A method and system for calculating the pose of a mobile robot based on lidar data
A mobile robot and laser radar technology, applied in control/regulation systems, two-dimensional position/channel control, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as integral error, accuracy impact, and large integral error, and achieve cost reduction and ease of implementation , the effect of improving reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
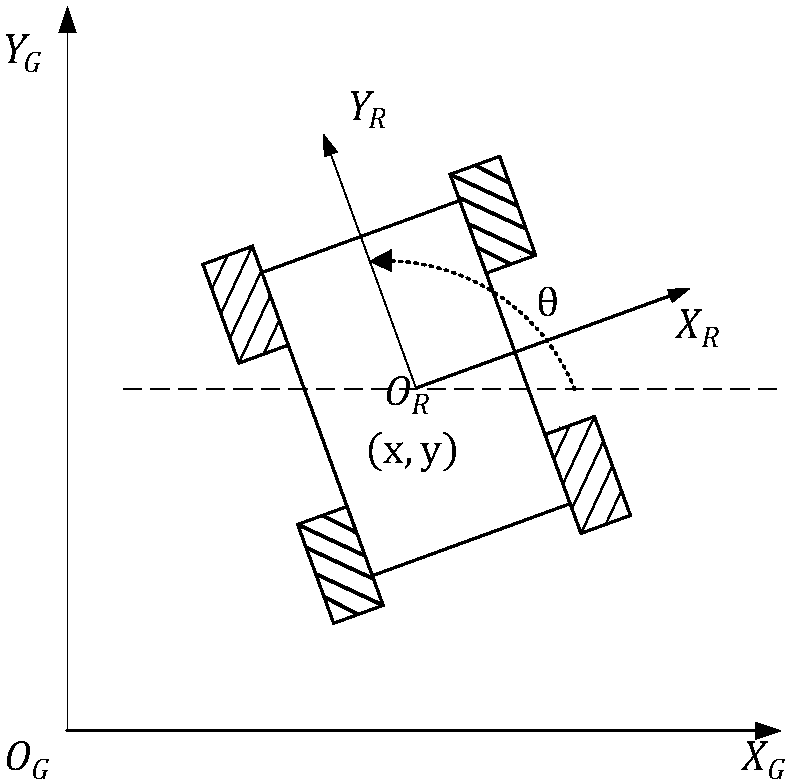
[0091] As shown in the figure, a method for calculating the pose of a mobile robot based on lidar data provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0092] Step1: Receive and preprocess lidar data;
[0093] Step2: Segment and cluster environmental data;
[0094] Step3: Select clusters from lidar data;
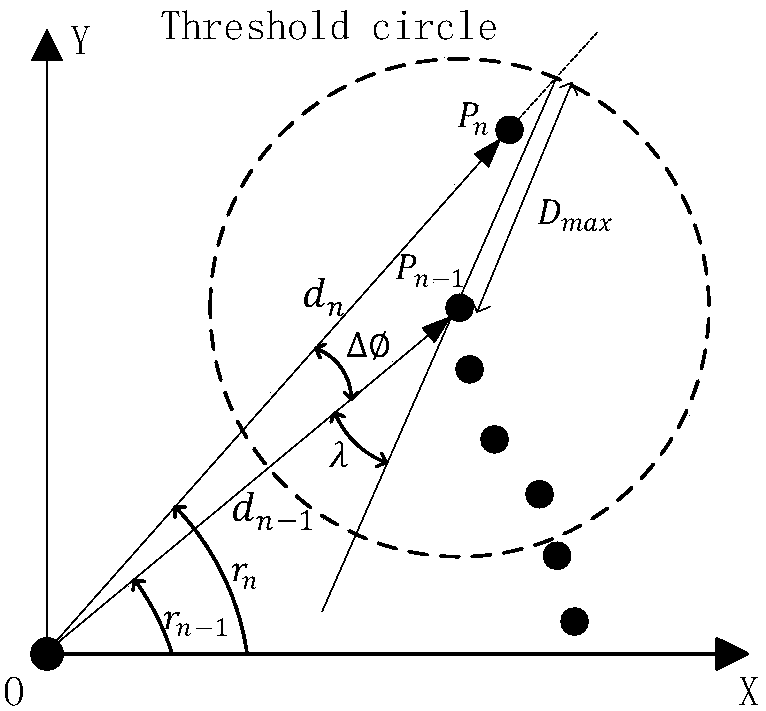
[0095] Step4: Tracking of the target cluster; obtain the coordinate data of the vertices of each sub-cluster in the cluster in the local coordinate system, obtain the coordinates of the vertices of the cluster and the inclination angle of each connecting line;
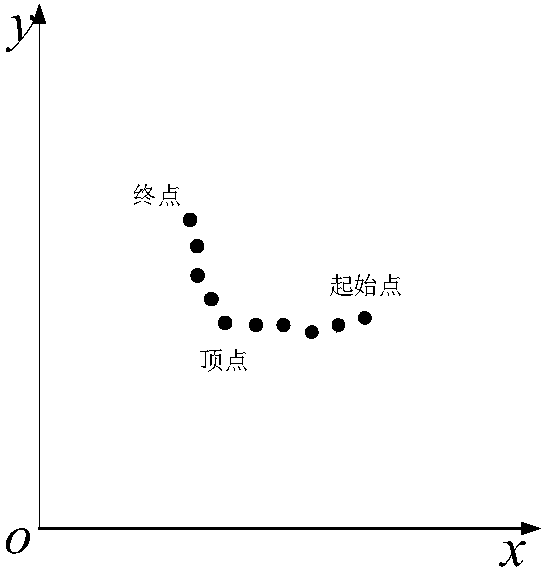
[0096] Step5: Form the starting point and the end point into a connecting line and calculate the deflection angle of the connecting line in the cluster;
[0097] Step6: Calculate the position coordinates of the robot after the position coordinates change through sliding filtering;
[0098] Step7: Initialize the pose of the starting point and store the position coordinates.
[0099] The specific steps o...
Embodiment 2
[0159] The method for estimating the pose of a mobile robot based on laser radar data provided in this embodiment, firstly, receives and preprocesses the laser radar data, as follows:
[0160] Connect the two-dimensional scanning laser radar sensor with the computer to obtain the environmental data, and store them in the computer in the form of an array. The environmental data is mainly represented by the distance information D={d 1 , d 2 , d 3 ,...,d i ,...,d N}. The distance data is then preprocessed, including removing data points outside the effective range, filtering out isolated noise points, and compensating for defects in the lidar measurement mechanism. In addition, the environmental data is converted from the data in the polar coordinate system of the lidar to the local rectangular coordinate system coordinates of the robot or intelligent vehicle, that is, the data set is expressed as: bg={P 1 ,P 2 ,P 3 ,...,P i ,...P N}, where P i Expressed as the informat...
Embodiment 3
[0209] This embodiment describes in detail the implementation of the mobile robot pose estimation method based on lidar data, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0210] Step1: Lidar data reception and preprocessing
[0211] Connect the two-dimensional scanning laser radar sensor with the computer to obtain the environmental data, and store them in the computer in the form of an array. The environmental data is mainly represented by the distance information D={d 1 , d 2 , d 3 ,...,d i ,...,d N}, N usually takes a value of 500, corresponding to the scanning range of the lidar 180°, and the angular resolution ξ=0.36°. The distance data is then preprocessed, including removing data points outside the effective range, filtering out isolated noise points, and compensating for defects in the lidar measurement mechanism. In addition, the environmental data is converted from the data in the polar coordinate system of the lidar to the local rectangular coordinate sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com