance imaging sensor for determining lead ions, comprising: magnetic nanoparticles are respectively coupled to a pair of DNA probes, the DNA-coupled magnetic nanoparticles are assembled under the action of DNase, and the magnetic nanoparticles are assembled The body is detected by magnetic resonance signals; the specific steps are:
[0025] (1) Magnetic nanoparticles are coupled to a pair of DNA probes respectively
[0026] The well-dispersed magnetic nanoparticles used are carboxyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles with a particle size of 10.3 ± 1.6 nm. amine (NHS) for activation, namely: 0.15mg magnetic nanoparticles were dissolved in 100μL 0.01M PBS (containing 50mM NaCl), and then 0.0746mg EDC and 0.12mg NHS were added to the above solution; after 15min of activation, two Add one of a pair of DNA probes S1 and S2 to the above-mentioned magnetic nanoparticles, so that the final concentration of the DNA probes is 1 μM, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com