Composite absorbent paper
A technology of absorbent paper and absorbent layer, used in absorbent pads, medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of difficult diffusion, affect the secondary absorption speed, and reduce the dryness of the surface layer, so as to improve the dryness of penetration and good liquid permeability. , the effect of improving utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
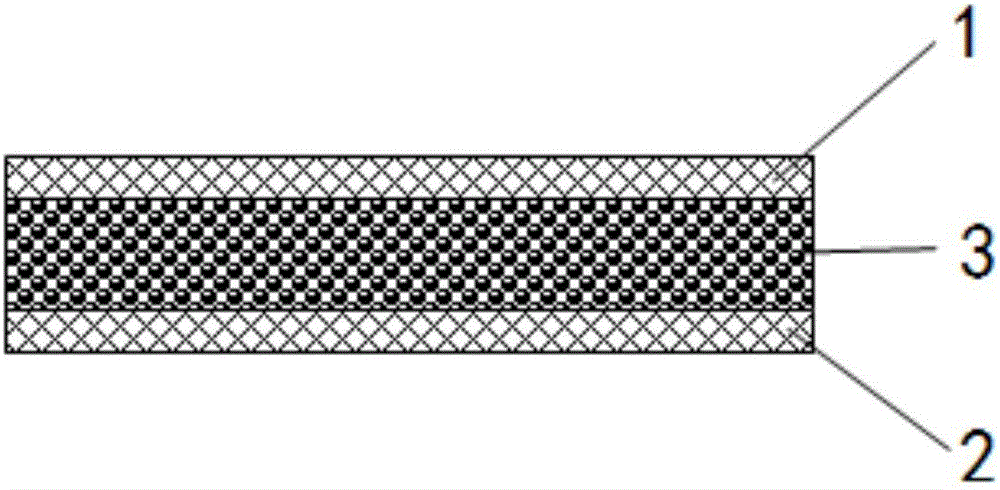
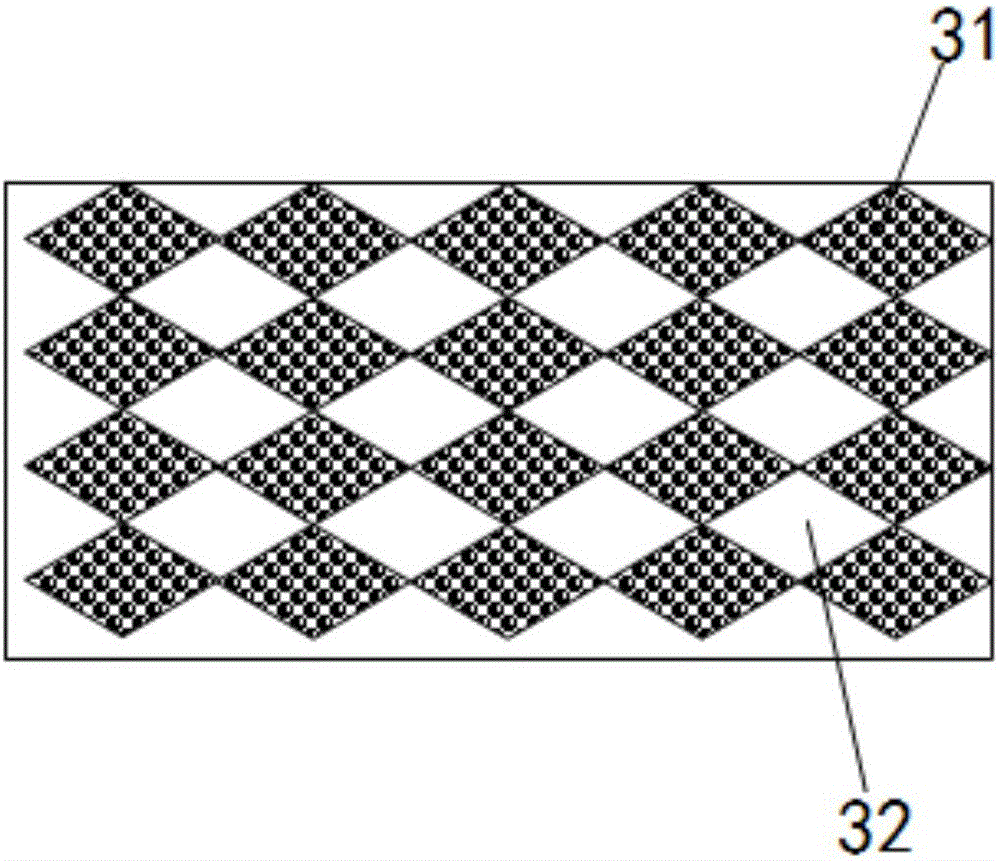
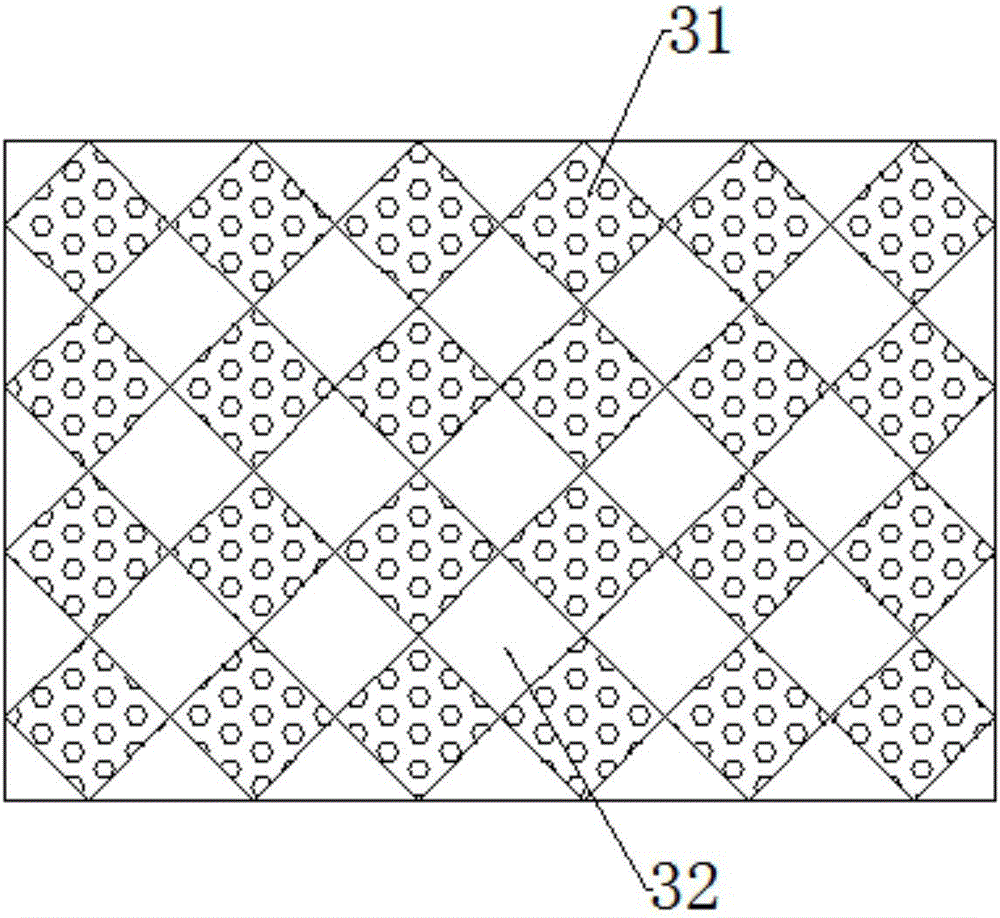
[0031] A composite absorbent paper, comprising an upper isolation layer 1 and a lower isolation layer 2; a water absorption layer 3 is arranged between the upper isolation layer 1 and the lower isolation layer 2; the layers are glued or thermally bonded together; the The water-absorbing layer 3 includes several SAP-absorbing units 31 and gap units 32 arranged at intervals.
[0032] The outer periphery of the SAP absorption unit 31 is a gap unit 32 .
[0033] The contact between the two adjacent SAP absorption units 31 on the same cross-section of the water-absorbing layer 3 is point contact; the contact between the two adjacent gap units 32 on the same cross-section of the water-absorbing layer 3 is point contact .
[0034] The inner edges of the three layers of the water-absorbing layer are gap units 32 .
[0035] The distribution quantity of the SAP absorption units 31 and the gap units 32 in the water absorption layer 3 along the length direction is greater than their dis...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The basic structure of the embodiment 2 is the same as that of the embodiment 1. The difference between the embodiment 2 and the embodiment 1 is that the cross-sectional shape of the SAP absorption unit 31 is a square, and the upper isolation The material of layer 1 is wet-strength paper, and the material of the lower isolation layer 2 is non-woven fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The basic structure of the embodiment 3 is the same as that of the embodiment 1. The difference between the embodiment 3 and the embodiment 1 is that the cross-sectional shape of the SAP absorption unit 31 is circular, and the upper The material of the isolation layer 1 is toilet paper, and the material of the lower isolation layer 2 is non-woven fabric.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap