Fixed type constant velocity joint
A constant velocity joint and torque transmission technology, applied in the field of constant velocity joints, can solve problems such as the difficulty of assembling fixed constant velocity joints, and achieve sufficient rigidity and ensure rigidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] Hereinafter, preferred embodiments will be cited, and the fixed type constant velocity joint according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In addition, for easy understanding, the torque transmission ball and drive shaft are attached with Figure 7 ~ Figure 11 The attached reference numerals are the same reference numerals.
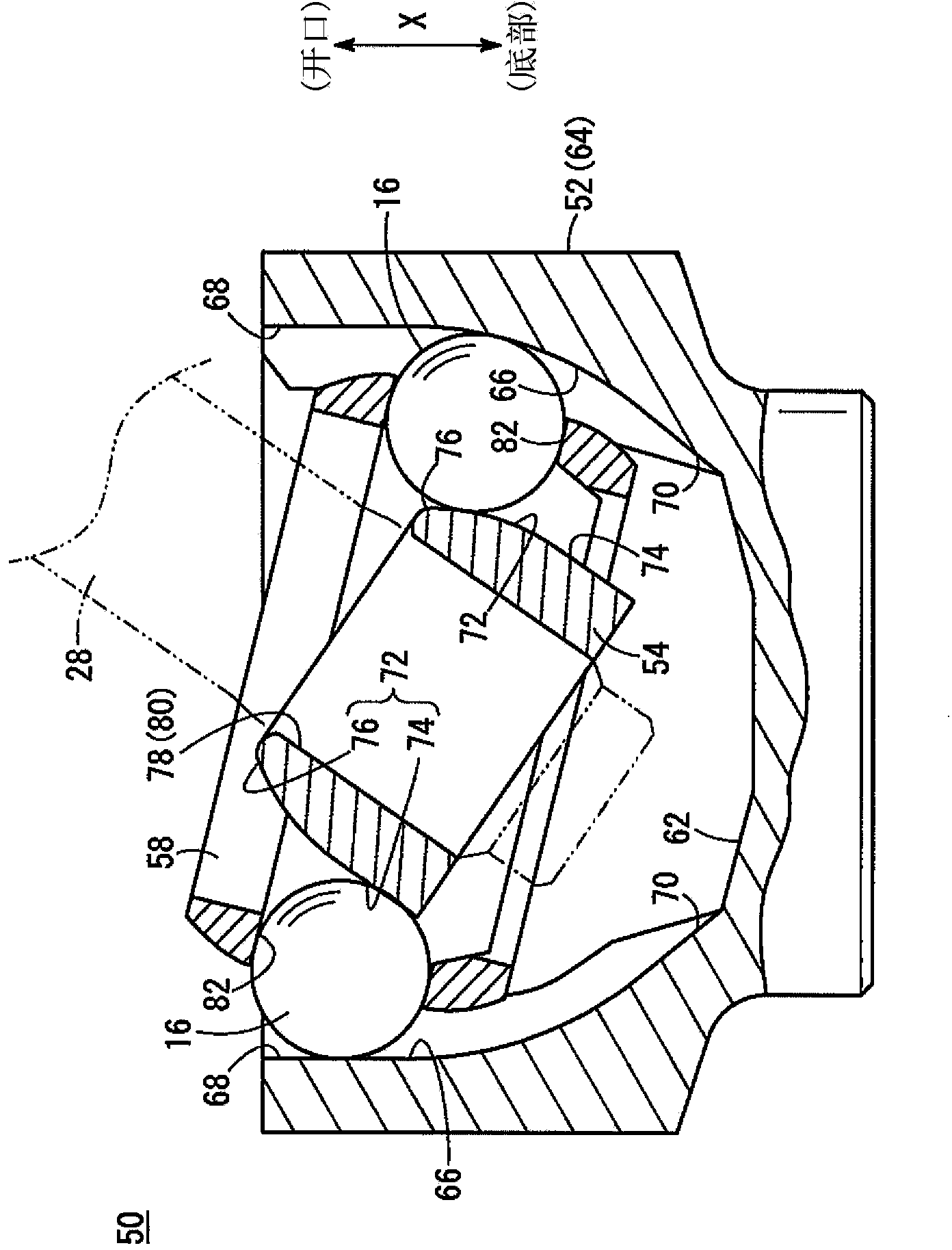
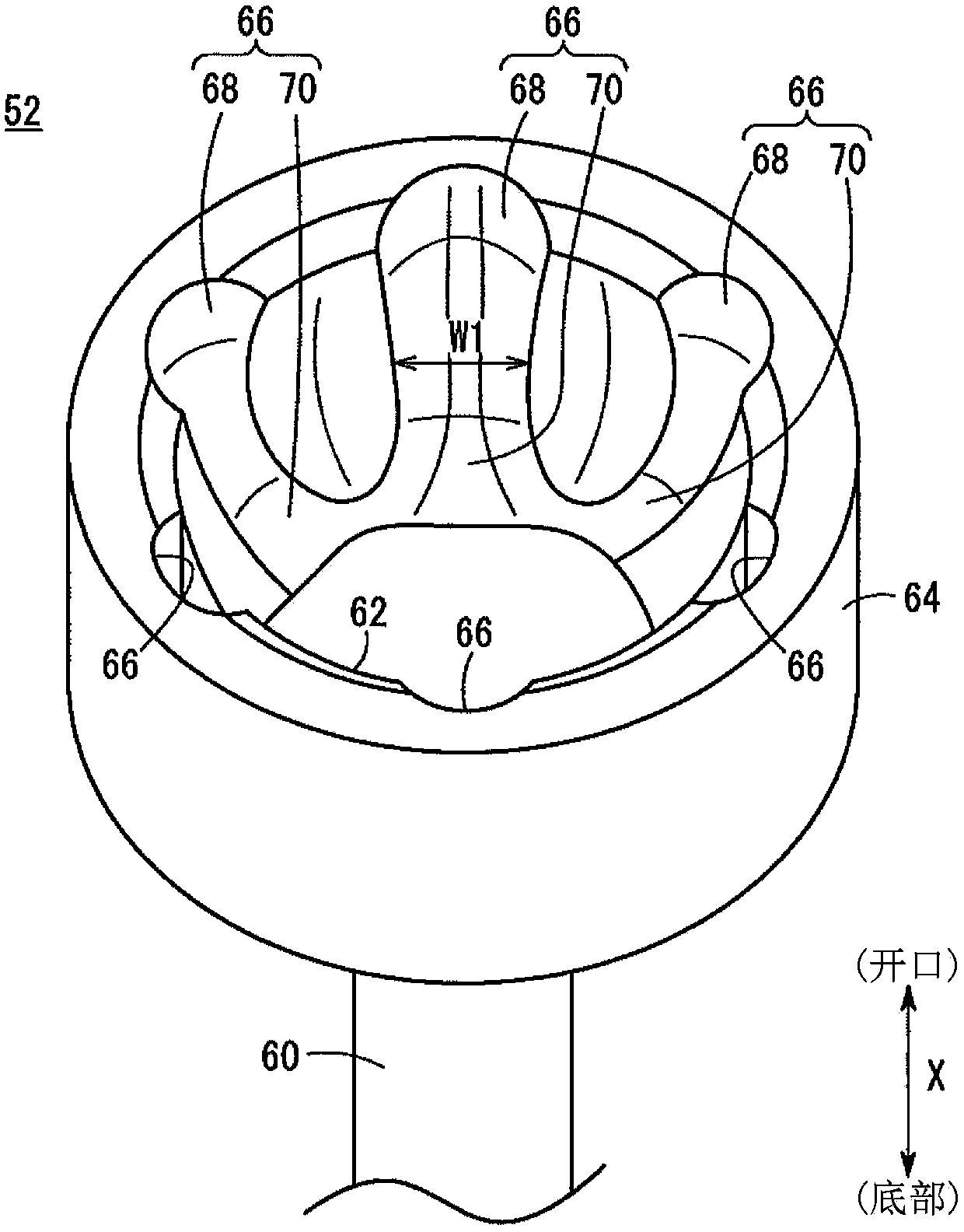
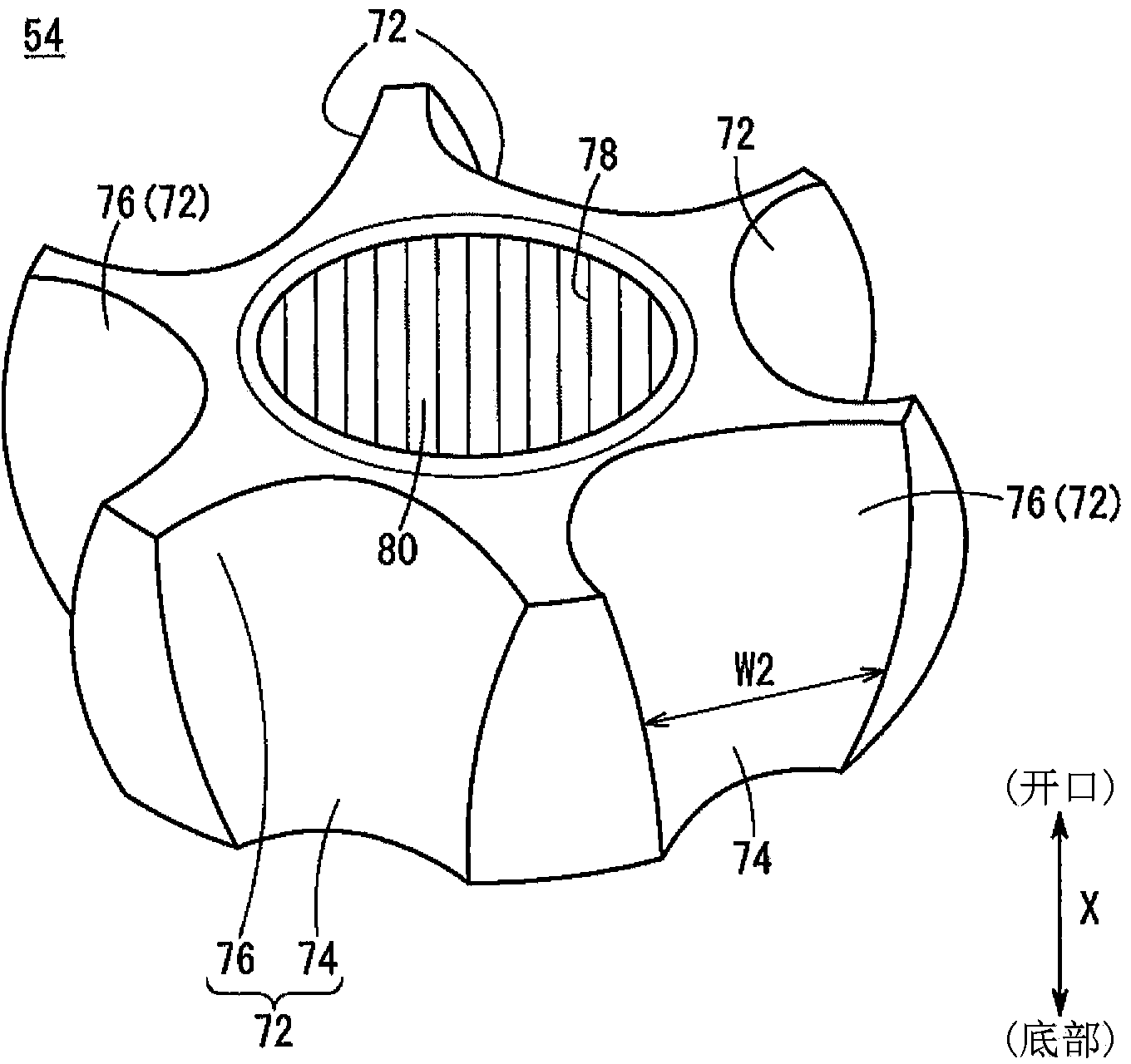
[0044] figure 1 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of main parts in a state where an operating angle is generated in the fixed constant velocity joint 50 according to the embodiment of the present invention. The fixed constant velocity joint 50 has an outer member 52 , an inner member 54 , a torque transmission ball 16 interposed between the outer member 52 and the inner member 54 , and a retainer 58 holding the torque transmission ball 16 .
[0045] figure 2 It is a schematic perspective view of main parts of the outer member 52 . in addition, figure 1 and figure 2 Arrow X in , indicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com