Blunt impact indicator methods
An indicator, blunt technology, used in the field of systems for monitoring and indicating high-energy impacts on structures, which can solve the problem of visible indication of damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
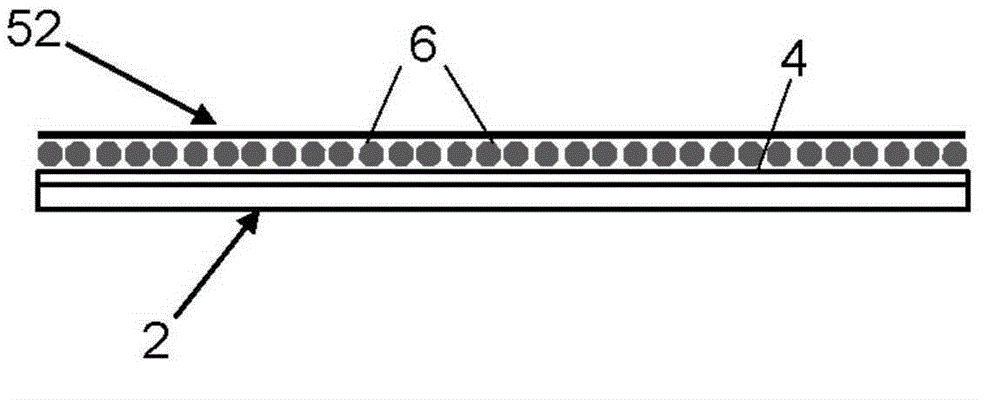
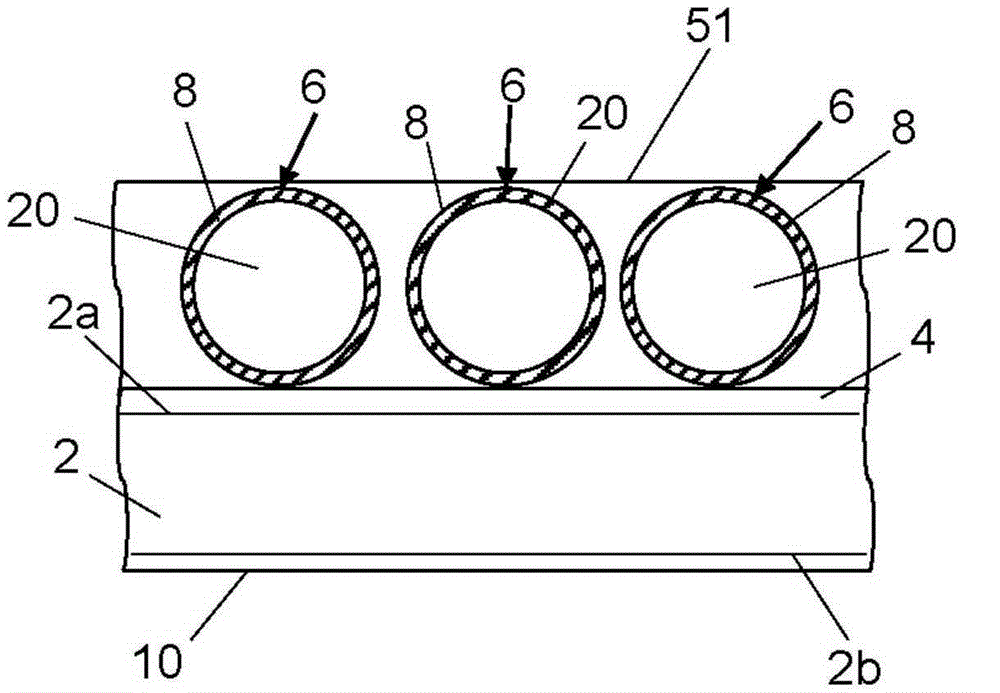
[0101] For purposes of illustration only, various embodiments of blunt impact indicators employing fluid-filled microspheres will now be described in detail. These blunt impact indicators may be applied to the surface of the structure in the form of a substrate (eg, a tape or applique) with an adhesive backing. Microspheres can be attached to a substrate or embedded in a coating applied to the substrate.
[0102] figure 1 A first illustrative embodiment of a blunt impact indicator of the aforementioned type is schematically depicted. The blunt impact indicator comprises a substrate 2 having a plurality of hollow microspheres 6 attached to one surface of the substrate 2 by a layer 4 of adhesive material (hereinafter "adhesive layer 4") and distributed thereon . Optionally, the microspheres 6 are covered by a cover layer 52 .
[0103] The substrate 2 can have different forms. In some cases, substrate 2 may be in the form of a strip comprising thin strips of plastic material...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com