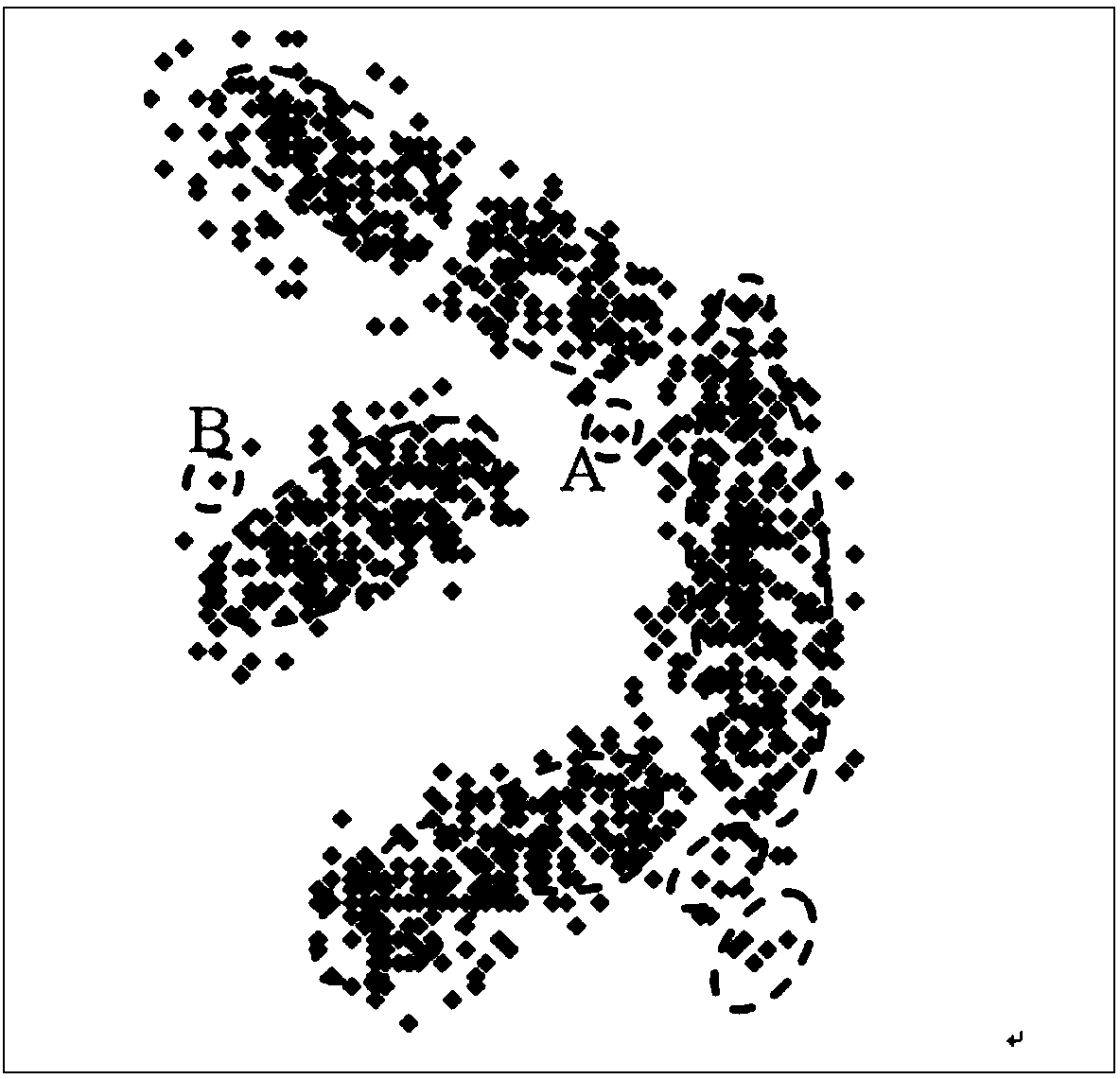
K-means clustering method based on quotient space theory
A k-means clustering and quotient space technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of high time complexity, achieve good clustering results and good overall effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0043] Relevant theorem among the present invention, definition are as follows:
[0044] Definition (Granularity) Granularity refers to the degree of refinement and comprehensiveness of data in a dataset. The principle of granularity division is: the higher the degree of refinement, the smaller the granularity; the lower the degree of refinement, the larger the granularity.
[0045] Define X as the domain of discourse of the problem to be studied, f as the attribute function on the domain of discourse, and T as the structure of the domain of discourse, and describe the problem by constructing a triple (X, f, T).
[0046] Theorem 1 (False Guaranteed Principle) If the problem A→B has a solution on (X,f,T), then on the quotient space ([X],[f],[T]), the problem [A]→[B ] There must also be a solution.
[0047] Theorem 2 (fidelity principle I) I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com