Positioning method for single-phase earth fault sections of isolated neutral system
A single-phase-to-ground fault, neutral point ungrounded technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problems of inaccurate fault location, long fault line, large influence of "S" injection method transition resistance, etc., and the accuracy requirements are not high. , the effect of improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
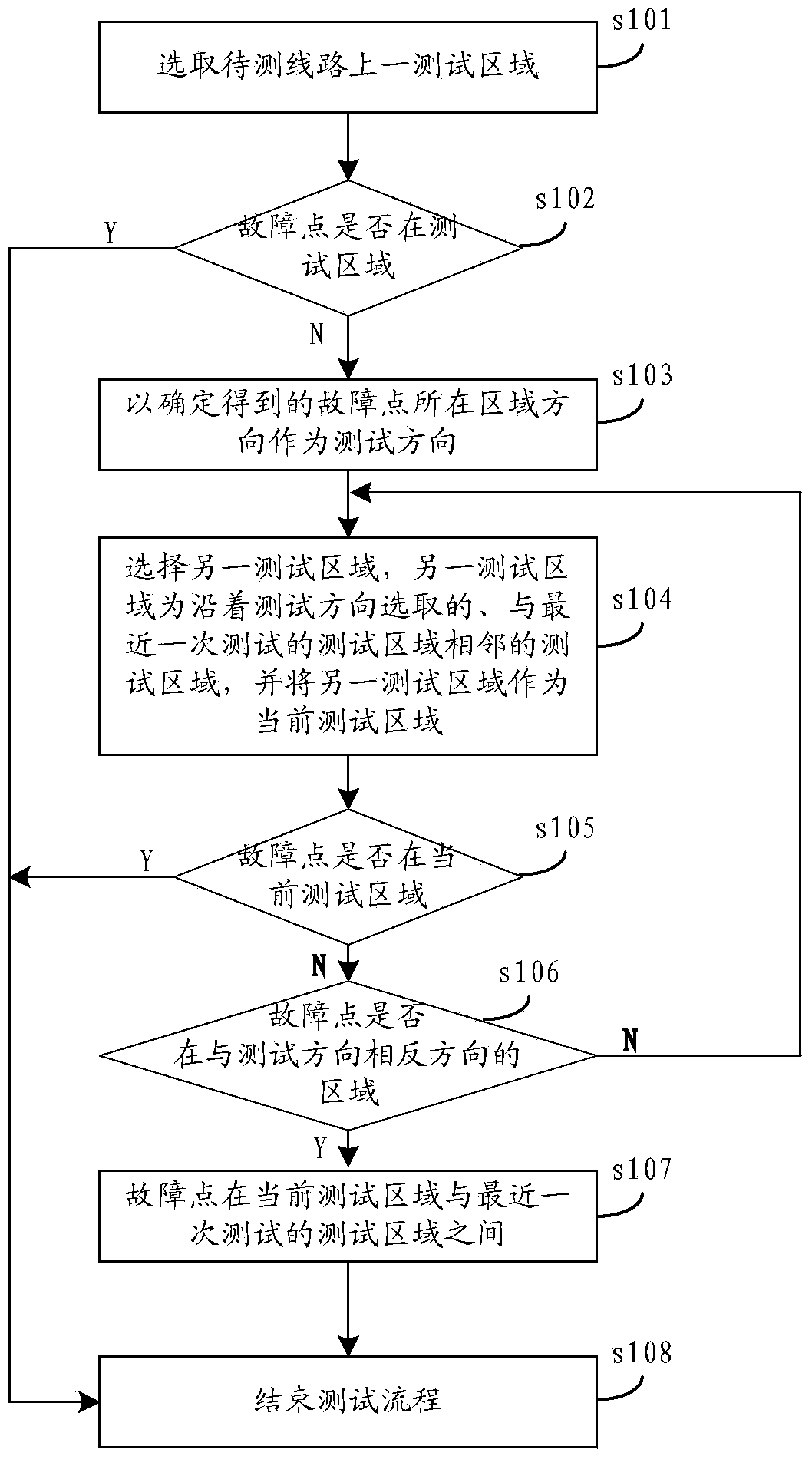
[0052] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 A flow chart of the process of a method for locating a single-phase ground fault section in a neutral point ungrounded system provided by the present invention, the method includes:
[0053] Step s101: selecting a test area on the line to be tested;
[0054] It can be understood that at first a line is selected as the line to be tested, and a test area is selected on the line to be tested, where the line to be tested and the selection of the test area on the line can be an important area on the important line, or can be It is randomly selected from multiple lines, and is not specifically limited here.
[0055] In addition, the test area mentioned here refers to the area between the two ends when the double-terminal detection device collects the synchronous steady-state zero-sequence current at both ends. It is worth noting that the double-terminal detection device here refers to a device capable of synchronously collecting the stea...
