Displacement Detection Method and Imaging Method Based on Acoustic Radiation Force Echo
An acoustic radiation force and displacement detection technology, which is applied in ultrasonic/acoustic/infrasonic image/data processing, echo tomography, acoustic wave diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as system noise and organism's own motion interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
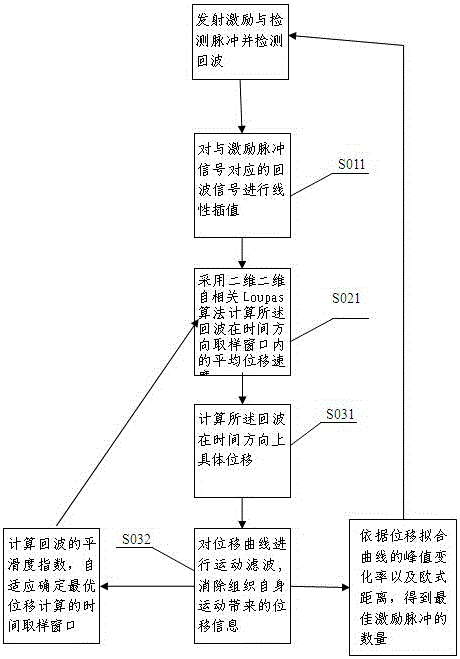
[0062] Example 1: Such as figure 1 As shown, the purpose of this embodiment is to overcome the problem that the echo is easily interfered by system noise and the body's own motion (such as heartbeat, breathing), and provide an echo displacement detection method based on acoustic radiation force:
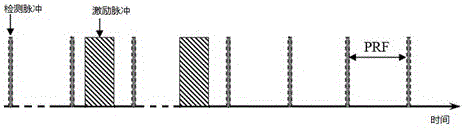
[0063] The step S011 includes linear interpolation of the echo signal corresponding to the excitation pulse signal. In the ultrasonic radiation force detection process, the single pulse sequence includes the reference detection pulse, the excitation pulse (long pulse), and the detection pulse (short pulse), The echo signal has the echo signal corresponding to the above-mentioned pulse one-to-one, but the echo signal corresponding to the excitation pulse (long pulse) has no calculation value due to the interference of the transmitted long wave, so it needs to be removed and linear interpolation is used If the number of pulse repetitions (sampling volume) in the time direction is 24, the ...
Embodiment 2
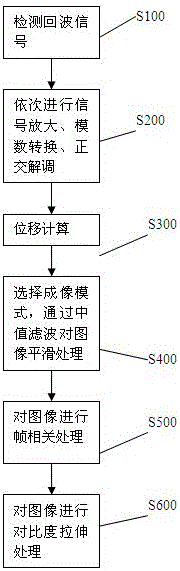
[0072] Example 2: Such as figure 2 As shown, in order to overcome the existing medical ultrasound acoustic radiation force imaging generally only provides displacement imaging at a fixed time, and fails to make full use of the diagnostic information generated by acoustic radiation force imaging and the flicker effect introduced by system electronic noise and speckle noise in ultrasound images. This will greatly reduce the image resolution and make clinical diagnosis extremely difficult. This embodiment provides an imaging processing method for detecting tissue displacement based on acoustic radiation force:
[0073] Including step S100 of detecting echo signals of acoustic radiation force;
[0074] Including step S200 of sequentially performing signal amplification, analog-to-digital conversion, and quadrature demodulation on the echo signal;
[0075] Including the step S300 of detecting the displacement of the echo signal by using the displacement detection method as described in E...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3: Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides an echo displacement detection system based on acoustic radiation force, including a control module 1, a linear interpolation module 2, an echo displacement rate calculation module 3, and an echo displacement calculation module 4; the linear interpolation module 1. The echo displacement rate calculation module 2, and the echo displacement calculation module 3 are respectively connected to the control module 1; the linear interpolation module 2 is used to linearly interpolate the echo signal corresponding to the excitation pulse signal, which is used in the ultrasonic radiation In the force detection process, the single pulse sequence includes reference detection pulse, excitation pulse (long pulse), detection pulse (short pulse), and the echo signal has an echo signal corresponding to the above-mentioned pulse one-to-one, but it is the same as the excitation pulse ( The echo signal corresponding to the long p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com