Application of Rhodococcus erythrococcus in degrading aflatoxin b1 in brewing seasoning or its raw materials
A technology of Rhodococcus erythrococcus and aflatoxin, applied in bacteria, food science, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of toxin degradation, difficulty in large-scale implementation, complex degradation operation process, etc., to solve the problem of detoxification activity and environmental pollution The effect of less energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Preparation of embodiment 1 Rhodococcus erythrococcus strain fermented liquid and supernatant thereof
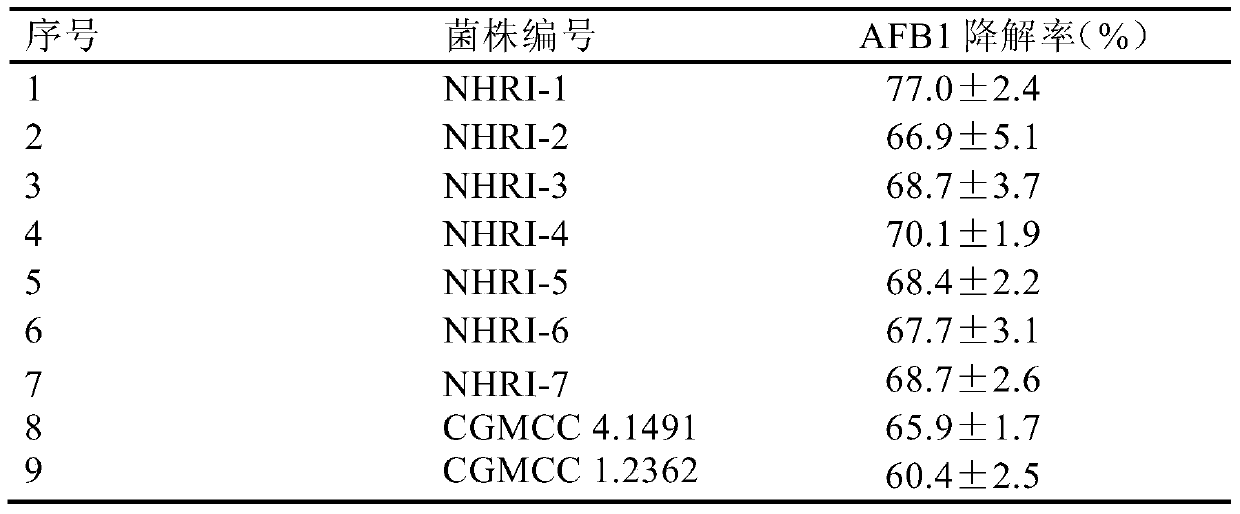
[0042] Seven strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis NHRI-1, NHRI-2, NHRI-3, NHRI-4, NHRI-5, NHRI-6 and NHRI-7 preserved in glycerol tubes at -80℃ General Microorganism Center (CGMCC), deposit numbers are CGMCC No.8590, CGMCC No.8591, CGMCC No.8592, CGMCC No.8593, CGMCC No.8594, CGMCC No.8595 and CGMCC No.8596) and purchased Add 50 μL of frozen storage solution of two strains of Rhodococcus erythrococcus CGMCC4.1491 and CGMCC1.2362 from the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee to 50mL liquid medium (composition: peptone 1.00%, beef extract 0.50%, glucose 0.50%, sodium chloride 0.50%; pH7.2-7.4, 121°C autoclave for 20min) activation culture, the culture conditions are: temperature 30°C, rotation speed 100r / min, culture time 48h. After confirming the purity of the corresponding activated culture solution by microscopi...
