A Method of Predicting Thermal Conductivity of Materials Based on Finite Difference Method of Three-Dimensional Images
A finite difference method and three-dimensional image technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as loss of numerical simulation, increase of computer resources in analysis time, etc., to improve computing speed, save computing time, The effect of saving system resources and computing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
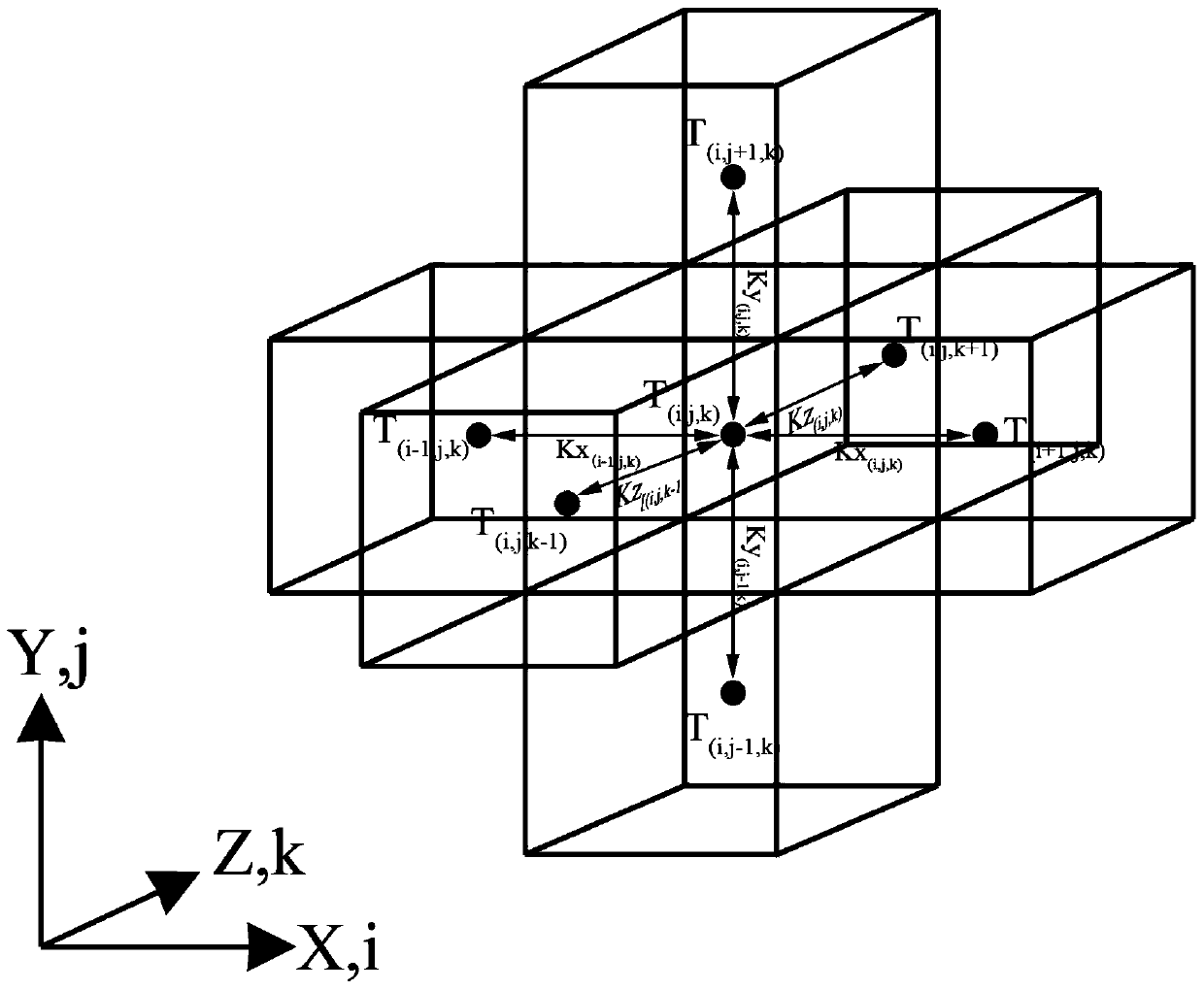
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Example 1: Prediction of thermal conductivity along the spray direction of a plasma sprayed yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coating.
