Prospective greedy method for solving 1-neighborhood backpack problem
A knapsack problem, knapsack technique, applied in the field of forward-looking greed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
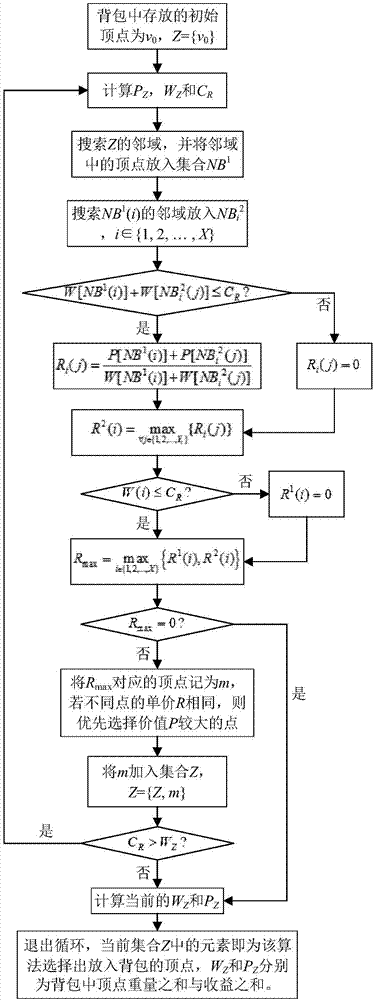
[0058] A forward-looking greedy method for solving the 1-neighborhood knapsack problem of the present invention will be described in detail below in combination with embodiments and drawings.
[0059] A forward-looking greedy method for solving the 1-neighborhood knapsack problem of the present invention, the research object belongs to the undirected graph, the values of P and W are arbitrary, and the 1-neighborhood constrained knapsack problem. Therefore, the present invention proposes a forward-looking greedy algorithm for the 1-neighborhood knapsack problem. This algorithm adds a forward-looking link on the basis of the ordinary greedy algorithm, making it easier for the algorithm to jump out of the local minimum that the traditional greedy algorithm may fall into. In the optimal solution, it becomes an effective algorithm for solving the 1-neighborhood knapsack problem.
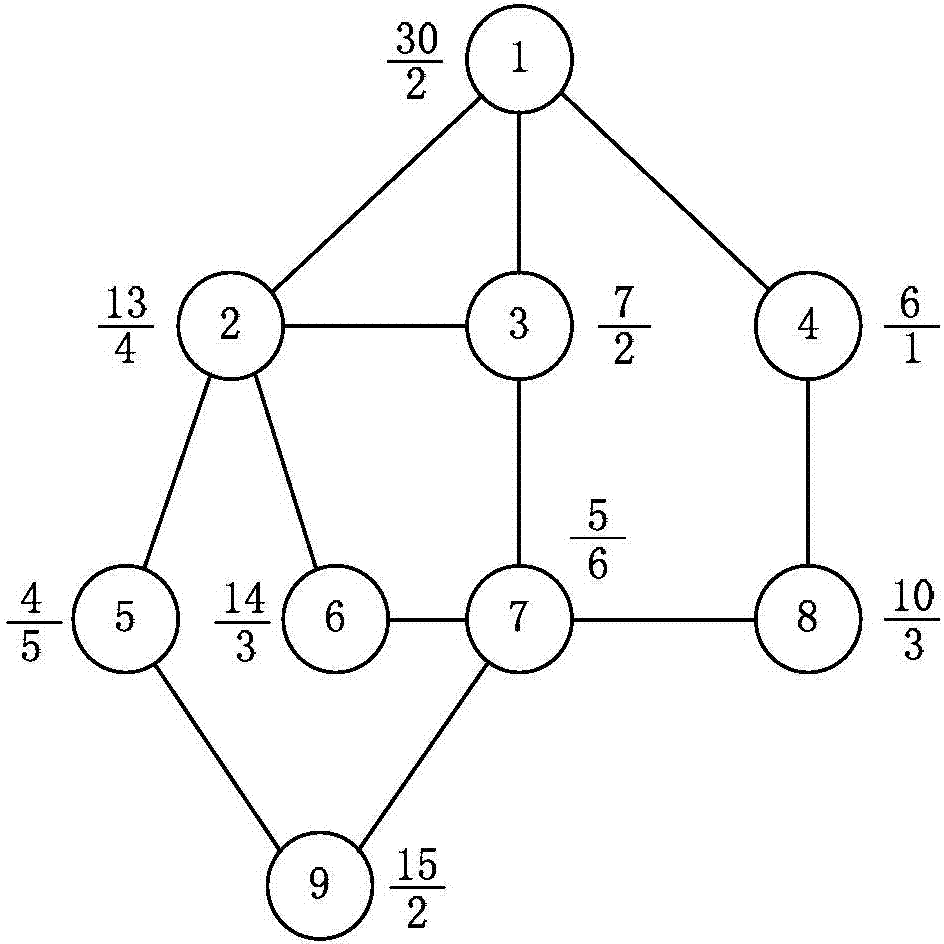
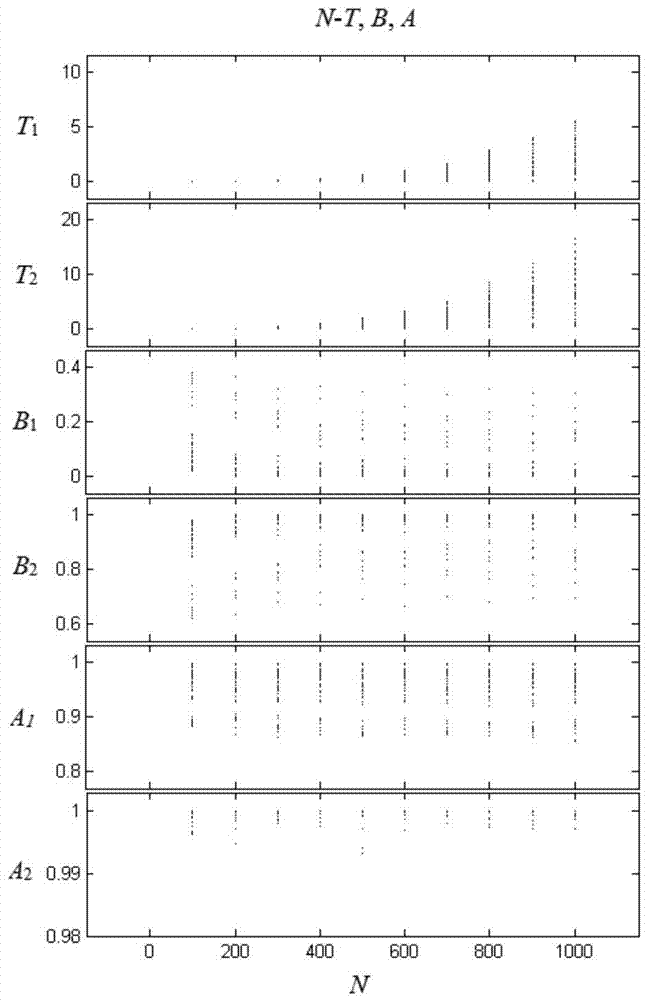
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, a kind of forward-looking greedy method that solves 1-neighborhoo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com