Method of estimating water use efficiency of temperate forest
A utilization and forest technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high-time acquisition, limited application, difficult and large scope, etc., to achieve the effect of improving usability and improving estimation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
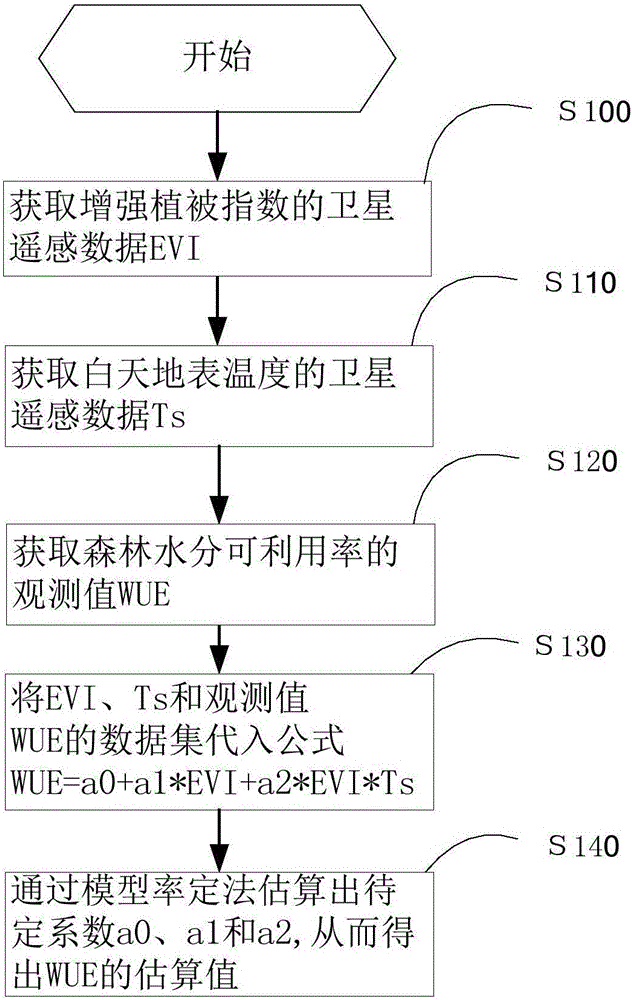
[0043] Such as figure 1 Shown, the method for estimating temperate forest moisture availability of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0044] S100: Obtain satellite remote sensing data EVI of Enhanced Vegetation Index from several flux stations respectively;
[0045] S110: Obtain satellite remote sensing data Ts of daytime surface temperature from several flux stations;
[0046] S120: Obtain the daily fluxes GPP and LE from several flux sites, and convert LE into ET, where GPP is the total productivity of the ecosystem, LE is the latent heat flux, and ET is the evapotranspiration, calculated by WUE=GPP / ET Get the observed value of WUE;
[0047] S130: Substituting the data set of Ts in step S100, EVI in S110 and WUE in S120 into the model calculation formula of water availability in temperate zone forest as follows:
[0048] WUE=a 0 +a 1 EVI+a 2 EVI·T s ,
[0049] In the formula, WUE is the water availability rate of the temperate forest, a 0 、a 1 and a 2 i...
