Method for judging convex figure shape similarity in digital image
A technology of geometric graphics and digital images, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve problems such as high computational complexity, reduced reliability of recognition, and limited application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] This embodiment illustrates the effectiveness of the GCT transformation on closed convex shapes.
[0078] Include the following steps:
[0079] S1, yes figure 2 The closed convex shape shown in the GCT transformation
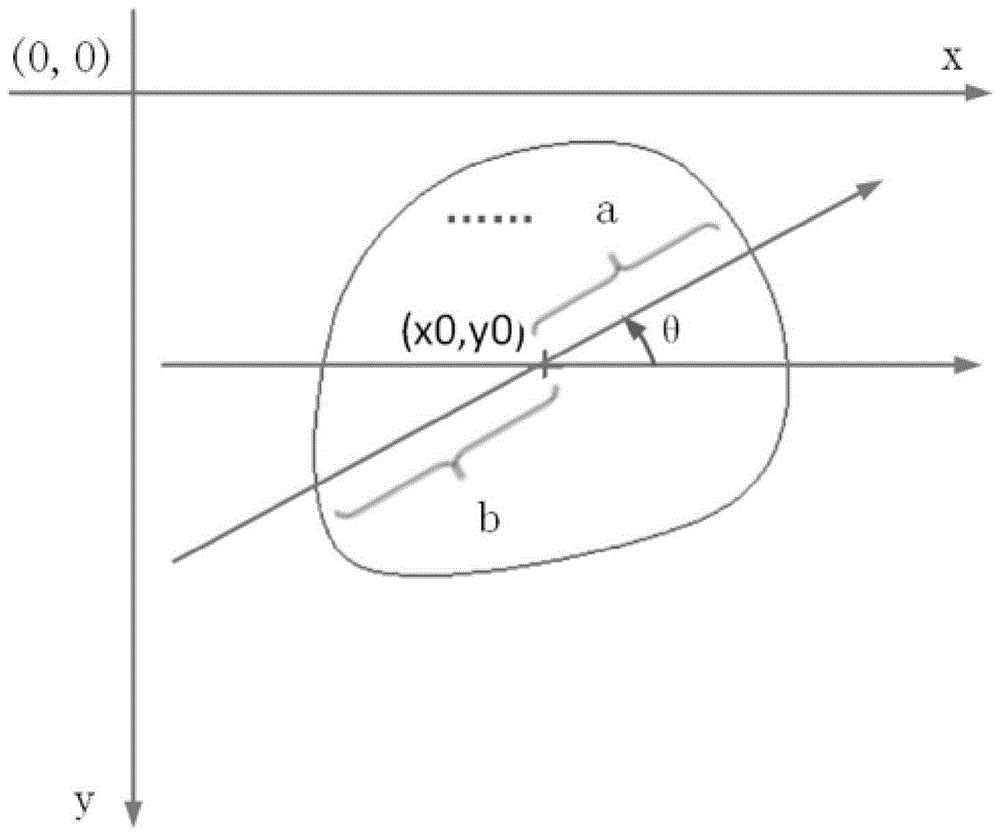
[0080] (1) adopt the form of digital image to preserve the convex geometric figure shape, suppose the coordinates of the boundary point of the convex geometric figure shape in the digital image to be (x 1 ,y 1 ), (x 2 ,y 2 ), (x 3 ,y 3 ),..., (x n ,y n ); Find the coordinates of the center point of the convex geometric figure (x 0 ,y 0 );
[0081] x 0 ,y 0 Calculated using the following formula:
[0082] x 0 = 1 n Σ i = 1 i = n x i , y 0 =...
Embodiment 2
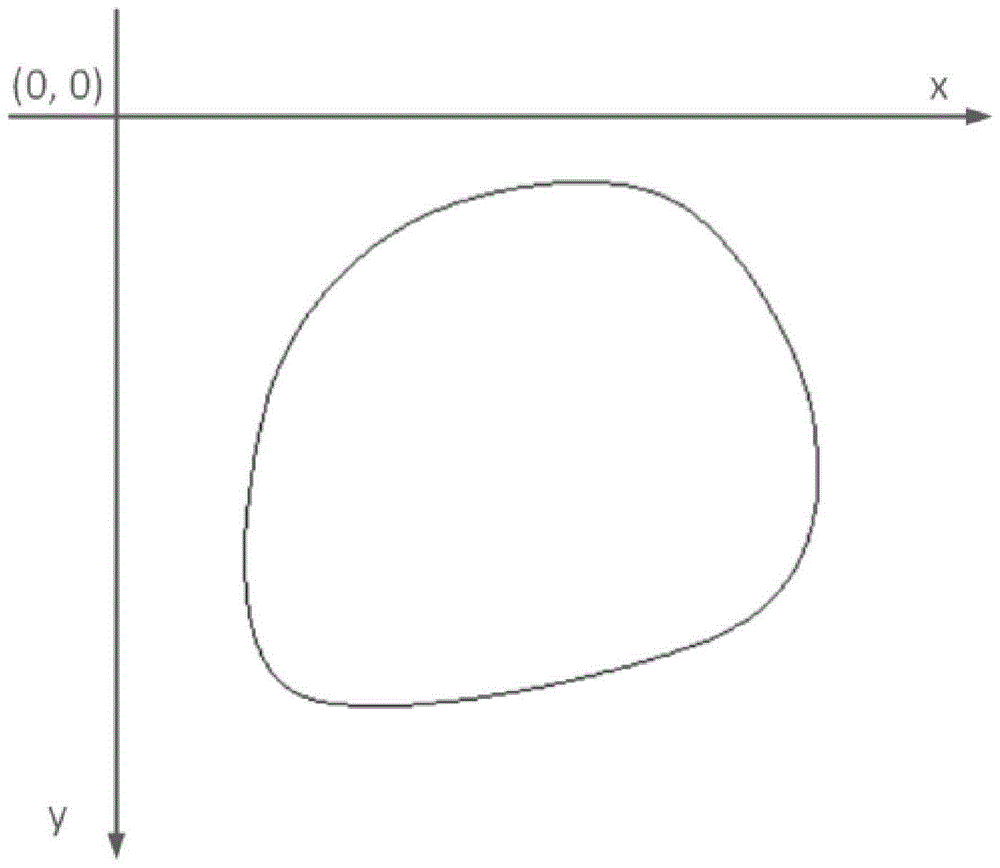
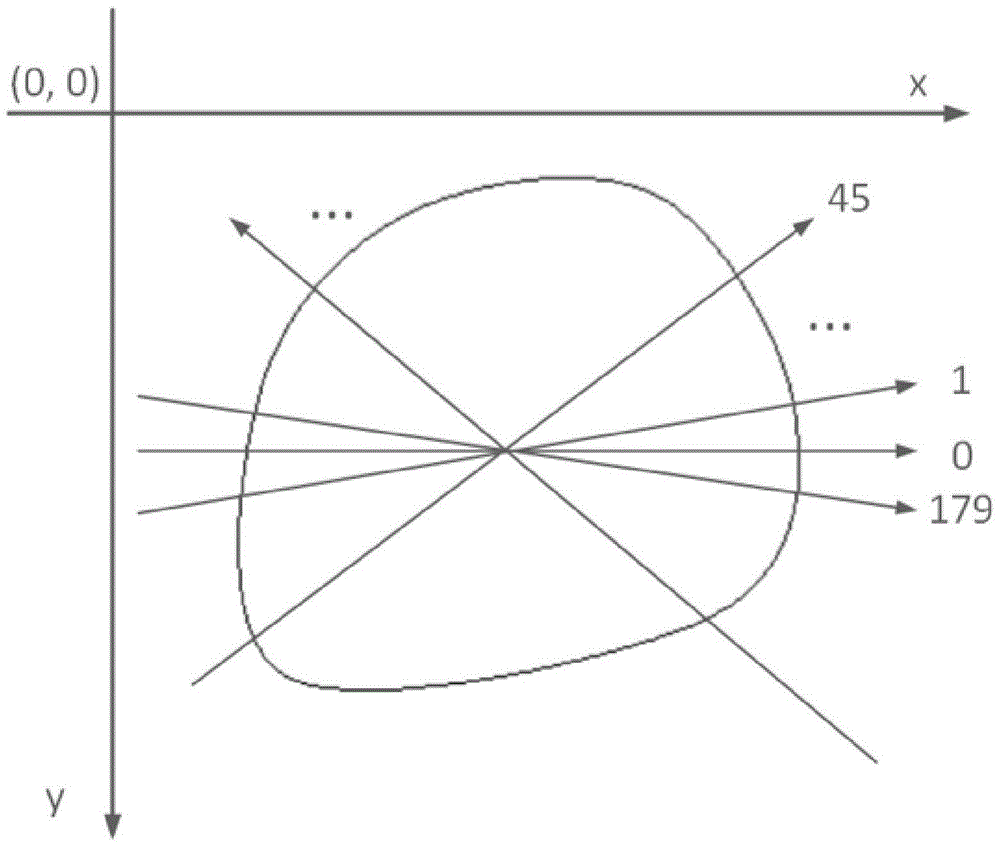
[0088] This embodiment illustrates the effectiveness of GCT transformation for non-closed convex shapes.
