Active and reactive current coordination control-based photovoltaic grid-connected inverter control method
A current coordination and control method technology, applied in the direction of reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, photovoltaic power generation, reactive power compensation, etc., can solve problems such as lack of compensation requirements, waste of photovoltaic power plants, backward construction of reactive power compensation devices, etc. Achieve the effect of improving transient stability and improving transient voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the preferred embodiments described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
[0042] Specifically, the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter control method based on active and reactive current coordinated control includes the following steps:
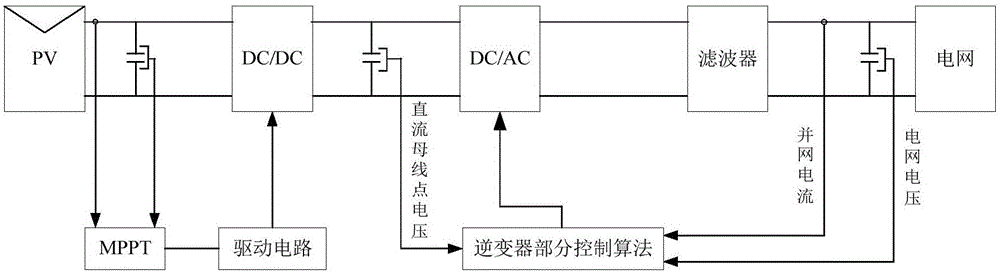
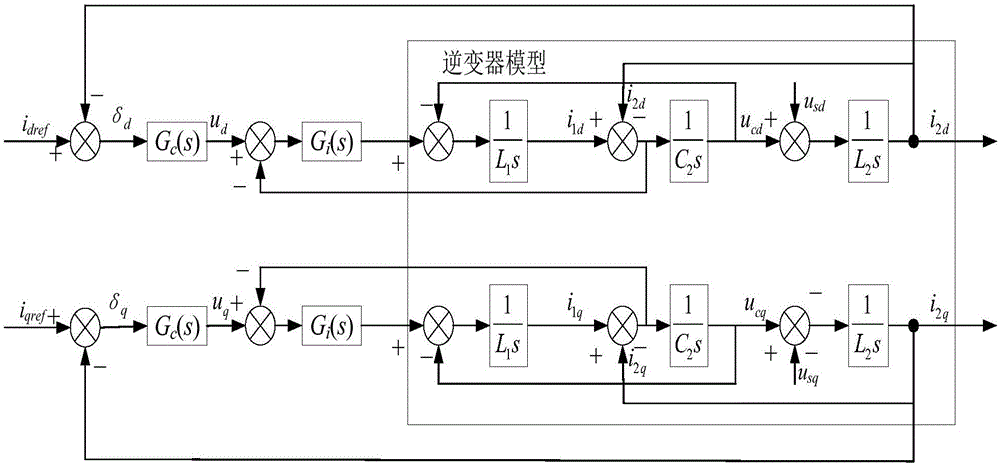
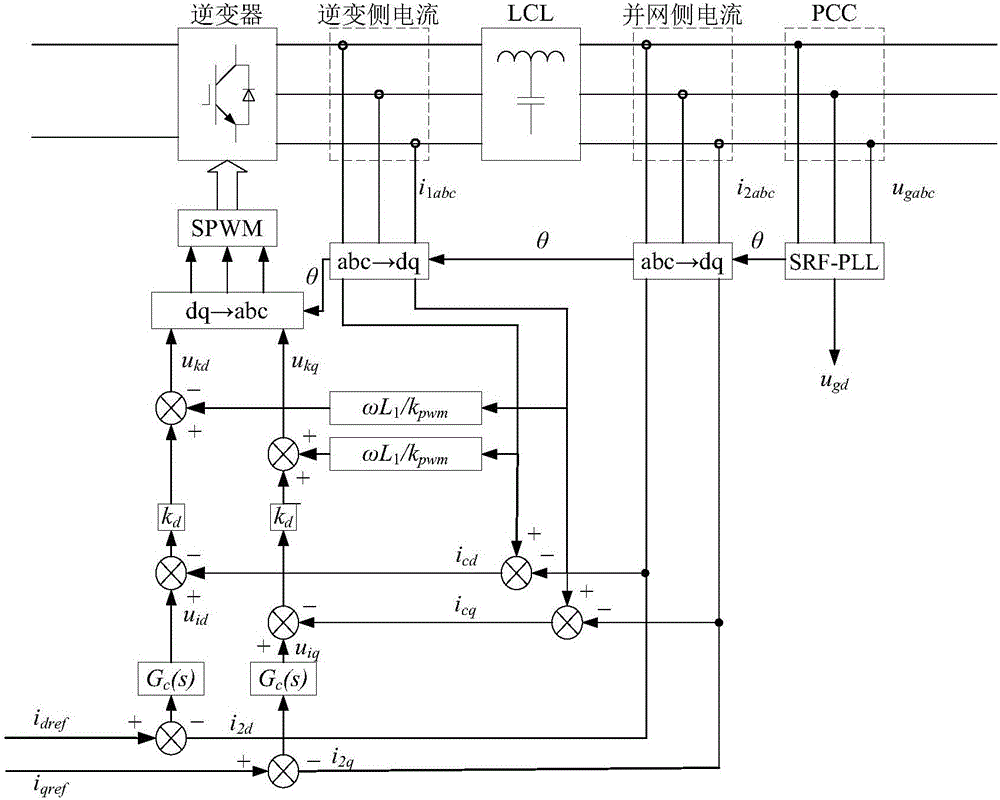
[0043] Step 1: Introduce a capacitive current control loop into a two-stage grid-connected inverter based on a grid voltage-oriented control strategy to form a dual current loop control;
[0044] Step 2: Control the normal operation condition and the transient operation condition respectively by giving the current reference value.
[0045] The two-stage grid-connected inverter uses the front-stage Boost circuit to realize the voltage control of the photovoltaic power station, and uses the rear-stage inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com