A Realization Method of 3D Space Positioning Based on RFID Middleware
A technology of three-dimensional space and realization method, which is applied in the field of RFID, positioning middleware, and three-dimensional space positioning algorithm, can solve the problems of inability to meet the three-dimensional space indoor positioning requirements, high cost of readers, and harsh use conditions, etc., to shorten the development cycle, The effect of masking differences and reducing estimation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] In order to make the technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, further detailed description will be given below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the implementation and protection of the present invention are not limited thereto.
[0025] 1. The three-dimensional space passive tag positioning algorithm involved in this method
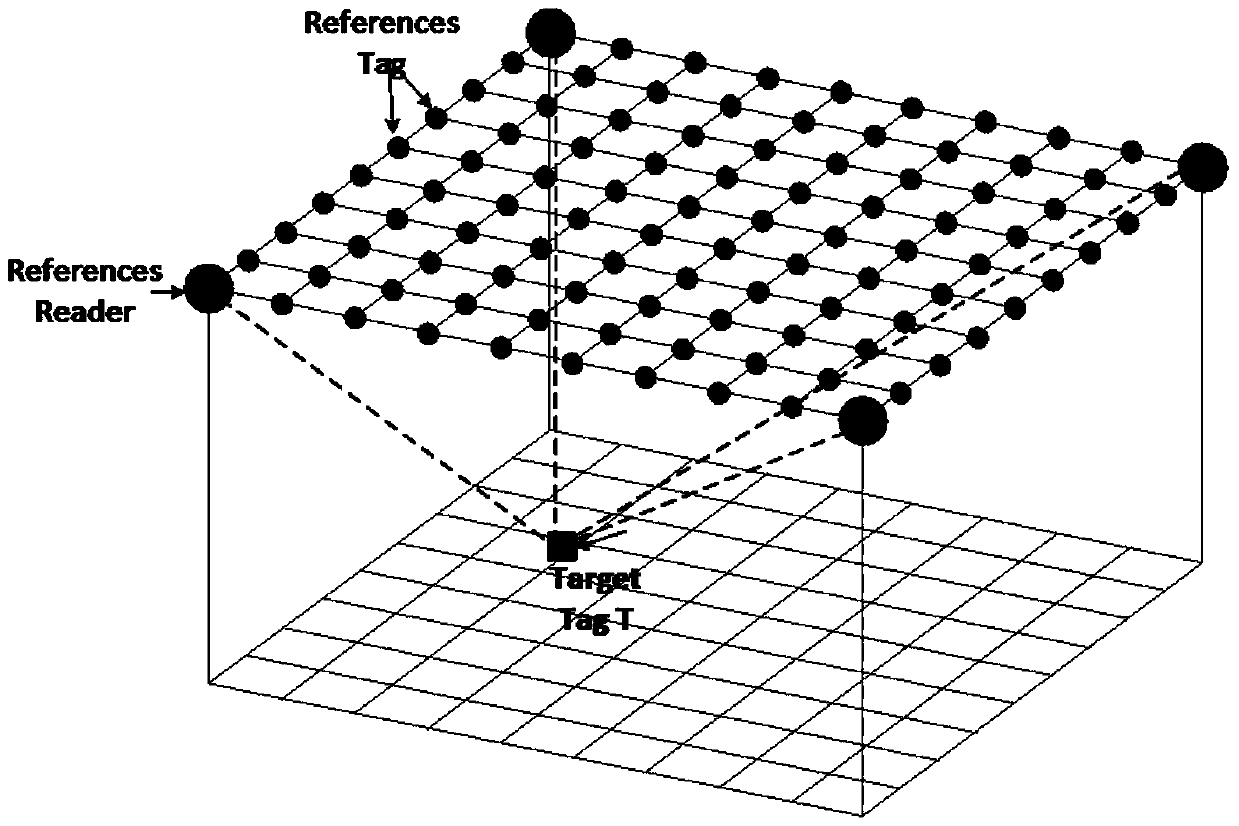
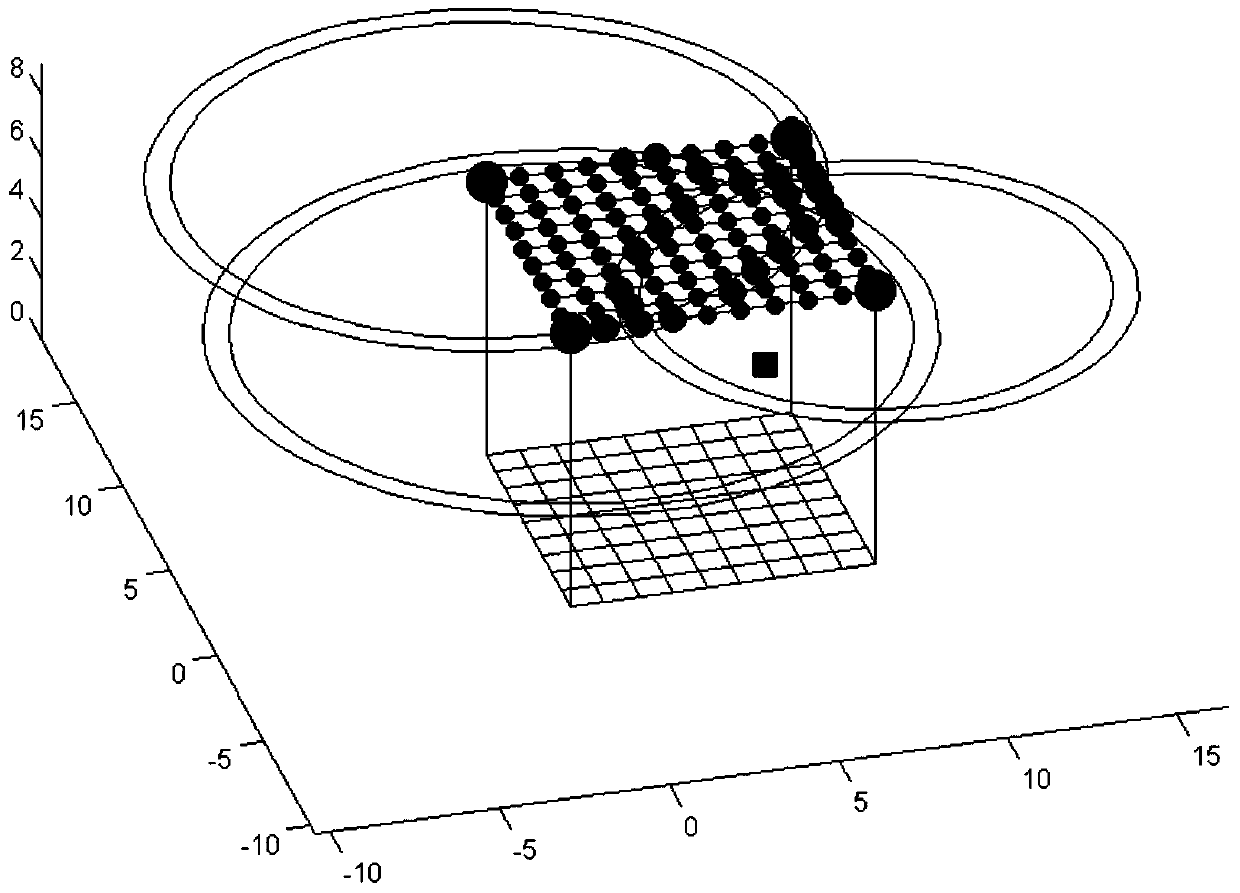
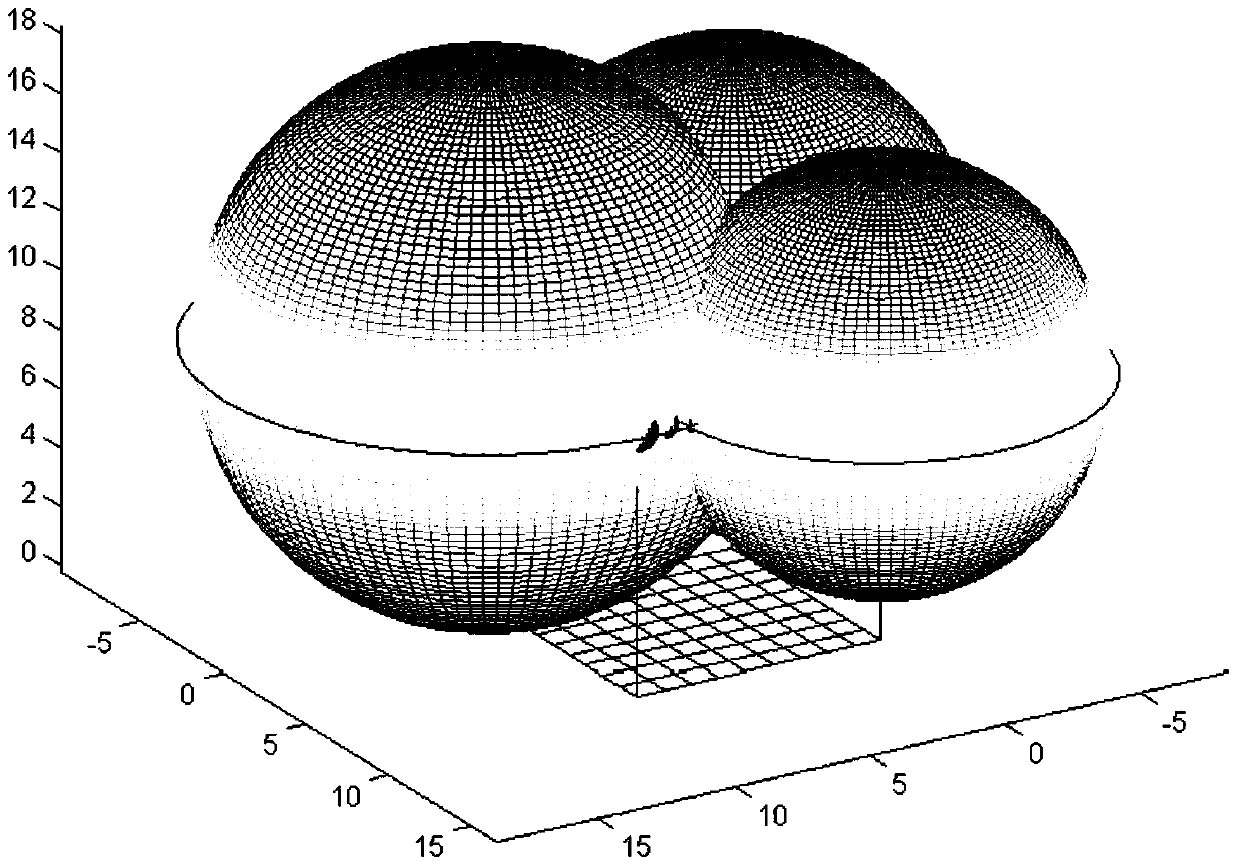
[0026] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, this algorithm includes three parts, 1. Signal strength classification; 2. Three-sphere intersection calculation; 3. Least square method plane fitting
[0027] The basic components of this system include RFID readers, RFID passive reference tags, and target tags to be located. The system deployment of this algorithm is as follows: figure 1 As shown, in the preprocessing stage, the passive reference tags with known coordinate positions are deployed on the upper plane of the hexahedron. By default, four readers are deployed on the fou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com