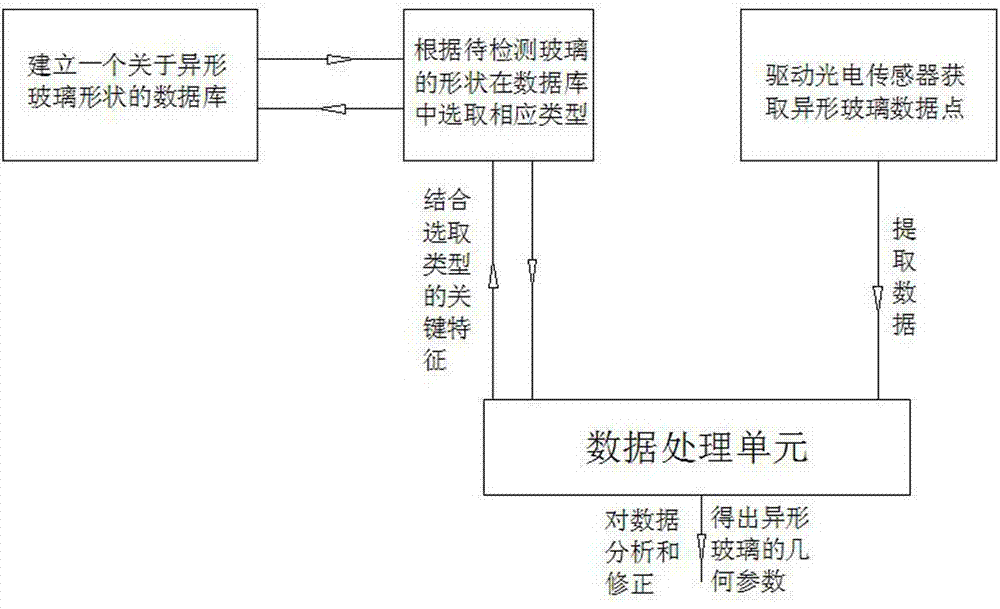
Measuring method for detecting geometric parameters of irregular glass
A special-shaped glass, geometric parameter technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of being easily affected by ambient light, cumbersome installation and debugging, inaccurate data, etc. Simple, Accurate Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Detecting parallelograms
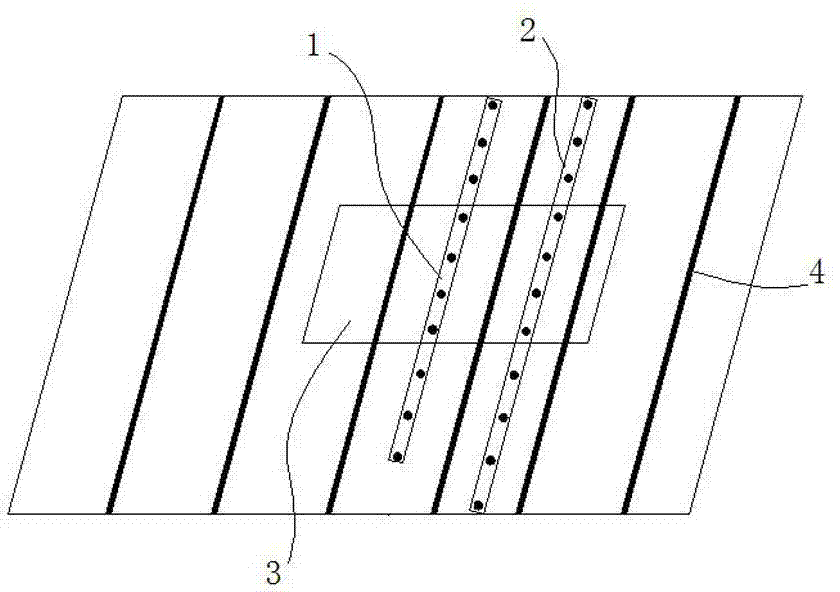
[0039] Such as image 3 As shown, first determine the coordinates of each photoelectric sensor in the mobile measuring ruler 1 and the fixed measuring ruler 2, for example: when 10 photoelectric sensors are evenly distributed on the moving measuring ruler, A represents the moving ruler, and the coordinates of each point on the moving ruler, The unit is 0.1mm, followed by A1(0,0), A2(1983,0), A3(3985,0), A4(5991,0), A5(7987,0), A6(9992,0), A7( 11981,0), A8(13987,0), A9(15951,0), A10(17979,0);
[0040] Determine the coordinates of the sensor on the fixed measuring ruler, S represents the fixed ruler, take setting 11 as an example, the order is: S1(0,920), S2(2000,920), S3(4000,920), S4(6000,920), S5(8000,920), S6(10000,920), S7(12000,920), S8(14000,920), S9(16000,920), S10(18000,920), S11(20000,920);
[0041] It can be seen from the above coordinates that the coordinates of the first photoelectric sensor on the mobile measuring rul...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: Detecting triangles
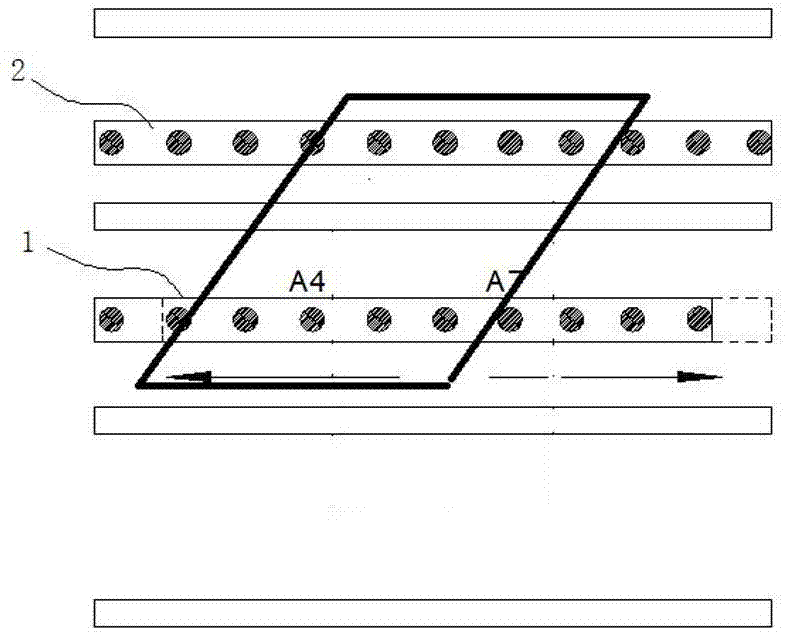
[0065] Such as Figure 4 As shown, first determine the coordinates of each photoelectric sensor in the mobile measuring ruler 1 and the fixed measuring ruler 2, for example: when 10 photoelectric sensors are evenly distributed on the moving measuring ruler, A represents the moving ruler, and the coordinates of each point on the moving ruler, The unit is 0.1mm, followed by A1(0,0), A2(1983,0), A3(3985,0), A4(5991,0), A5(7987,0), A6(9992,0), A7( 11981,0), A8(13987,0), A9(15951,0), A10(17979,0);