Embodiment 2
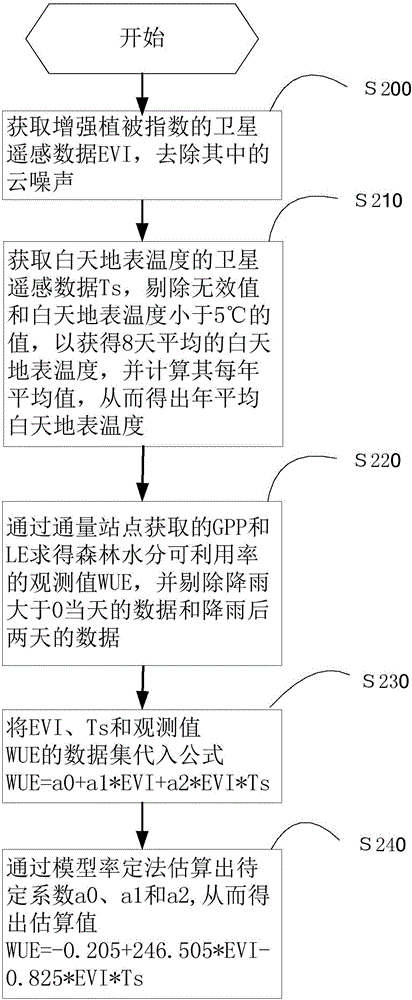
[0053] Such as figure 2 Shown, the method for estimating temperate forest moisture availability of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0054] S200: Obtain satellite remote sensing data EVI of Enhanced Vegetation Index from several flux stations, and remove the cloud noise in it through a preprocessing algorithm to obtain EVI time series data that meets the standard every 16 days; the preferred preprocessing algorithm is Savitzky– Golay filtering;
[0055] S210: Obtain the satellite remote sensing data Ts of the daytime surface temperature from several flux stations, and obtain the 8-day average daytime surface temperature through a preprocessing algorithm, and calculate its annual average, so as to obtain the annual average daytime surface temperature; preferred The preprocessing algorithm is to eliminate invalid values and values whose daytime surface temperature is less than 5°C, invalid values such as blank or 0 values;
[0056] S220: Obtain the daily flu...
Embodiment 3
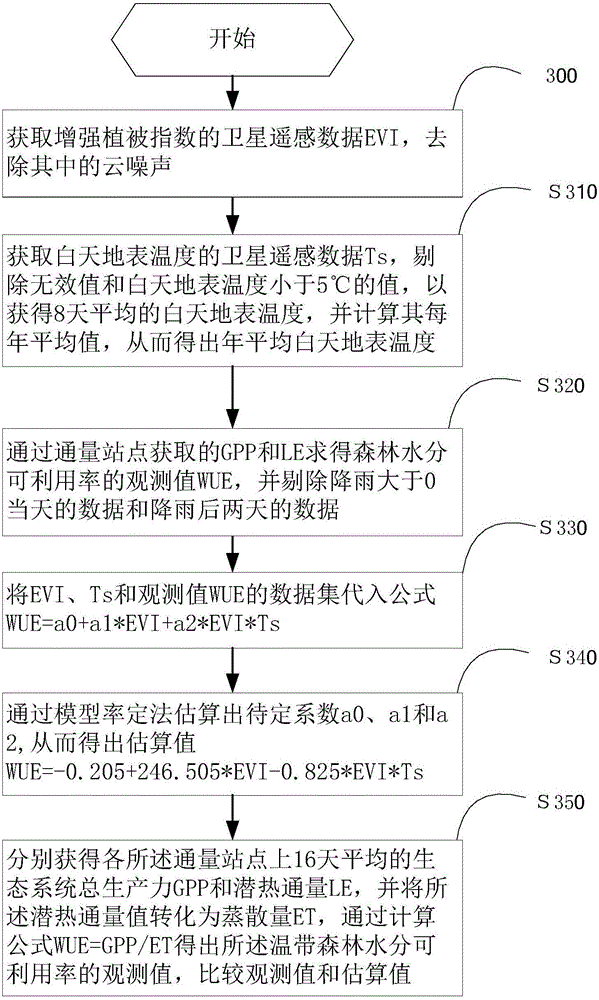
[0063] Such as image 3 Shown, the method for estimating temperate forest moisture availability of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0064] S300: Obtain satellite remote sensing data EVI of Enhanced Vegetation Index from several flux stations, and remove the cloud noise in it through a preprocessing algorithm to obtain EVI time series data that meets the standard every 16 days; the preferred preprocessing algorithm is Savitzky– Golay filtering;
[0065] S310: Obtain the satellite remote sensing data Ts of the daytime surface temperature from several flux stations, and obtain the 8-day average daytime surface temperature through a preprocessing algorithm, and calculate its annual average, so as to obtain the annual average daytime surface temperature; preferred The preprocessing algorithm is to eliminate invalid values and values whose daytime surface temperature is less than 5°C, invalid values such as blank or 0 values;
[0066] S320: Obtain the daily flux...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com