A Design Method of Coiled Tubing
A design method, oil pipe technology, applied in computing, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of increased computing costs and poor results, and achieve the effect of reducing the working process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Tubing length and tubing weight calculation:
[0039] In the H-I mathematical model, set oil pipe diameter A, drum outer diameter B, drum inner diameter C, drum inner width D, flange height E, oil pipe turns F, oil pipe layers G, oil pipe length H, oil pipe weight I, and oil pipe density J , tubing wall thickness K, where:
[0040] E=(B-C) / 2, F=int(D / A), G=int[(B-C) / 2×A];
[0041]
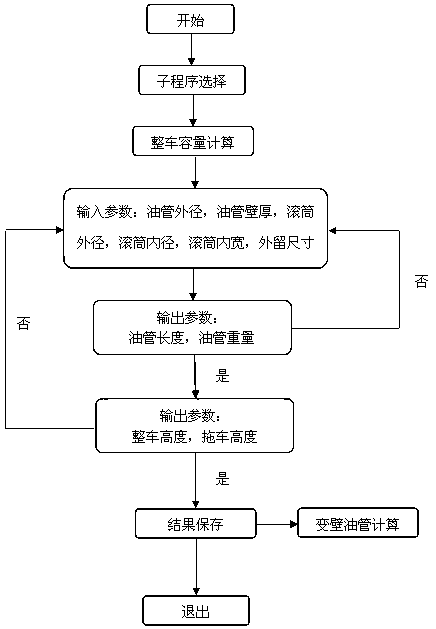
[0042] Depend on figure 1 , if the calculation result obtained after calculation is that the size of the tubing drum cannot meet the requirements of the tubing length desired by the user, then adjust the outer diameter and inner width of the tubing drum until the requirements can be met.
[0043] The calculation results are often non-round sizes. For example, it is expected that the tubing drum can accommodate 1.5” tubing 5 with a length of 5000m, but the actual calculated result is 5150m and the weight of the tubing with a length of 5150m. You can set the expected tubing length and the...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Tubing tensile load, yield load and bearing load calculation:
[0047] In the Q-P model, the tensile strength L of the tubing, the yield strength M, the tensile load O, the yield load P, and the withstand load Q are set, where:
[0048] O={[A×A-(A-2K)×(A-2K)] / 4}×3.14×L;
[0049] P={[A×A-(A-2K)×(A-2K)] / 4}×3.14×P
[0050] Q=P-∑I
[0051] Where ∑I is the sum of the tubing weights.
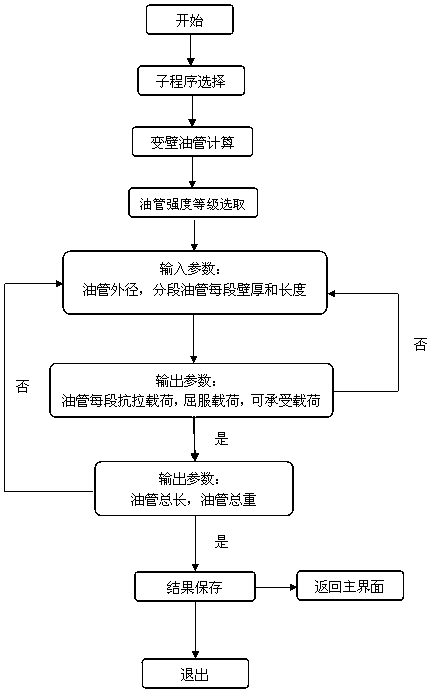
[0052] The variable-wall tubing calculation can realize the selection of the tubing strength grade, input the outer diameter of the tubing, and input the length and wall thickness of the segmented tubing. The calculation program can automatically calculate the weight of each section of tubing, the maximum tensile load, the maximum yield load and the section of tubing able to withstand the load.
[0053] The number of variable-wall-thickness tubing sections that can be calculated by this method is up to 5 sections.
[0054] It can be determined whether the design of variable-wall-thickness ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Vehicle height calculation and distributed load calculation:
[0058] u 0 -U 1 In the mathematical model, the load on the front axle is T, the load on the rear axle is U, and the weight of the body is G 0 , the distance L between the bodywork and the front axle 1 , the distance L between the bodywork and the rear axle 2 , the distance L between the front and rear axles 0 , then G 0 Loads on the rear axle and G 0 The loads on the front axle are:
[0059] f 0 =G 0 × L 1 / L 0 , F 1 =G 0 × L 2 / L 0
[0060] Then the total load on the rear axle is U 0 =∑F 0 , the total load U on the front axle 1 =∑F 1 ;
[0061] Then the load ratio of the front axle to the rear axle is:
[0062]
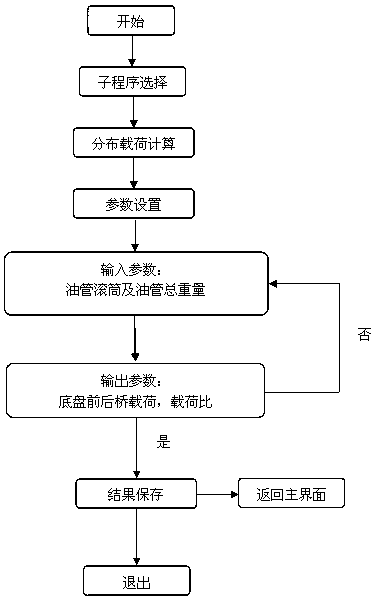
[0063] Depend on image 3 , The distributed load calculation can realize the setting of the allowable load of the front and rear axles. After inputting the weight of the tubing drum and tubing, the calculation program automatically calculates and outputs the relationship be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com