[0089] This example takes the plasma sprayed YSZ coating as an example to demonstrate the prediction process of the present invention for the thermal conductivity of porous materials.
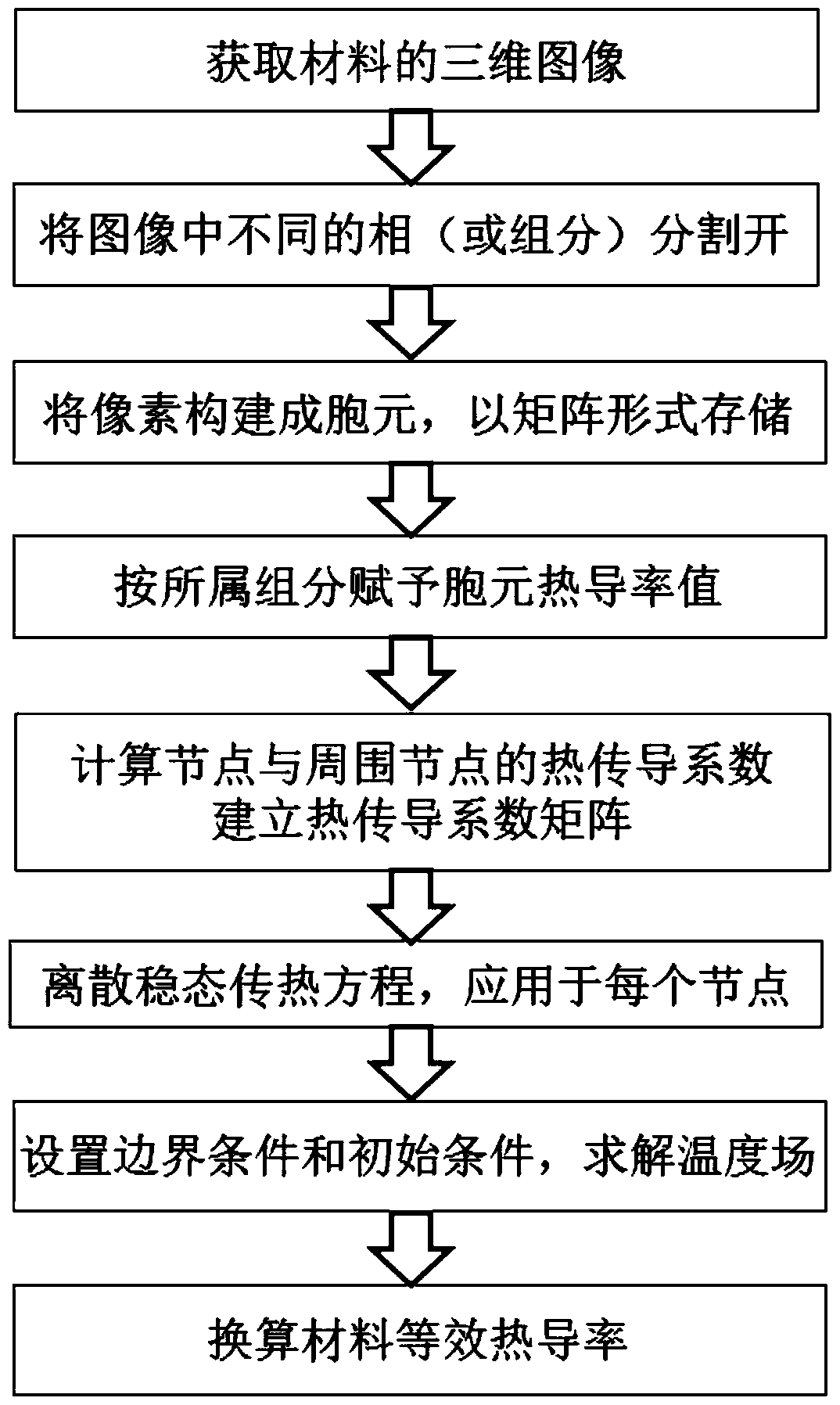
[0090] Adopt the present invention to predict the thermal conductivity of ion-sprayed yttrium oxide stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coating, comprise the following steps:
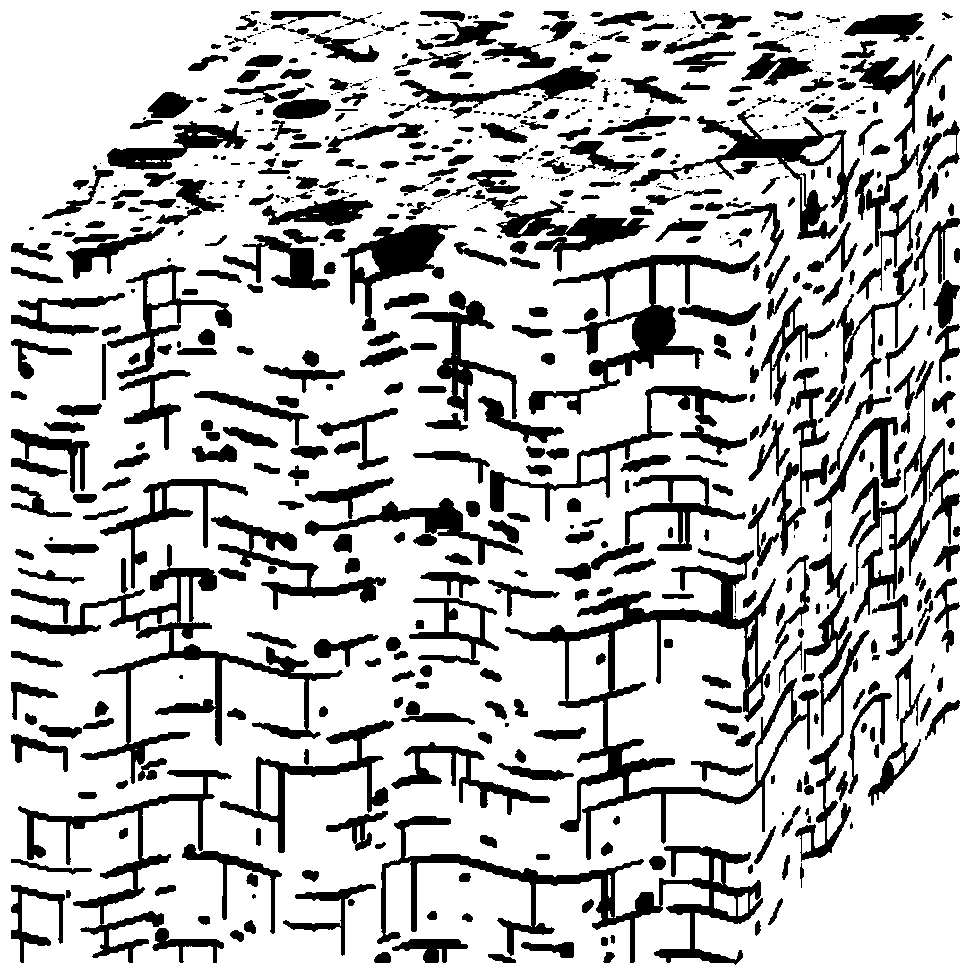
[0091] (1) Reconstruct the three-dimensional image of the plasma sprayed YSZ coating structure, such as image 3 shown; image 3 is a three-dimensional reconstruction image (300×300×300 pixels) of the plasma sprayed yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) coating of the present invention. The black in the picture is the pores and cracks, and the white is YSZ.
[0092] (2) Using a computer language program, the image 3 The image shown is read into memory and stored in a three-dimensional matri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com