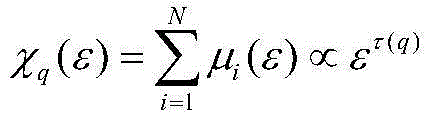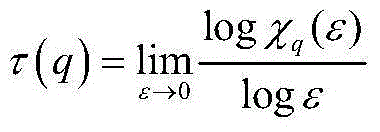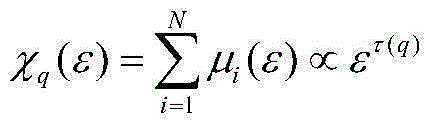Nonlinear method for describing urban surface landscape structure
A landscape structure, nonlinear technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as single fractal failure to reflect multi-scale characteristics of thermal fields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The specific content of the present invention is as follows:
[0034] A non-linear method for describing the structure of the urban landscape. First, the temperature difference in the measurement area is selected in the study of the thermal field pattern. Assuming that the image is M×N pixels, a set of square boxes with different scales are used to cover the entire image area ( Need (M / ε)×(N / ε)), calculate the temperature difference ΔT in each box ε =(T max -T min ) / ε, put ΔT ε Imagine the height of the image surface, and then use ΔT ε +1 box to cover, you can use μ(ε)=(ΔT ε +1) / Σ(ΔT ε +1) to obtain the area measure;
[0035] Take -10 q (ε), find the quality index τ(q) in the double logarithmic coordinate system;
[0036] Use the formula α(q)=(τ(q+1)-τ(q-1)) / 2 to calculate α(q);
[0037] Calculate f(α) using the formula f(α)=qα(q)-α(q).
[0038] The multifractal theory is briefly described as follows:
[0039] For continuous random spatially distributed variables with geometri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com