Array type photobioreactor light splitting method
A photobioreactor, array technology, applied in the direction of bioreactor/fermenter combination, specific-purpose bioreactor/fermenter, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low spectral efficiency and sunlight utilization rate low problems, to achieve the effect of improving the light splitting rate and improving the overall light utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] In the present embodiment, the spectroscopic method of the array photobioreactor comprises the following steps:
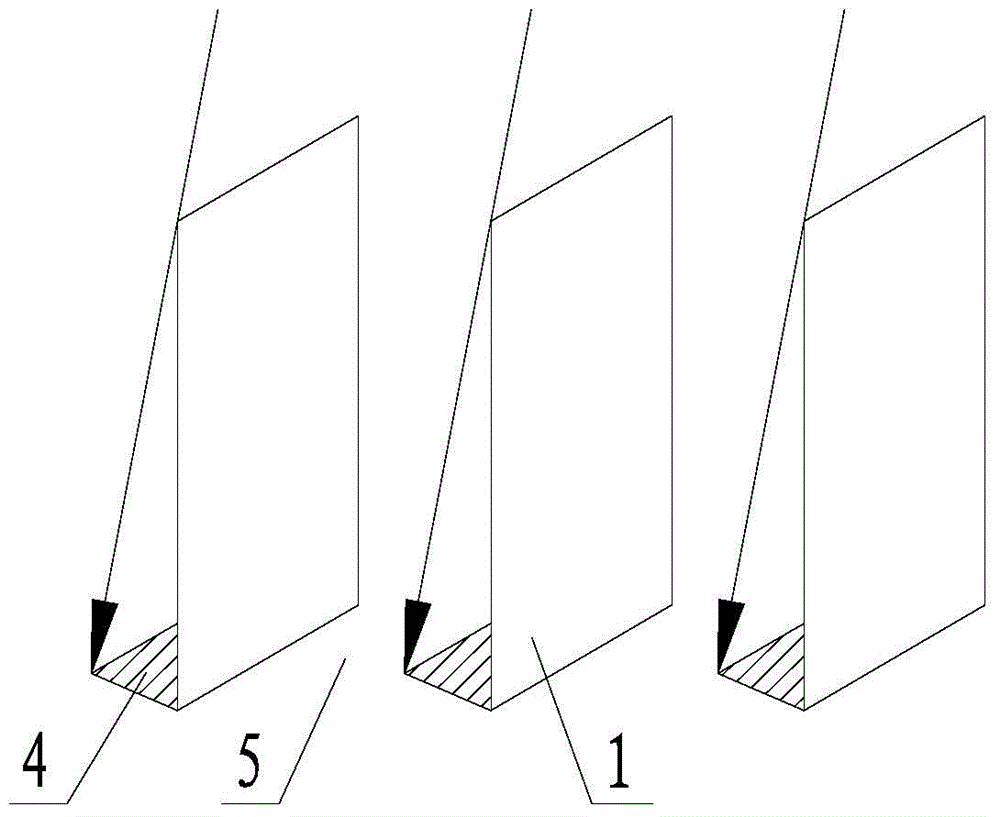
[0052] Step 1, a plurality of photobioreactors 1 are arranged in parallel in front and back, and arranged in an array at a certain interval on a horizontal plane, such as image 3 shown;
[0053] Step 2. With the change of the sun's altitude and azimuth, adjust the elevation angle α of the effective cultivation surface of the photobioreactor so that the vertical shadow length (i.e. the length of the normal shadow 4) produced after the sunlight is projected onto the photobioreactor 1 value) is not less than the distance between the bottom edges of adjacent photobioreactors in the shadow length direction.
[0054] The photobioreactor 1 in this embodiment is a device for cultivating photosynthetic organisms on the surface by means of liquid, and the materials of each photobioreactor 1 can be the same or different.
[0055] In this embodiment, a horizontal sha...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The similarities between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here.