[0066] Determine the coordinates of the sensor on the fixed measuring ruler, S represents the fixed ruler, take setting 11 as an example, the order is: S1(0,920), S2(2000,920), S3(4000,920), S4(6000,920), S5(8000,920), S6(10000,920), S7(12000,920), S8(14000,920), S9(16000,920), S10(18000,920), S11(20000,920);
[0067] It can be seen from the above coordinates that the coordinates of the first photoelectric sensor on the mobile measuring ruler...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3: Detecting pentagons
[0092] Such as Figure 5 As shown, first determine the coordinates of each photoelectric sensor in the mobile measuring ruler 1 and the fixed measuring ruler 2, for example: when 10 photoelectric sensors are evenly distributed on the moving measuring ruler, A represents the moving ruler, and the coordinates of each point on the moving ruler, The unit is 0.1mm, followed by A1(0,0), A2(1983,0), A3(3985,0), A4(5991,0), A5(7987,0), A6(9992,0), A7( 11981,0), A8(13987,0), A9(15951,0), A10(17979,0);
[0093] Determine the coordinates of the sensor on the fixed measuring ruler, S represents the fixed ruler, take setting 11 as an example, the order is: S1(0,920), S2(2000,920), S3(4000,920), S4(6000,920), S5(8000,920), S6(10000,920), S7(12000,920), S8(14000,920), S9(16000,920), S10(18000,920), S11(20000,920);
[0094] It can be seen from the above coordinates that the coordinates of the first photoelectric sensor on the mobile measuring ru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com