Embodiment 2
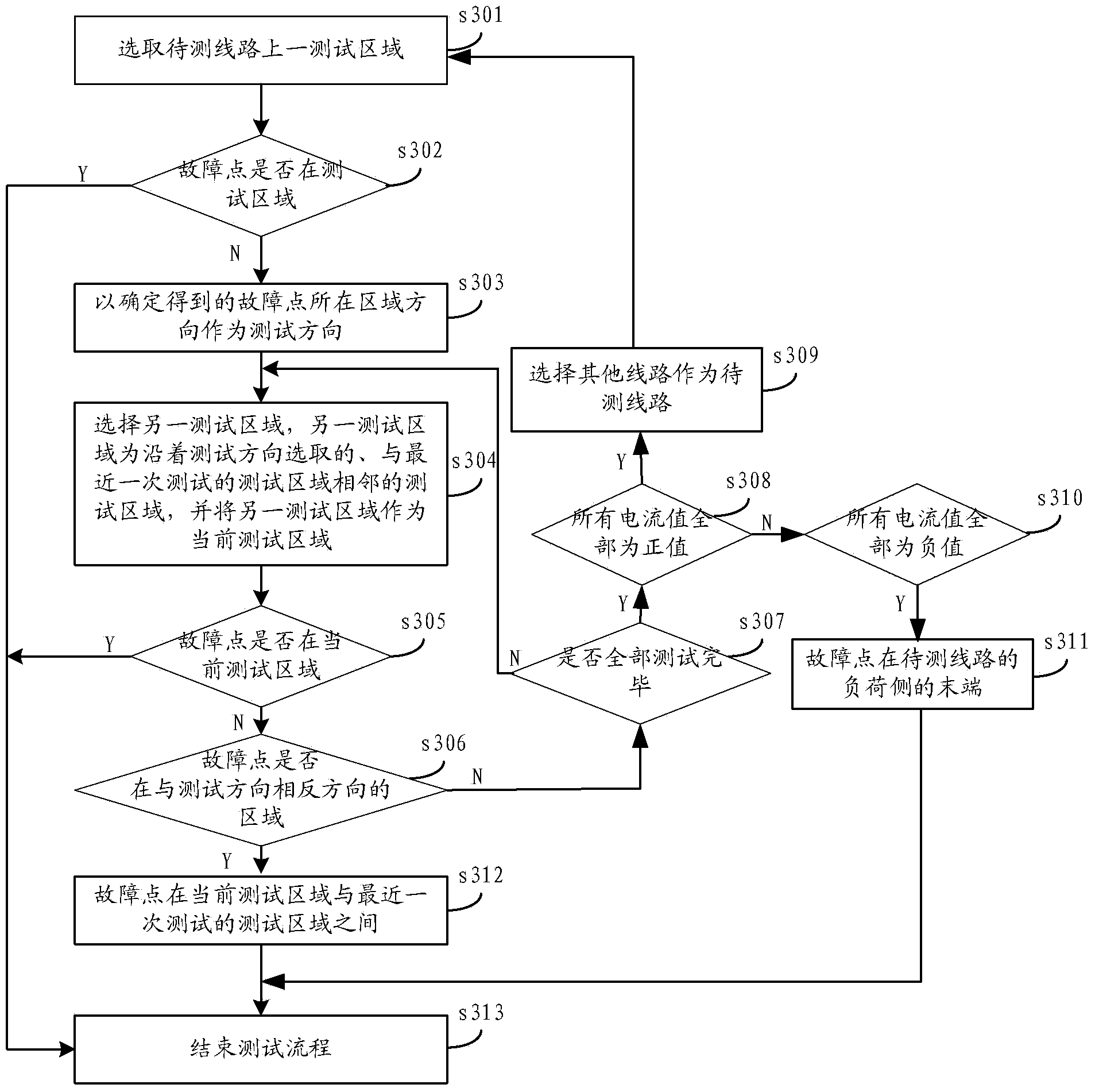
[0083] Please refer to image 3 , image 3 It is a flow chart of the process of another method for locating the single-phase ground fault section of the neutral point ungrounded system provided by the present invention. On the basis of the method provided in Embodiment 1, the method also includes:
[0084] Step s307: Judging whether all tests are completed, if yes, proceed to step s308; otherwise, proceed to step s304;
[0085] Step s308: Judging whether the instantaneous values of the steady-state zero-sequence current collected on the line to be tested are all positive values, if yes, proceed to step s309; if not, proceed to step s310;
[0086] It can be understood that firstly judge whether all tests are completed, if not, then return to step s304 to continue fault diagnosis; if yes, then judge whether the instantaneous values of the steady-state zero-sequence current collected on the line to be tested are all positive values, If both are positive, it means that the f...
