Malicious website prompt method and router
A malicious URL and router technology, applied in the network field, can solve the problems of low user network security, weak security awareness of netizens, and the inability of user terminals to install malicious URL blocking software, so as to achieve the effect of improving security.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
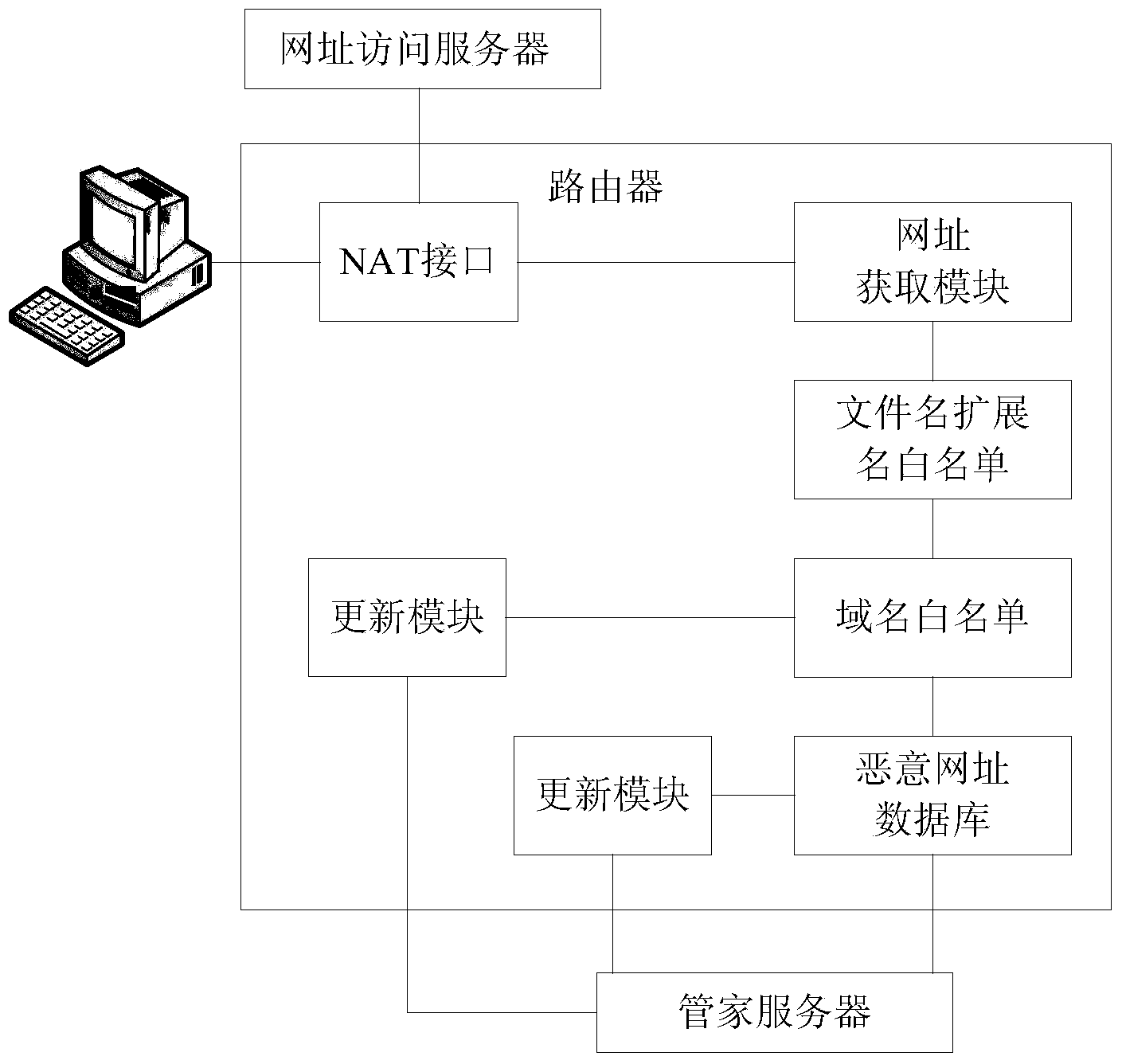
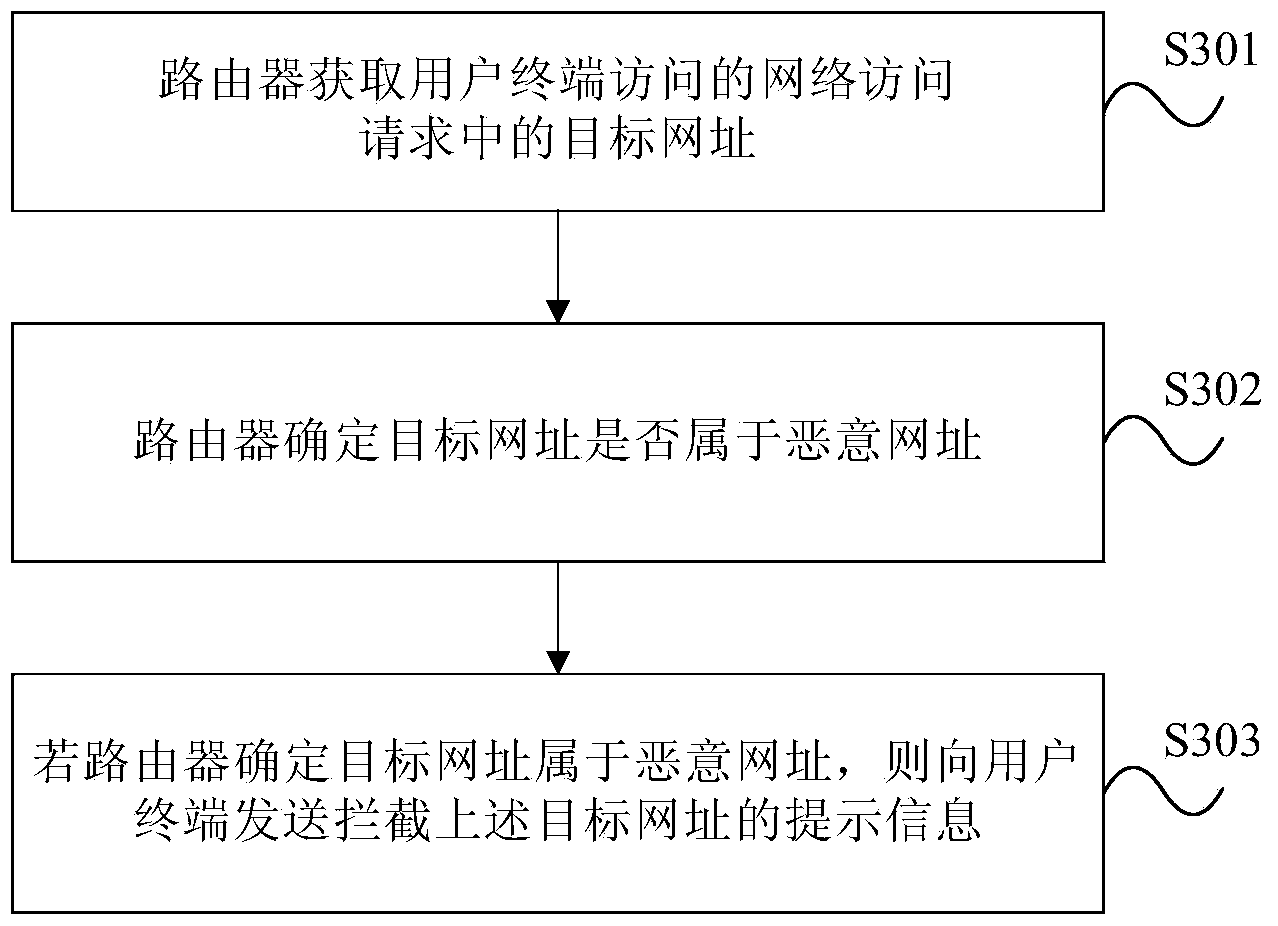
[0021] The present invention detects malicious URLs on routers, prompts user terminals according to the detection results, and eliminates the need for user terminals to install malicious URL interception software. Surf safety.
[0022] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below with specific embodiments.