Embodiment 2
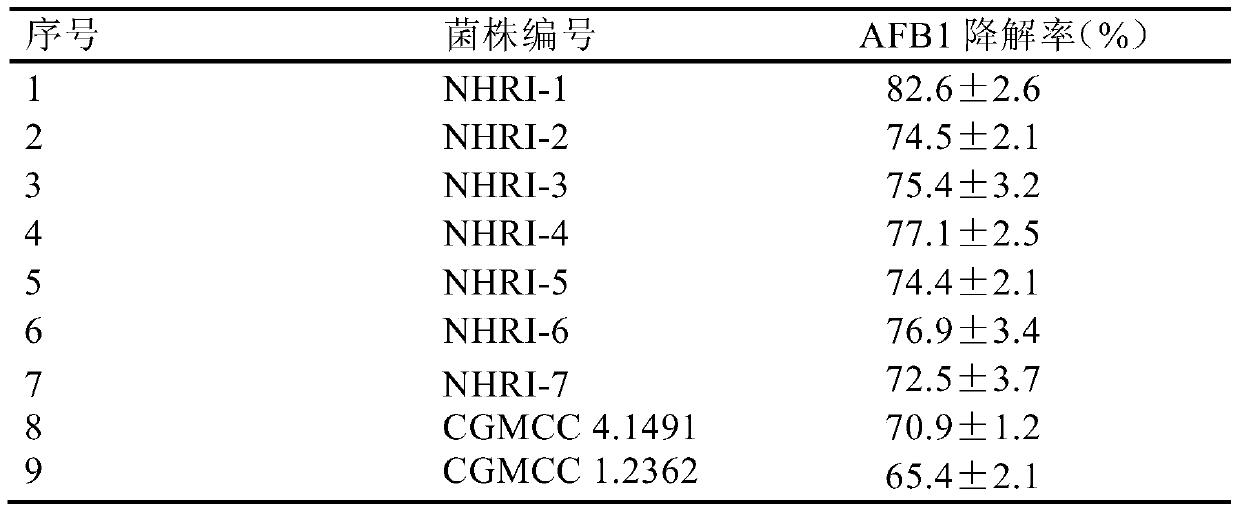
[0044] Example 2 Degradation test of AFB1 in brewing condiment raw material powder by fermented liquid of Rhodococcus erythrococcus strain with a mixing ratio of 5%
[0045] The fermented liquid of the bacterial strain preserved in Example 1 is evenly mixed into the pulverized brewing condiment raw materials (mixtures such as soybean flour, corn flour and rice flour) polluted by AFB1 at a ratio of 5% (volume / weight ratio) (the content of AFB1 is 0.80mg / kg), 3 mixed test samples were prepared from the fermentation broth of each strain, each sample was 500g, the humidity was adjusted to 80%-100% with sterile water, and the sterile gauze was wrapped and placed in a 32cm×25cm×8cm In a well (hole diameter about 0.15cm) tray, at a temperature of 30°C, use sterile water to maintain the humidity of the sample, ventilate and react for 48 hours, and keep the pH value at 7.2-7.4 during the process. At the same time, under the same conditions, a 5% mixed sample of fermentation medium with...
Embodiment 3
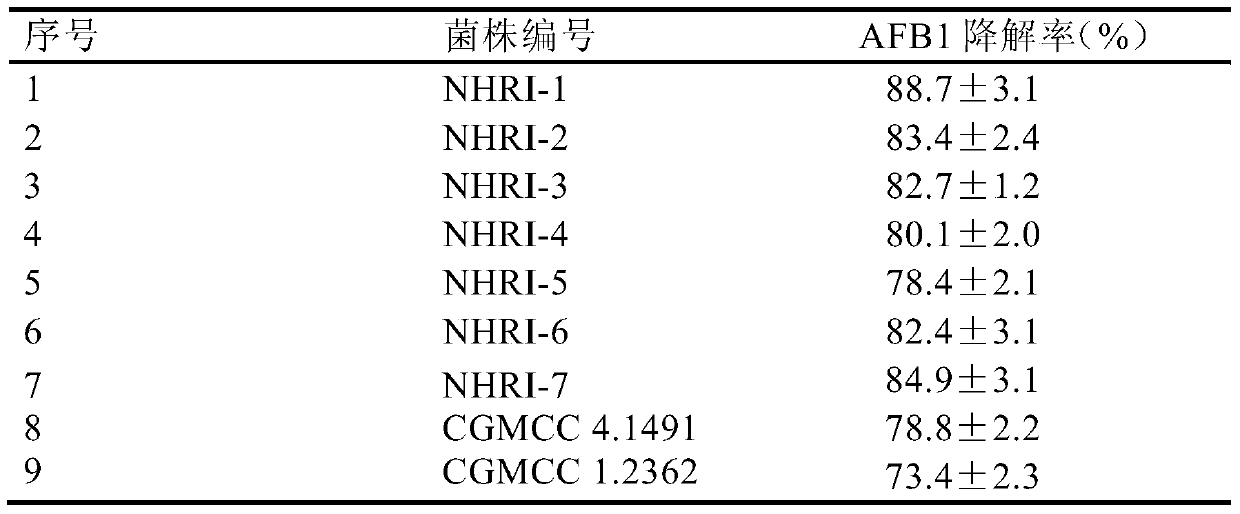
[0051] Example 3 Degradation test of AFB1 in fermented condiment raw material powder by fermented liquid of Rhodococcus erythrococcus strain with a mixing ratio of 12%
[0052] The fermented liquid of the bacterial strain preserved in Example 1 is evenly mixed into the pulverized brewing condiment raw materials (mixtures such as soybean flour, corn flour and rice flour) polluted by AFB1 in a ratio of 12% (volume / weight ratio) (the content of AFB1 is 0.80mg / kg), 3 mixed test samples were prepared from the fermentation broth of each strain, each sample was 500g, the humidity was adjusted to 80%-100% with sterile water, and the sterile gauze was wrapped and placed in a 32cm×25cm×8cm In a well (hole diameter about 0.15cm) tray, at a temperature of 30°C, use sterile water to maintain the humidity of the sample, ventilate and react for 48 hours, and keep the pH value at 7.2-7.4 during the process. At the same time, under the same conditions, a 12% mixed sample of fermentation medium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com