[0089] The basic steps are as in Example 1. This example differs from Example 1 in that the convex geometry of this example is non-closed, so each ray is obtained at the center point (x 0 ,y 0 ) is the ray direction of the starting point and the coordinates of the intersection with the convex geometric figure on the opposite direction. In this step, since the ray may not have an intersection with the non-closed convex geometric figure, in this case, change the intersection point to find The closest to the ray, and the center point (x 0 ,y 0 ) is the coordinates of the nearest discrete point of the convex geometric shape.
[0090] For any non-closed convex shape, such as Figure 4 As shown, it is a typical non-closed convex shape. Here, k is taken as 180, and the non-closed convex geometric shape starts from the ray parallel to the x-axis, passes through its center p...
Embodiment 3
[0093] This example illustrates that for any two similar closed convex geometric figures Ω 1 , Ω 2 , it can be judged that they are similar by this method. Two similar closed convex geometric figures have the shape of Image 6 shown.
[0094] Include the following steps:
[0095] S1, with reference to Embodiment 1, use GCT transformation (take the k value as 360 here) to generate Ω respectively 1 , Ω 2 The complex plane eigenvector F of 1 , F 2 ;
[0096] S2, respectively calculate their complex plane eigenvectors F 1 , F 2 The intensity sequence M 1 , M 2 and phase sequence S 1 , S 2 , using the following formula to calculate:
[0097] M 1 = ( a 1 , 1 2 + b ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com