Encoding an image
An image and encoding technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as low-quality encoded images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
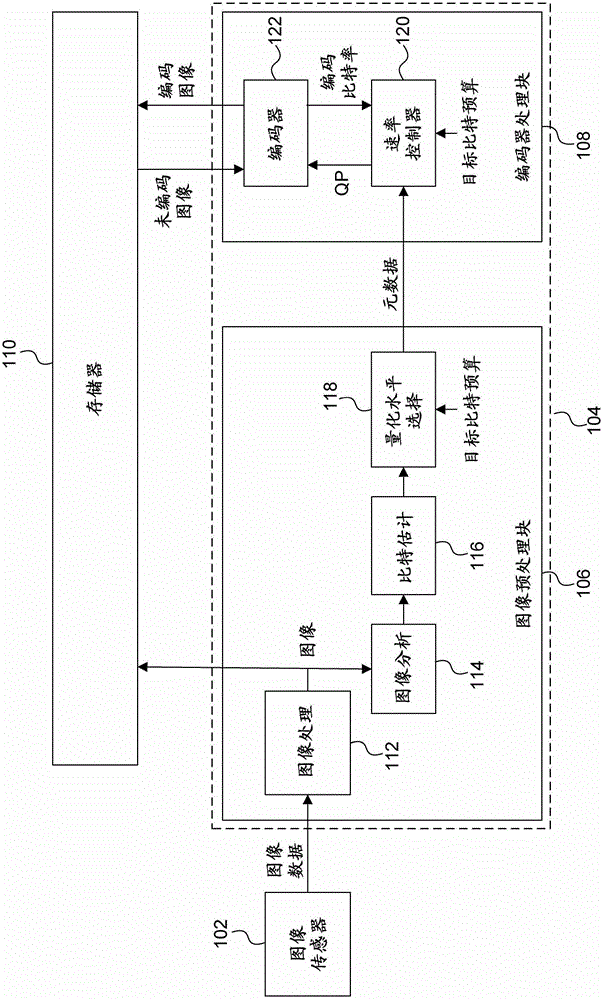
[0024] Embodiments will now be described by way of example only. First, an example is described involving pictures to be coded according to Intra coding, in which pictures are coded without reference to other pictures (eg other frames of a video sequence). As described subsequently, similar principles apply to pictures that are coded according to interactive (or "non-intrinsic") coding, where coding a picture requires reference to other pictures (eg other frames of a video sequence).
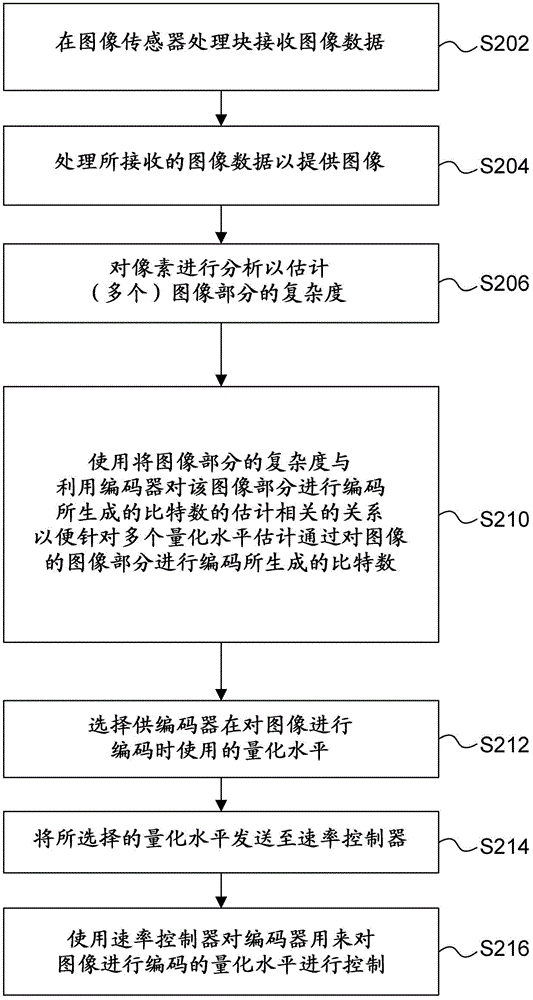
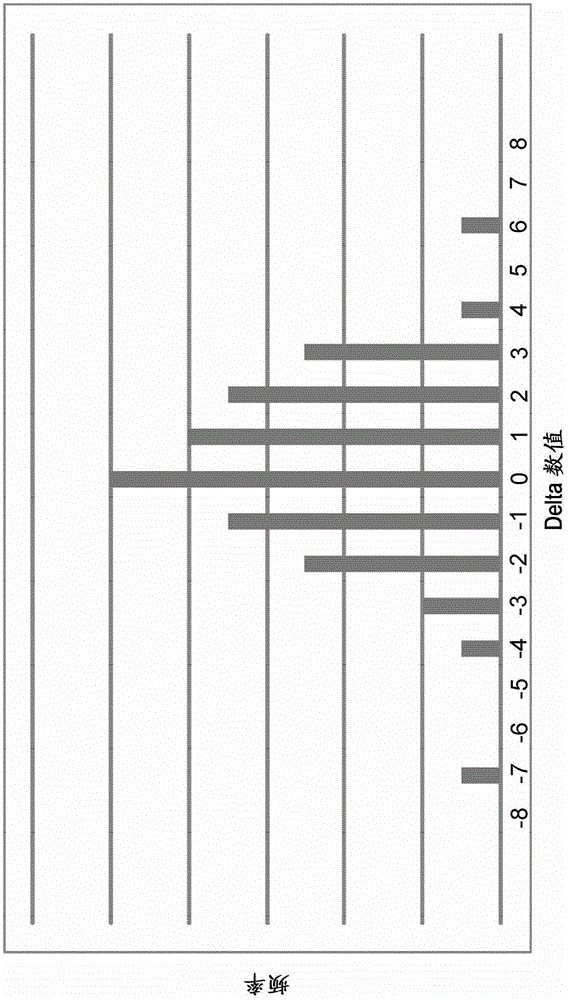
[0025] In the examples described herein, an image is analyzed to determine an indication of the complexity of the image (eg, the entropy of the image). The image analysis described here is a simple process performed before encoding the image. The complexity indication of the picture is used to estimate the number of bits that an encoder would generate by encoding the picture at each of a number of different quantization levels. One of the quantization levels is selected based on the estimate a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com