Airplane scheduling module and method based on probability theory
A scheduling method and probability theory technology, applied in data processing applications, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as flight delays, achieve the effect of reducing the degree of delay and the rate of flight delays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Specific embodiment one: the aircraft scheduling module based on probability theory described in this embodiment includes the following units:
[0030] Input unit: a that receives user input i and p(a i ), where p(a i ) means that the origin is M, the destination is N, and it is expected to be at T 1 ~T 2 The delay time of n flights departing in the time period is a i The probability of , i=1,2,...,m;
[0031] Average delay time calculation unit: according to E(a i ) = a i ·p(a i ) calculation is expected at T 1 ~T 2 The average delay time E(a i );
[0032] Departure Time Update Unit: According to Calculate the updated departure time T of the n flights newj , where T j is the expected departure time of the jth flight, j=1,2,...,n;
[0033] Scheduling unit: according to the updated departure time T new1 to T newn to schedule the n flights.
specific Embodiment approach 2
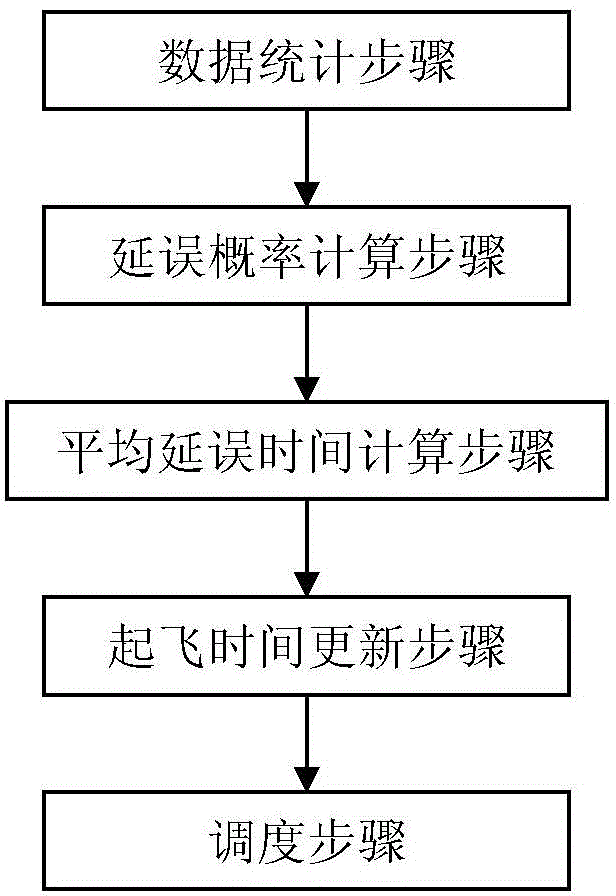
[0034] Specific embodiment two: the aircraft scheduling module based on probability theory described in this embodiment includes the following units:
[0035] Data statistics unit: Statistics within the past X months, the origin is M, the destination is N, and it is expected to be in T 1 ~T 2 The delay time a of n flights departing in the time period i ;
[0036] Delay probability calculation unit: calculate delay time a i The corresponding p(a i ), where p(a i ) means that the origin is M, the destination is N, and it is expected to be at T 1 ~T 2 The delay time of n flights departing in the time period is a i The probability of , i=1,2,...,m;
[0037] Average delay time calculation unit: according to E(a i ) = a i ·p(a i ) calculation is expected at T 1 ~T 2 The average delay time E(a i );
[0038] Departure Time Update Unit: According to Calculate the updated departure time T of the n flights newj , where T jis the expected departure time of the jth fligh...
