Light path planning method
A path planning and optical path technology, applied in multiplexing system selection devices, digital transmission systems, data exchange networks, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, easy to miss the optimal path, etc., to avoid missing the better path Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
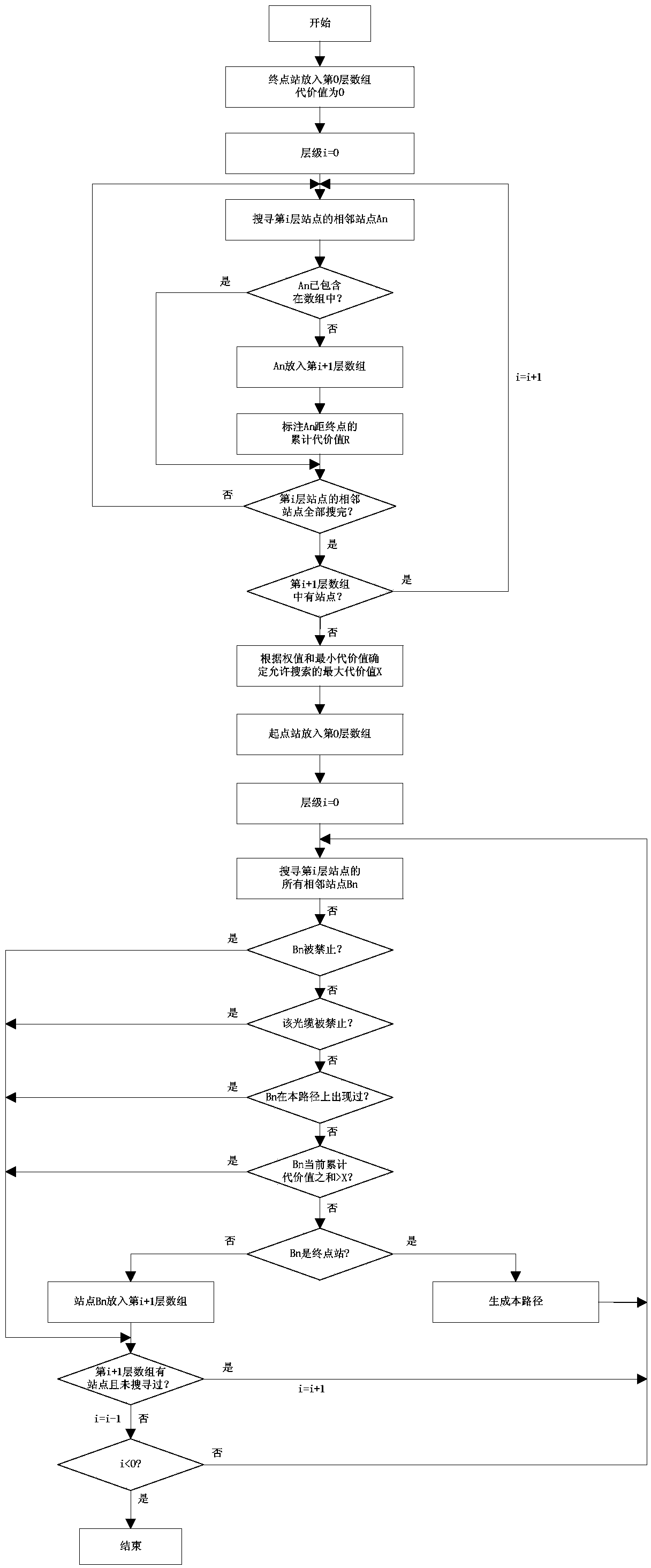
[0024] Embodiment one: as attached figure 1 An optical path planning method is shown, which is used to plan and select an appropriate path between certain two nodes in an optical fiber communication network composed of several optical cables and nodes on them.
[0025] The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0026] 1. Determine the starting and ending points:
[0027] Determine the starting point and the ending point of the path to be planned in the optical fiber communication network.
[0028] 2. Flood layer by layer and identify the cost value:
[0029] First define the end point as layer 0 node A 0 , its cost value is 0, and then the node A at layer 0 0 Flood outward, looking for node A with layer 0 0 directly adjacent nodes and defined as layer 1 node A 1 . At each layer 1 node A 1 mark the cost value of the optical path formed by the optical cable between it and the terminal. The cost value is based on the node A 1 The parameters of the optical c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com