Construction method of full duplex relay system based on sparse code multiple access
A sparse code multiple access and relay system technology, applied in transmission system, digital transmission system, duplex signal operation and other directions, can solve the problem that OFDMA system is difficult to meet the requirements of spectral efficiency and transmission rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0041] Specific embodiment 1: A method for constructing a full-duplex relay system based on sparse code multiple access in this embodiment is characterized in that the full-duplex relay system based on sparse code multiple access The build method of is implemented in the following steps:
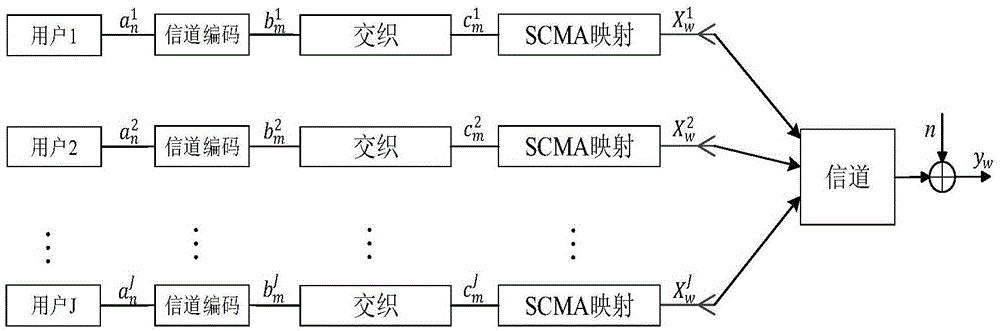
[0042] Step 1. Using sparse code multiple access, user A J Encode the information and send it to the relay station;
[0043] Step 2: The relay station uses full-duplex mode to send and receive information, and eliminates the interference from the feedback, and then forwards the information to user B J ;
[0044] Step 3. User B J After receiving the signal forwarded by the relay station, perform corresponding decoding to obtain user A J information sent.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0045] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that it is characterized in that the step 1 adopts the method of sparse code multiple access, and user A J Encode the information and send it to the relay station according to the following steps:
[0046] Step 11. It is assumed that the sparse code multiple access system SCMA has J users, wherein J≥1; each user sends information respectively, and the transmitted information bit sequence is subjected to forward error correction coding (FEC), and then interleaved;
[0047] All symbols in the structure of the SCMA system user transmitter use superscripts to distinguish different users, and subscripts to distinguish elements in the vector; for the jth user in the sparse code multiple access system, the transmitted The information bit sequence is Where 0≤j≤J-1, and N is the frame length; forward error correction coding is performed on the information bit sequence, that is, random er...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from specific embodiment 1 or 2 in that it is characterized in that the relay station in step 2 uses a full-duplex mode to send and receive information, and performs interference elimination on self-feedback interference, and then forwards the information to user B J Follow the steps below to achieve this:
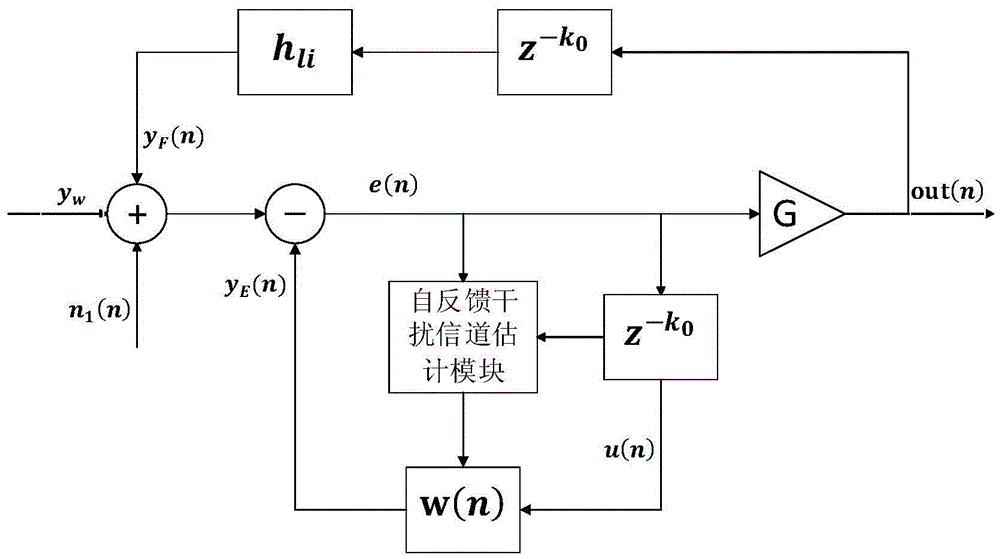
[0054] The signal y received by the full-duplex relay station w Perform amplification and forwarding, and use the least mean square algorithm LMS based on time-domain interference cancellation to cancel the interference;
[0055] The self-feedback channel is estimated by using the delayed samples of the transmitted signal and the transmitted signal; in the self-feedback interference cancellation module, w(n)=[w 0 (n),w 1 (n)...w L-1 (n)] T is the adaptive filter coefficient, where w k (n) is the kth element of the filter at the nth moment, and L is the order of the filter;
[0056] At the nth moment, the signal r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com