MMC-based low-voltage ride through control method and system of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
A low-voltage ride-through and control method technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, AC network circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as capacitor voltage fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
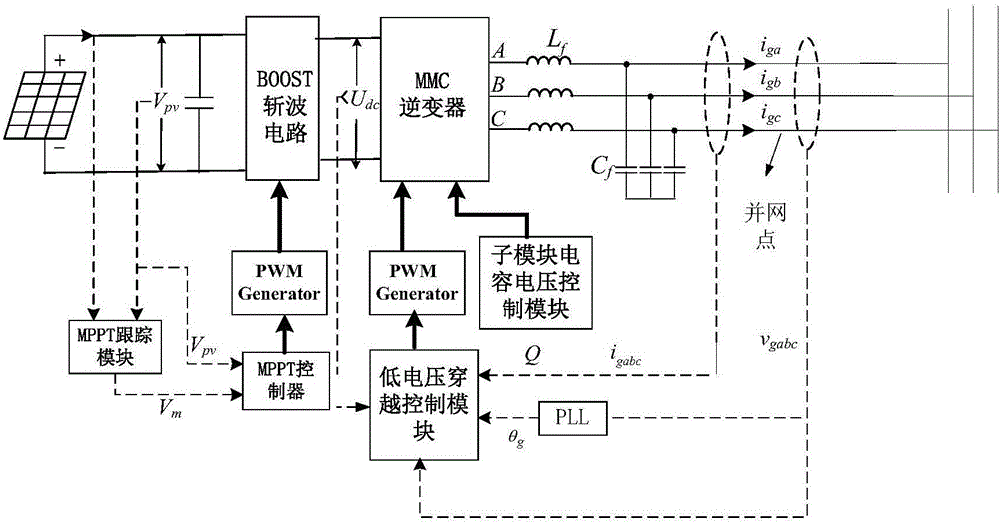
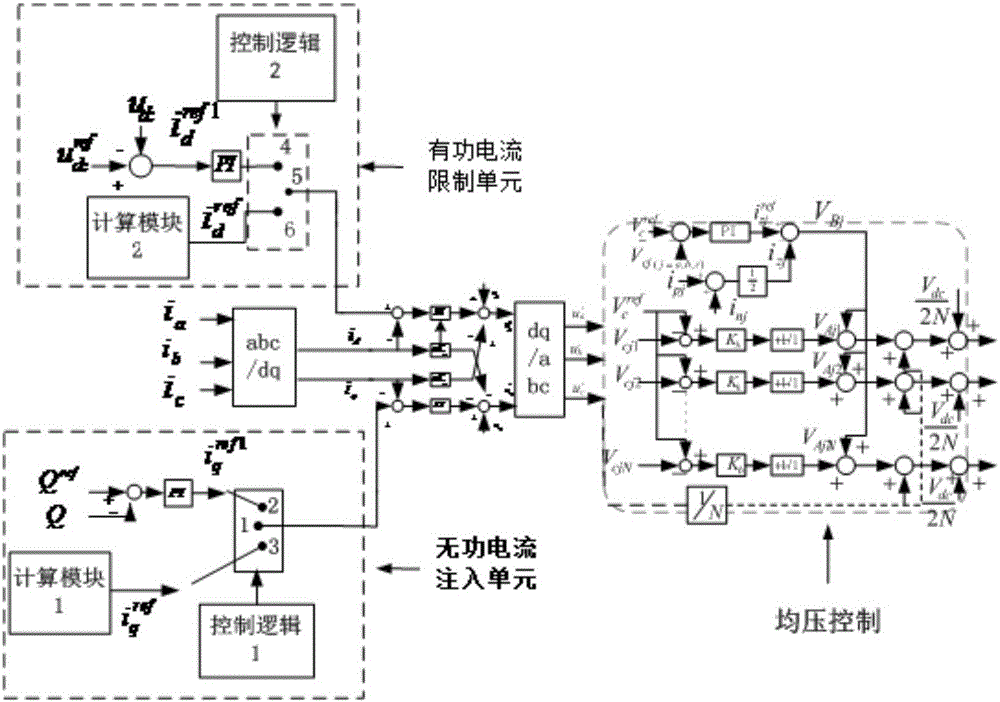
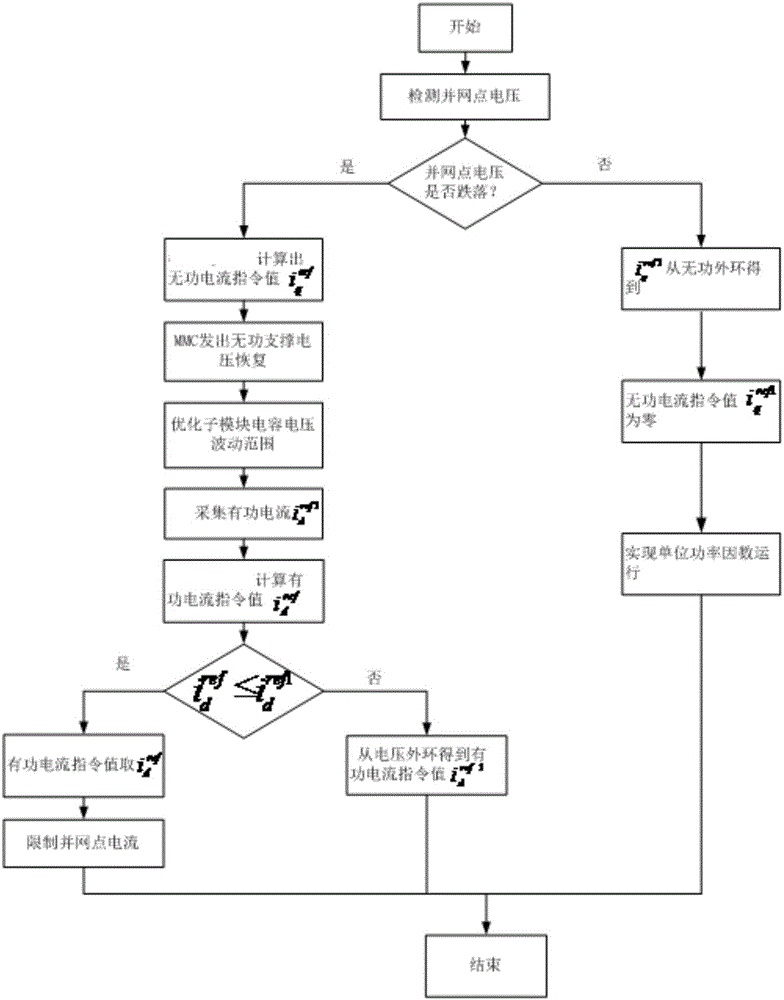
[0049] The present invention provides a low-voltage ride-through control method and system for a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. On the basis of the traditional double-closed-loop vector control of the current inner loop voltage outer loop, when the voltage drop at the grid-connected point is detected, the reactive power The combination of current injection, control of sub-module capacitor voltage fluctuation range and limitation of active current realizes low-voltage ride-through and ensures safe grid-connected operation of photovoltaics. The specific implementation is as follows:
[0050] When the grid-connected point voltage drop is detected, the reactive current command value is redistributed to achieve reactive current injection; by adding a new active current command value To redistribute the command value of the active current value to limit the active current; and adjust the fluctuation range of the capacitor voltage of the MMC sub-module by optimizing the bri...
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1, the method for optimizing bridge arm current:
[0059] In the power grid, there are three phases A, B, and C. Taking phase A as a representative, the corresponding formulas and corresponding values of phase B and C can be obtained in the same way; the capacitor voltage of the MMC sub-module is:
[0060]
[0061]
[0062] In the formula, U cpa In order to optimize the capacitor voltage of the sub-module on the front A phase, U cna In order to optimize the capacitor voltage of the sub-module in the front A phase, U dc is the DC side voltage, P dc is the DC side power, K is the voltage modulation coefficient, is the power factor.
[0063] From the analysis of the above formula, it can be seen that under the condition of keeping the transmission power constant, the capacitance value of the sub-module and the DC voltage constant, the fluctuation of the capacitor voltage of the sub-module is mainly affected by the power factor The smaller the powe...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Embodiment 2, the method of controlling the reference voltage of the sub-module:
[0074] When the number of sub-modules of the MMC reaches a certain number, there is the following formula for the fluctuation of the sub-module capacitor voltage:
[0075] Δu s m c _ p a ≈ ∫ P p a d t NCU c r e f
[0076] In the formula, N represents the number of sub-modules of the upper bridge arm, and U cref Indicates the sub-module reference voltage, C is the capacitance, Δu smc_pa Indicates the voltage fluctuatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com