Process for producing water-absorbing resin
A manufacturing method and a water-absorbing technology, which are applied in the field of absorbers and absorbent articles, can solve the problems of large water-absorbent resins, difficult to manufacture particle size, difficult to obtain appropriate particle size suitable for sanitary materials, etc., and achieve excellent liquid permeability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
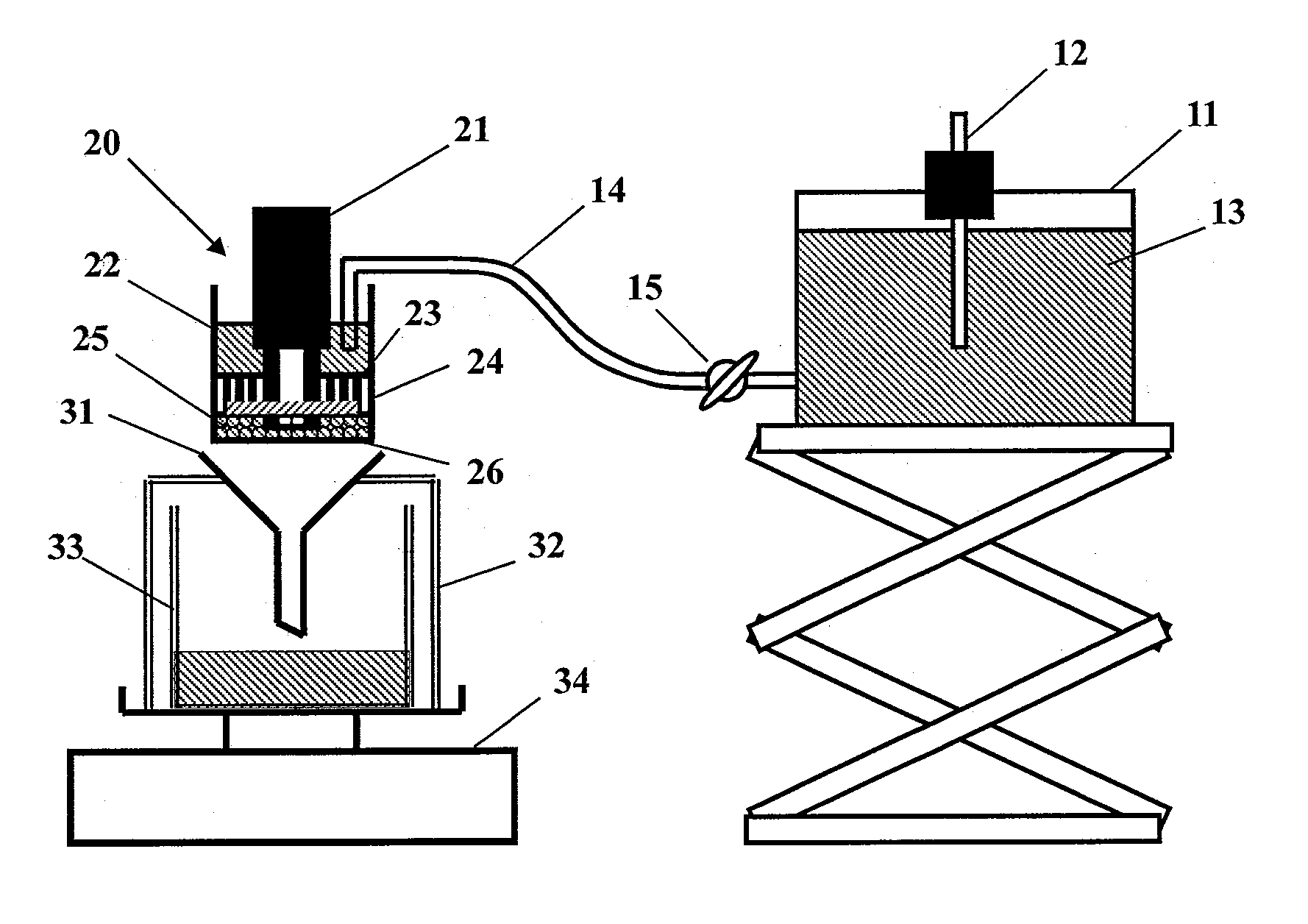
[0108] A round-bottomed cylindrical separable flask with a volume of 2 L equipped with a stirrer, dual paddle impellers, a reflux cooler, a dropping funnel, and a nitrogen inlet tube was prepared. 340 g of n-heptane was taken into the flask, and 0.92 g of sucrose stearate (Mitsubishi-Kagaku Foods Corporation, Ryoto Sugar Ester S-370) and maleic anhydride-modified ethylene / propylene copolymer (Mitsui Chemical Co., Ltd., Hivacs 1105A) 0.92 g, heated up to 80°C while stirring, and cooled to 50°C after dissolving the surfactant.
[0109] On the other hand, 92 g (1.02 moles) of an 80 mass % acrylic acid aqueous solution was taken into a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and while cooling from the outside, 146.0 g of a 21 mass % sodium hydroxide aqueous solution was added dropwise to neutralize 75 mol %. , add 0.11g (0.41 mmol) of potassium persulfate as a radical polymerization initiator, 1.6 mg of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (0.09×10 -1 Millimoles, 0.9×10 relative to 100 moles of mon...
Embodiment 2
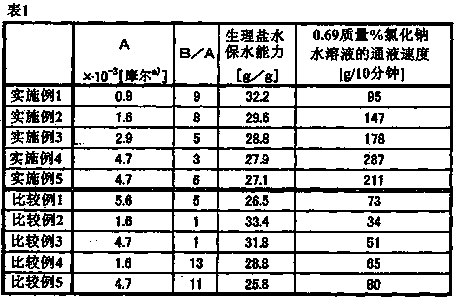
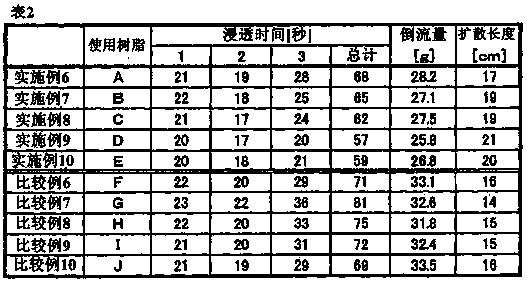
[0115] Change the addition amount of the first stage of the internal crosslinking agent in Example 1 to 2.8mg (0.16×10 -1 Millimoles, relative to 100 moles of monomers in the first stage is 1.6×10 -3 mol), and change the addition amount of the second stage to 0.03g (1.72×10 -1 Millimoles, relative to 100 moles of monomers in the second stage is 12.0×10 -3 mol), except that, the same operation as in Example 1 was carried out to obtain 230.1 g of a water-absorbent resin (B). The water-absorbent resin had a median particle size of 370 μm and a moisture content of 7.6%. Table 1 shows the measurement results of each property.
Embodiment 3
[0117] Change the internal crosslinking agent in Example 1 to N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide, and change the addition amount of the first stage to 4.6mg (0.30×10 -1 Millimoles, relative to 100 moles of monomers in the first stage is 2.9×10 -3 mol), and change the addition amount of the second stage to 0.03g (1.95×10 -1 Millimoles, relative to 100 moles of monomers in the second stage is 13.6×10 -3 mol), except that, the same operation as in Example 1 was carried out to obtain 229.5 g of a water-absorbent resin (C). The water-absorbent resin had a median particle size of 350 μm and a moisture content of 7.5%. Table 1 shows the measurement results of each property.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| relative humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| relative humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| relative humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com