specific Embodiment approach 3
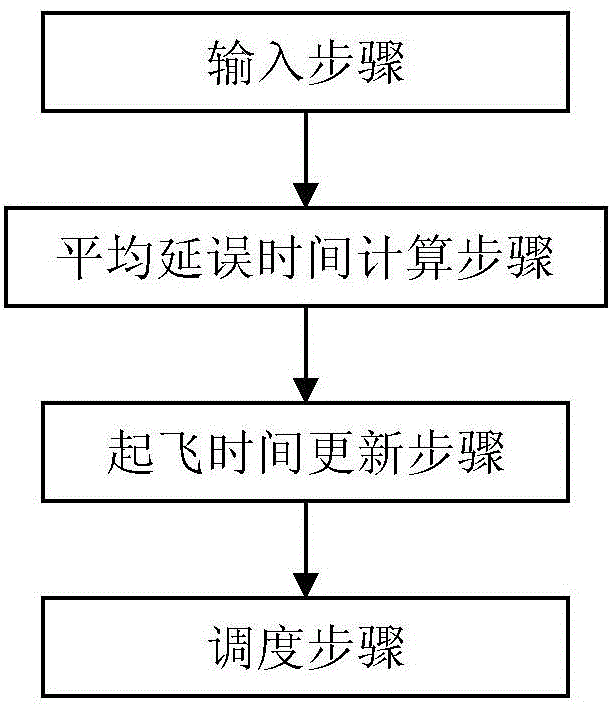
[0040] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the aircraft scheduling method based on probability theory described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] Input step: receive user input a i and p(a i ), where p(a i ) means that the origin is M, the destination is N, and it is expected to be at T 1 ~T 2 The delay time of n flights departing in the time period is a i The probability of , i=1,2,...,m;
[0042] Calculation steps of average delay time: according to E(a i ) = a i ·p(a i ) calculation is expected at T 1 ~T 2 The average delay time E(a i );
[0043] Departure time update steps: According to Calculate the updated departure time T of the n flights newj , where T j is the expected departure time of the jth flight, j=1,2,...,n;
[0044] Scheduling step: according to the updated departure time T new1 to T newn to schedule the n flights.
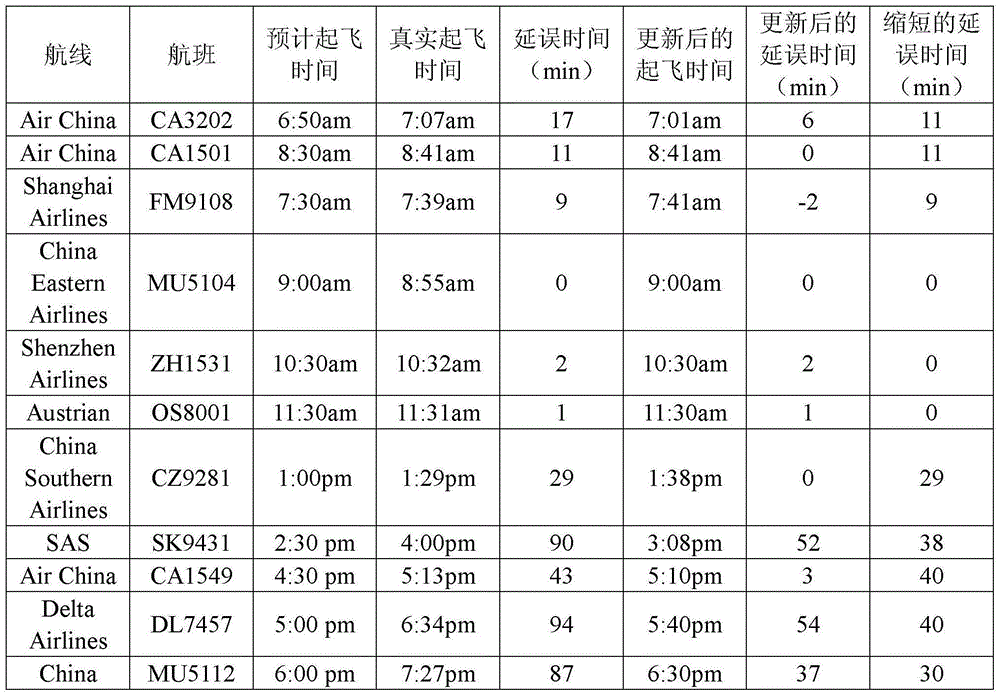
[0045] The delay of the aircraft is not only related t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com