Method, device and system for simulating particle transport and calculating body dosage in radiotherapy
A technology for simulating particles and particles, which is applied in radiation therapy, X-ray/γ-ray/particle irradiation therapy, computer-aided medical procedures, etc. It can solve the problems of high calculation intensity and long time consumption, so as to improve simulation efficiency and speed up simulation speed , to reduce the effect of particle transport
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Using the Monte Carlo algorithm to simulate the particle transport process is a method that uses a large number of random samples to achieve accurate calculations. In particular, in order to meet the user's requirements for particle transport uncertainty, it is often necessary to simulate a large number of particles, which is time-consuming. characteristic.
[0066] This embodiment provides a method for simulating particle transport, which is suitable for simulating the energy distribution of particles in a cell. It can be based on the Monte Carlo simulation algorithm, which calculates the uncertainty of the geometric cell and distinguishes the It can reduce the sampling of particles and save a lot of calculation time.
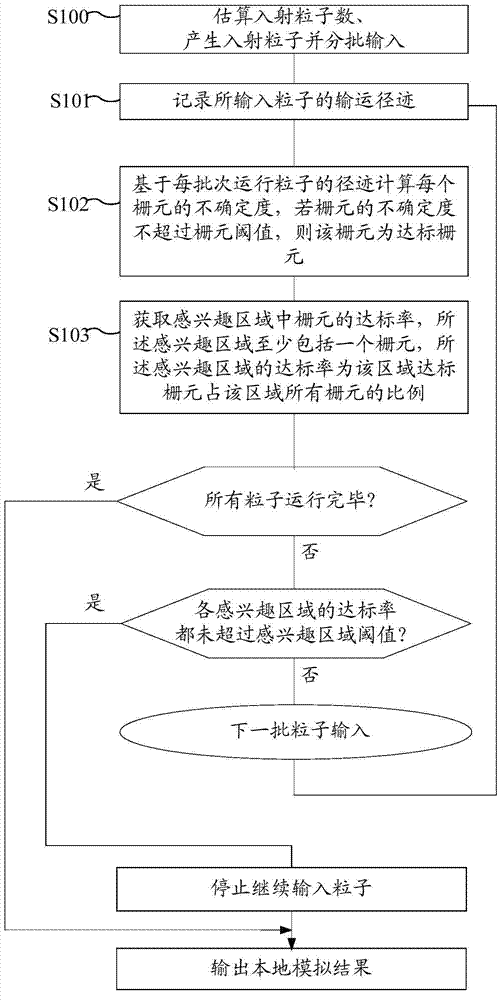
[0067] refer to figure 1 , the method for simulating particle transport provided in this embodiment includes:
[0068] Step S100, estimating the number of incident particles, generating incident particles and inputting them in batches.
[0069] The i...
Embodiment 2
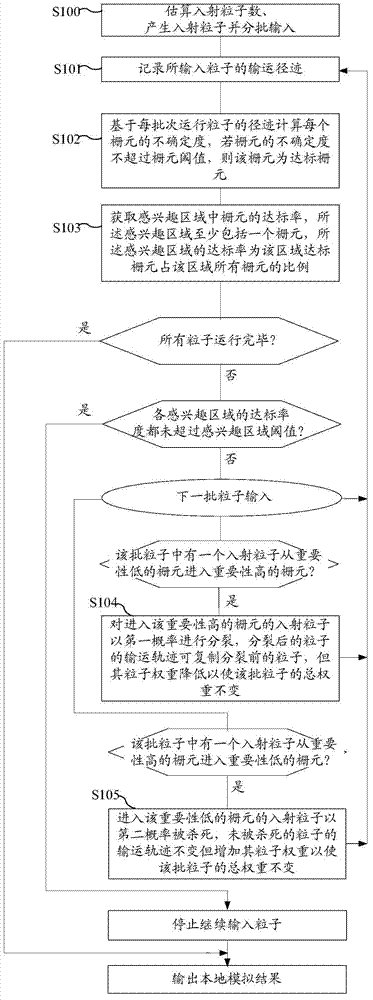
[0106] Based on Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a method such as figure 2 The shown method for simulating particle transport can balance the uncertainty according to the global uncertainty of the simulation process, and dynamically adjust the number of particle samples according to the distribution of uncertainty. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0107] Steps S100 to S103 are consistent with Embodiment 1.
[0108] When the next batch of incident particles is input, based on the transport process of the incident particles, the input particles are processed as follows:
[0109] Step S104, if the transport process of the incident particles shows that one of the incident particles in the batch of particles enters the cell with high importance from the cell with low importance, then the incident particle entering the cell with high importance is treated as Splitting with a certain probability, the transport trajectory of the split particles can copy...
Embodiment 3
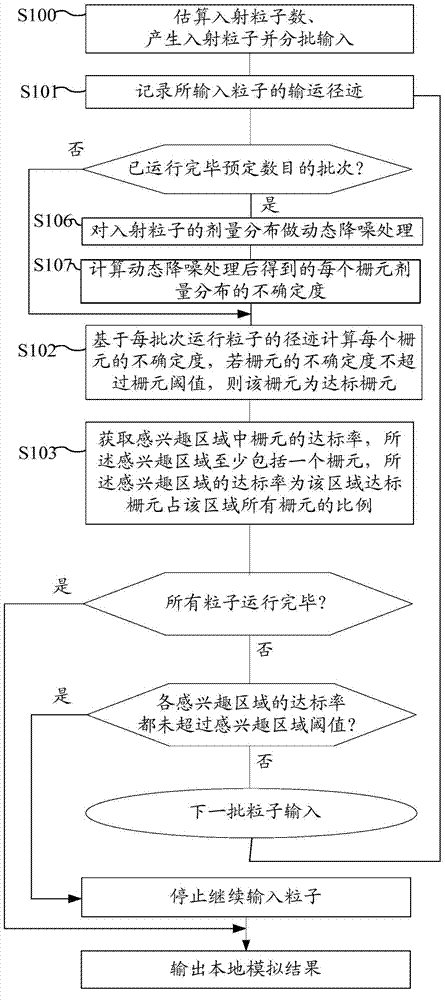
[0118] Based on Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a method such as image 3 The method for simulating particle transport shown can be based on the batch transport of particles during the simulation process. After the simulation completes the transport tracks of predetermined batches of particles, the transport tracks based on historical batches of particles are globally uncertain Dynamic noise reduction can be carried out at a high degree, thereby reducing the uncertainty of the simulated particle transport process, which helps to reduce the number of particle samples and improve the simulation efficiency. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0119] Steps S100 to S103 are consistent with Embodiment 1.
[0120] In the process of simulating particle transportation, if the batches of particle transportation reach the predetermined number, execute:
[0121] Step S106, performing dynamic noise reduction processing on the dose distribution of the incident p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com