Embodiment 3
[0099] The invention also provides another method for locating the single-phase ground fault section of the neutral point ungrounded system.
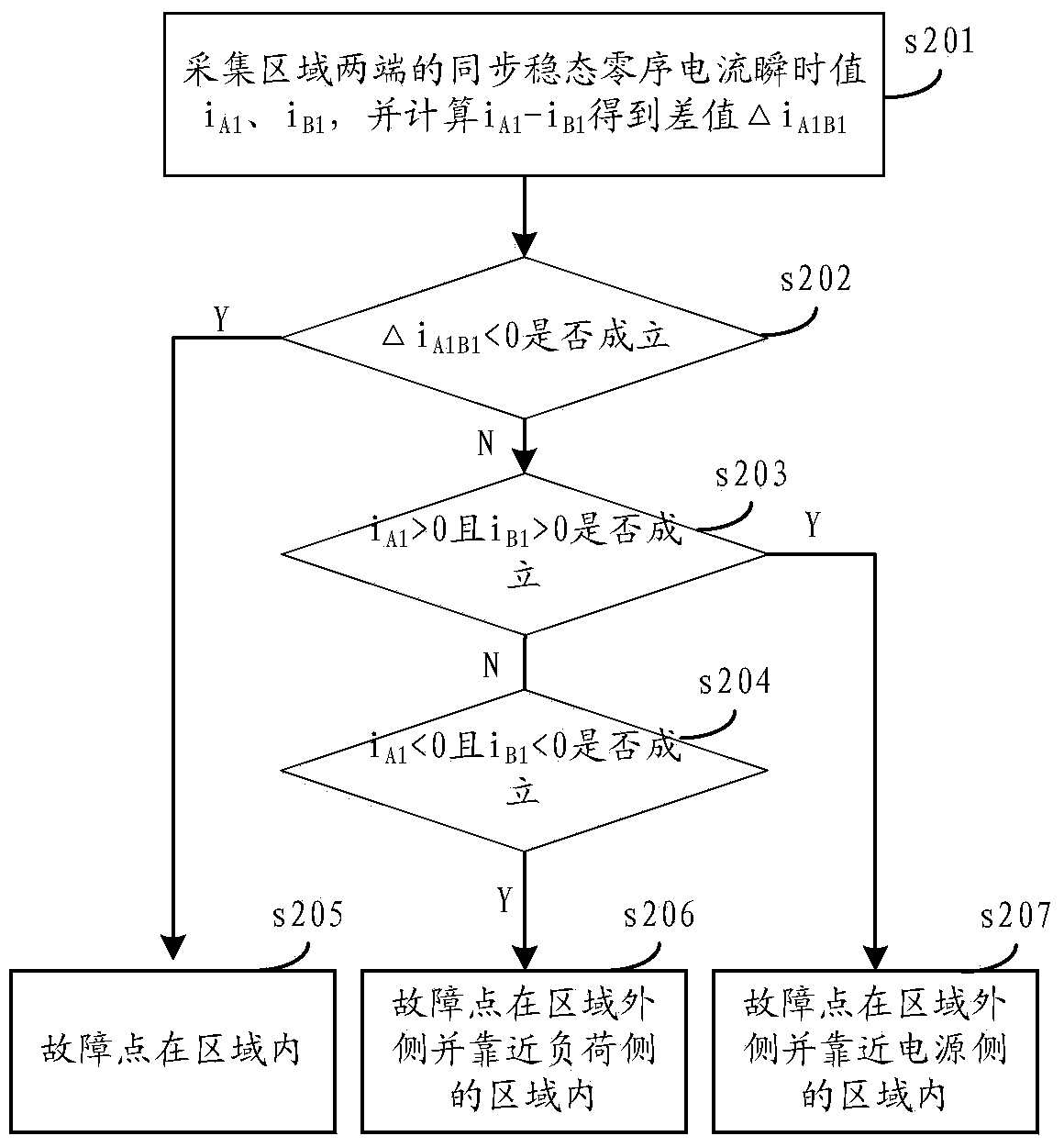
[0100] Because the principle of this method is the same as the method provided by the first embodiment above, the difference from the above method is emphasized here. The only difference is the specific process of judging the area where the fault point is located by combining the current conditions at both ends of the area. different, please refer to Figure 7 , Figure 7 The flow chart of another process for judging the area where the fault point is located in combination with the current situation at both ends of the area provided by the present invention, the process is:
[0101] Step s401: collecting the instantaneous value i of the synchronous steady-state zero-sequence current at both ends of the region A2 i B2 , and calculate i B2 -i A2 Get the difference △i B2A2 ;
[0102] Step s402: Judging △i B2A2 polarity, if △i B2A2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com