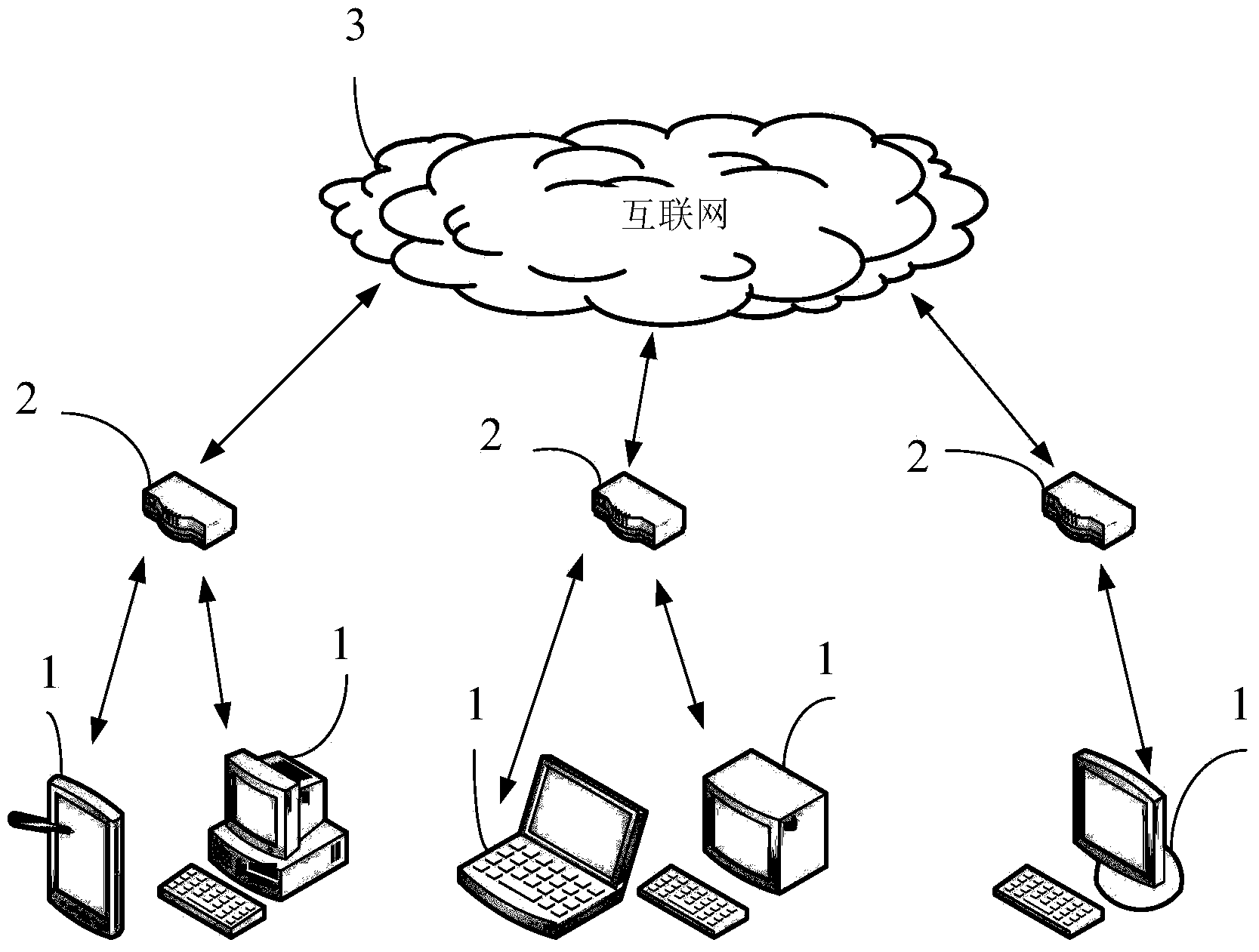
[0023] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of an application scenario prompted by a malicious URL in the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the application scenarios of the embodiments of the present invention include at least one user terminal 1, such as a personal computer (Personal Computer, hereinafter referred to as: PC), a mobile phone, a tablet computer (Tablet Computer), etc., and at least one router 2 and the Internet 3, wherein each user terminal 1 is connected to the Internet 3 through a router 2. The information sent by the user terminal 1 to the Internet 3 or the information received from the Internet 3 must pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com