Method for filtering uplink data based on characteristic of logical bearer
A logic bearing and characteristic technology, applied in the direction of access restriction, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., to achieve the effect of simple implementation, multi-flexibility, and simple specification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
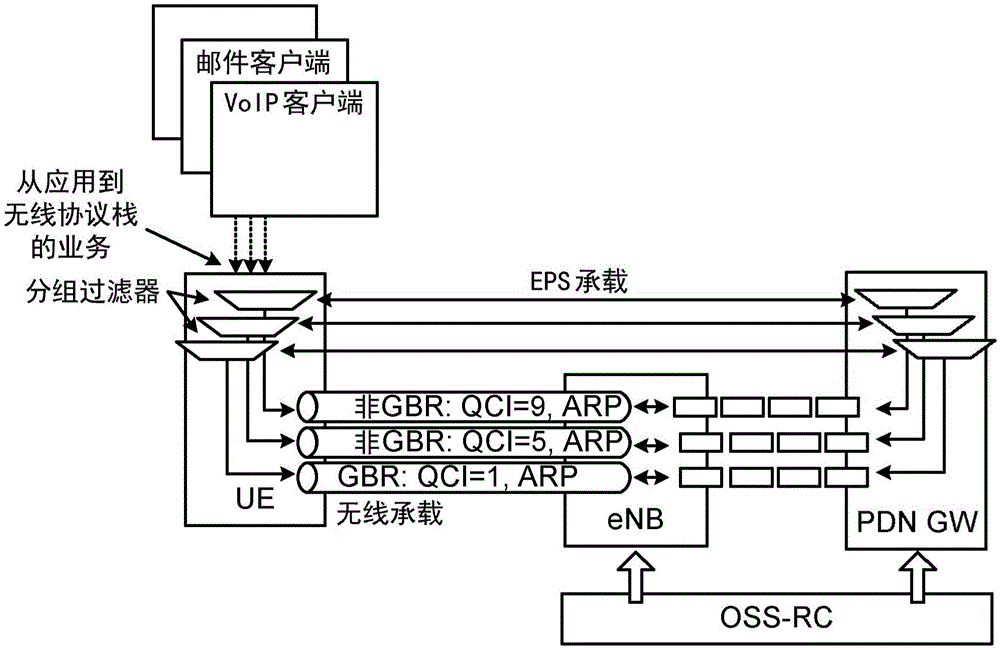
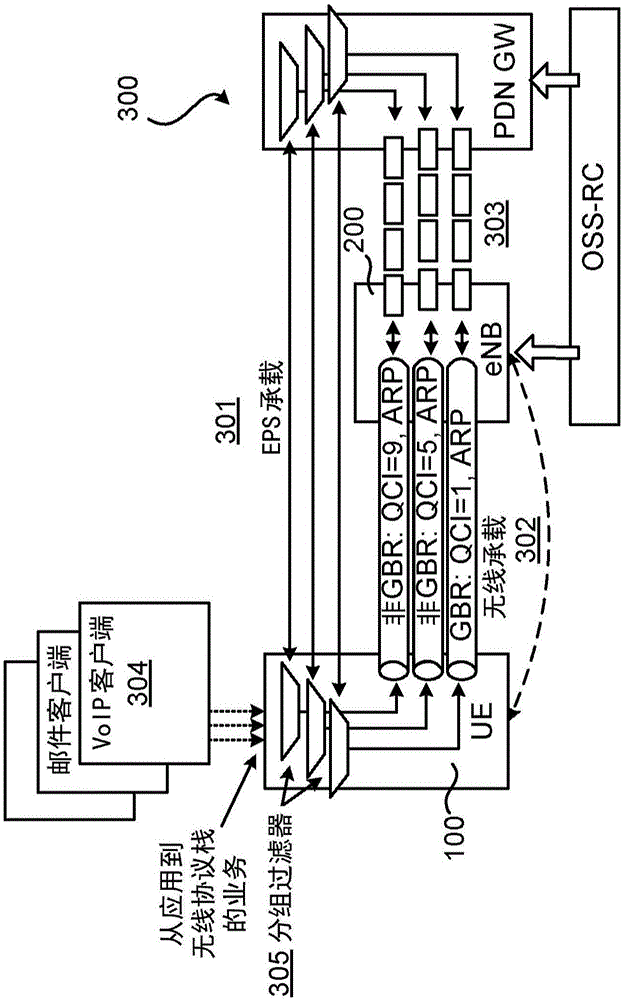
[0055] In a first example, a legacy barring parameter in system information may indicate that "mobile originating calls" is barred. However, when triggered by data belonging to, for example, QCI5 or QCI1, the NW may indicate explicit permission of access (overriding legacy access barring). Therefore, an established UE 100 in RRC connection or idle with a QCI5 or QCI1 bearer can still access the network to transmit corresponding data (eg, IMS signaling and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) data). However, for traffic that does not match any of the above QoS classes (using filter 305), they should not access the network. This can be indicated explicitly with a per-QCI (per-QCI) suppression parameter, or as a result of other suppression methods. Furthermore, access by UEs 100 that are only performing initial access or that do not have an established QCI5 (or QCI1) bearer for other reasons is not allowed to access, unless they wish to trigger e.g. an emergency call or some othe...
example 2