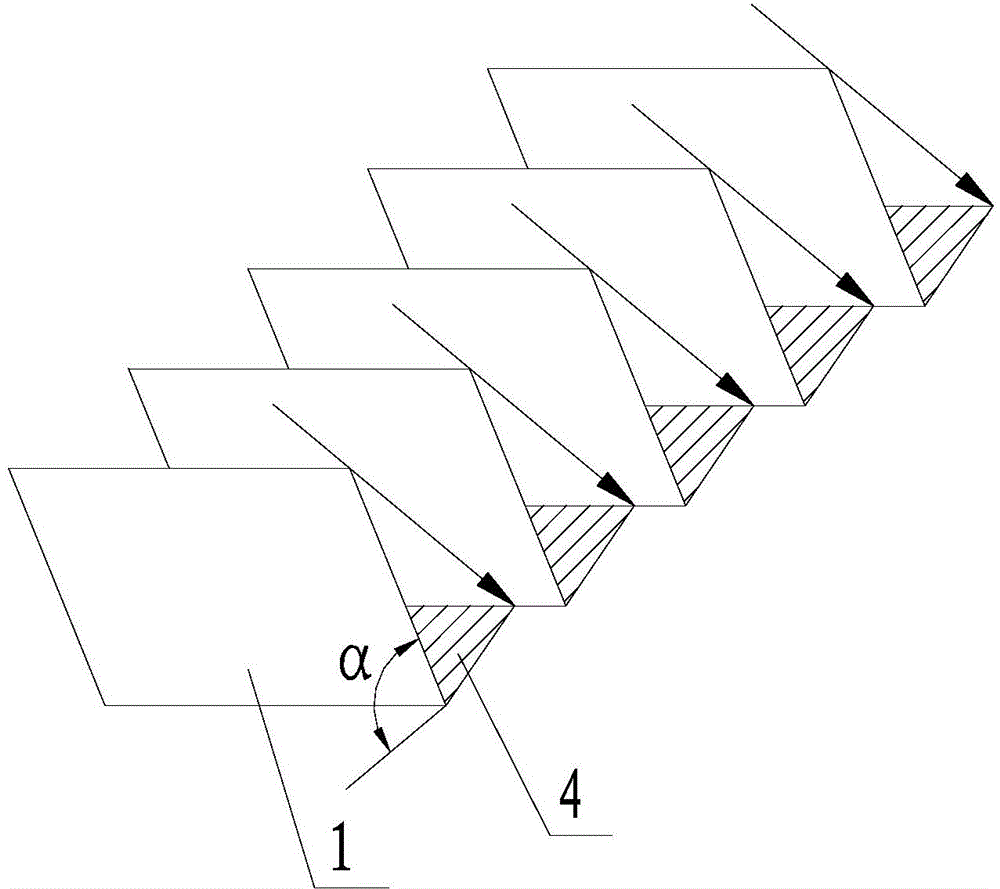
[0062] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: there are at least two photobioreactors 1 in Embodiment 1, and they are arranged in a single row; the arrayed photobioreactors 1 in this embodiment are multiple rows and multiple columns, Parallel front and back, straight lines left and right, and arranged in an array at a certain distance, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0063] In this embodiment, the adjustment of the vertical shadow length generated after the sunlight is projected onto the photobioreactor 1 is the same as that in embodiment 1, and it is also realized by adjusting the elevation angle α of the effective cultivation surface of the photobioreactor 1. The specific adjustment principle and process are as described in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The similarities between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here.
[0066] The differences between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 are as follows.
[0067] In the present embodiment, the spectroscopic method of the array photobioreactor comprises the following steps:
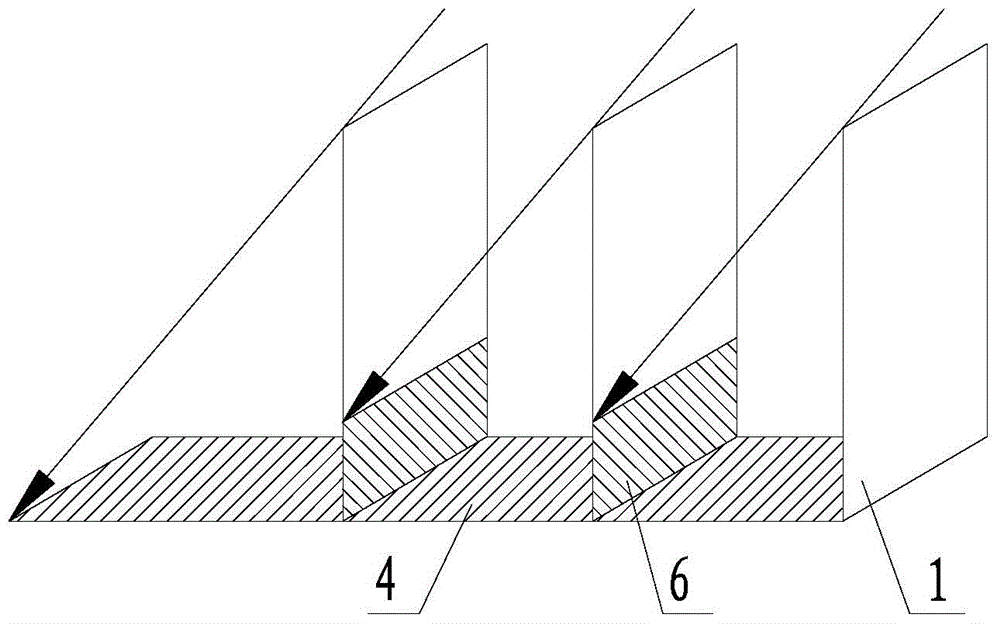
[0068] Step 1. Multiple photobioreactors are arranged in parallel in front and back, and arranged in an array at a certain distance on a horizontal plane, such as image 3 As shown; the photobioreactor in this embodiment is only arranged in one row.
[0069] Step 2. With the change of the sun's altitude and azimuth, and the changes of the sun's altitude and azimuth at each time of the year, adjust the azimuth β of the effective breeding surface of the photobioreactor so that the sunlight is projected to the photobioreactor The resulting vertical shadow length (that is, the length of the normal shadow 4) is not less than the distance between the bottom edges of adjacent photobioreacto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com