[0057]In a second example, per-QCI barring can be applied even if no legacy barring is configured. This is considered useful, for example, if a UE 100 that has not yet established a bearer should be allowed to access the network. Furthermore, it is possible that the network may not implement traditional access class barring mechanisms at all and rely only on per-QCI mechanisms. To achieve this, the network will not set traditional prohibition parameters (such as mobile-initiated calls, etc.), so that all UEs 100 are allowed to access the network by default. The UE 100 may access the network during initial attach or when the UE does not have a configured (EPS-) bearer 301 for other reasons. Once in the RRC Linked state, the UE will be configured with at least one default bearer (eg QCI9) and possibly a QCI5 bearer which is considered to carry time-critical IMS signaling. If the network experiences high load, it may indicate to the UE that access triggered by data on the QCI9 ...
example 3
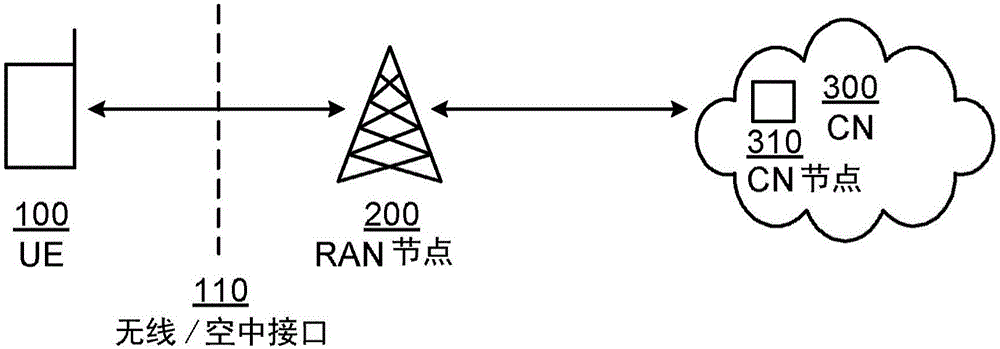
[0059] In one embodiment, barring per QCI / bearer may apply to UE 100 in idle or RRC connected. This means that it can prohibit or explicitly allow random access (in idle or connected state) or dedicated scheduling requests (in connected state). In other embodiments, the barring rule may only apply to UEs in connected mode or only to UEs in idle mode. To further increase the flexibility of embodiments of the present disclosure, the barring parameters provided to the UE 100 may explicitly indicate the state (idle and / or connected) to which they apply. In systems such as UMTS where there are more than two states, it may be beneficial to further distinguish the sub-states (CELL_FACH, URA_PCH, etc.) to which prohibition should apply
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com