Autonomous navigation method for space multi-robots operating against targets in geostationary orbit
A technology of geostationary orbit and target operation, applied in the direction of integrated navigator, navigation calculation tool, etc., can solve the problem of low navigation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0078] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings;
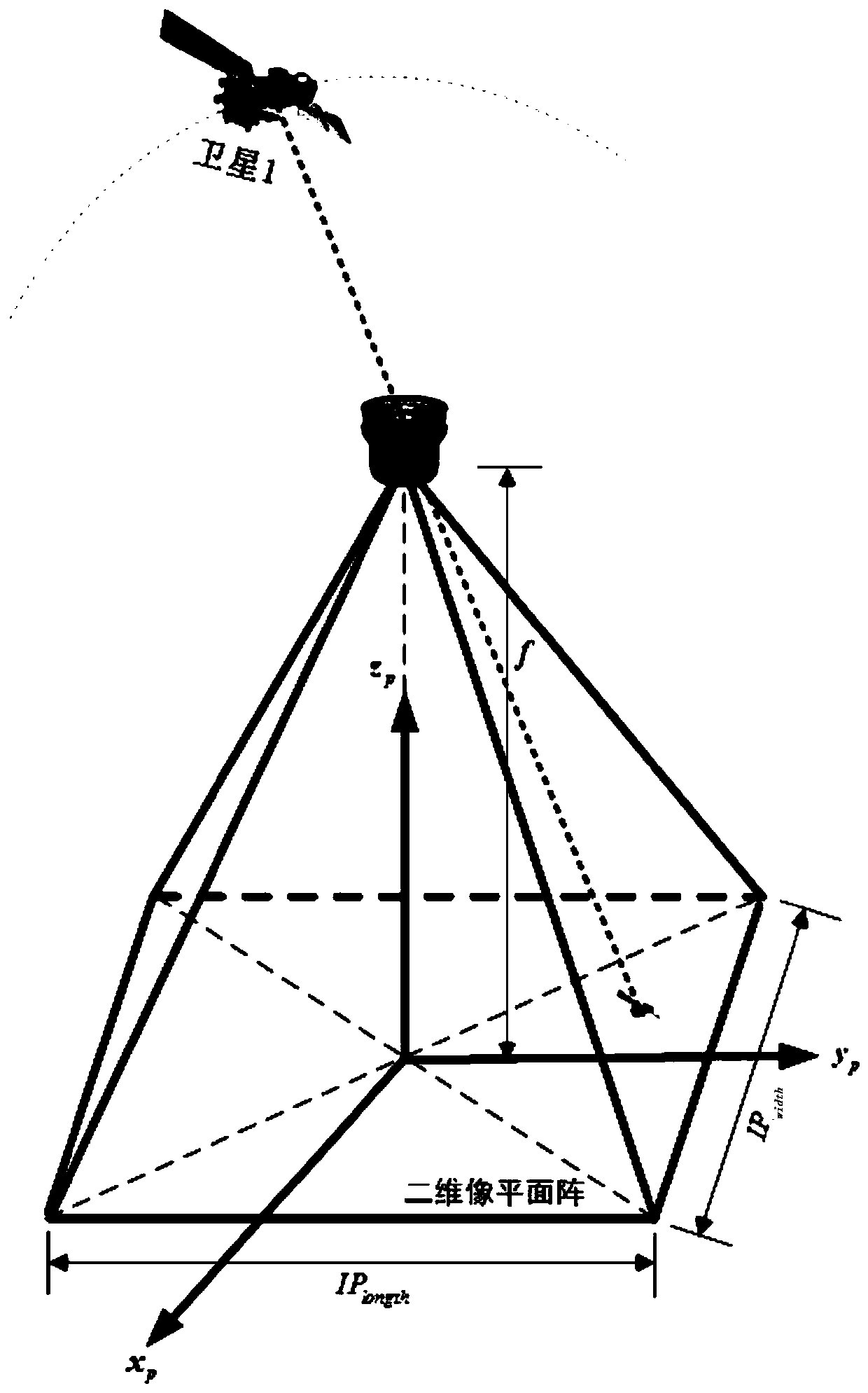
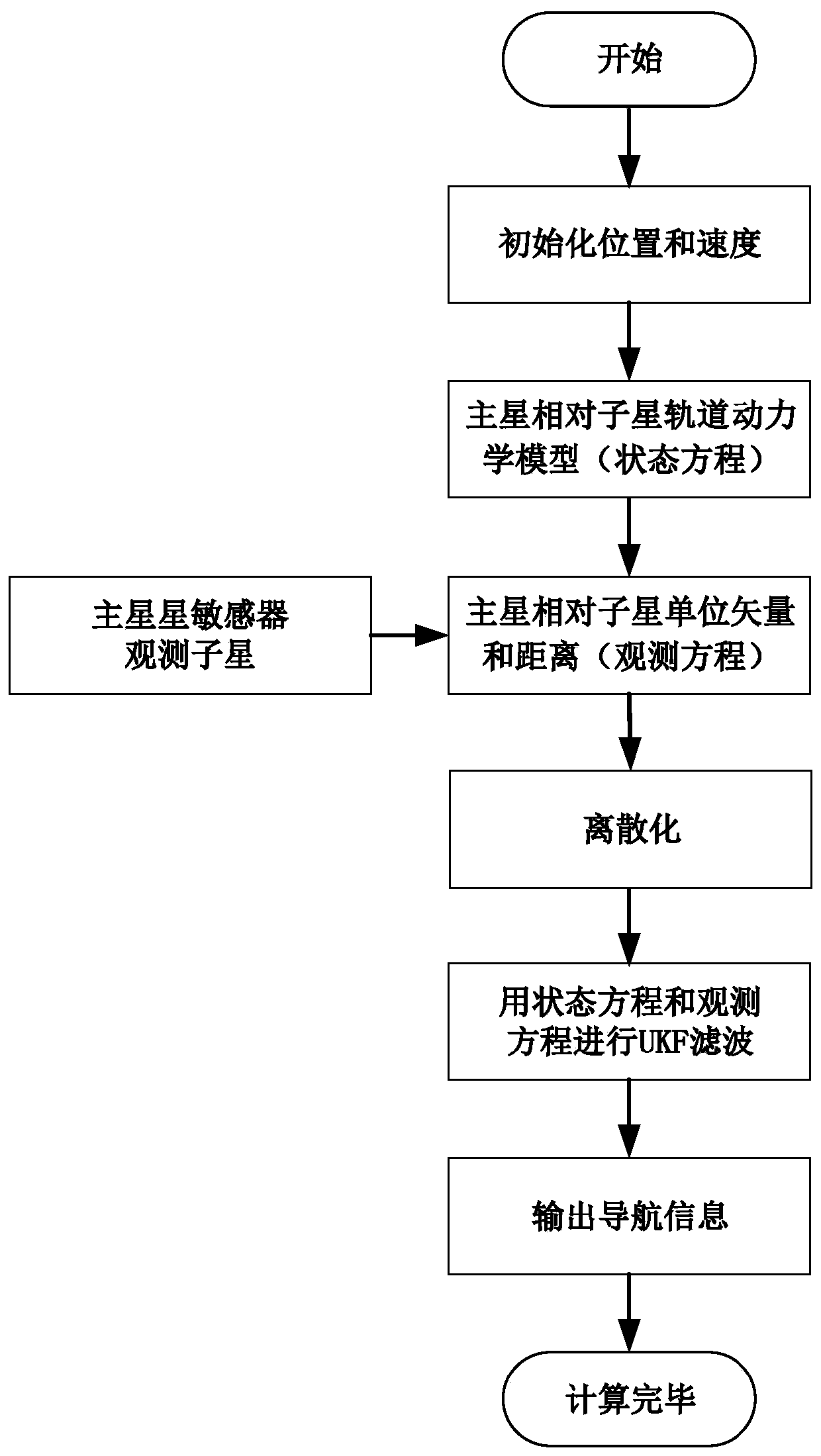
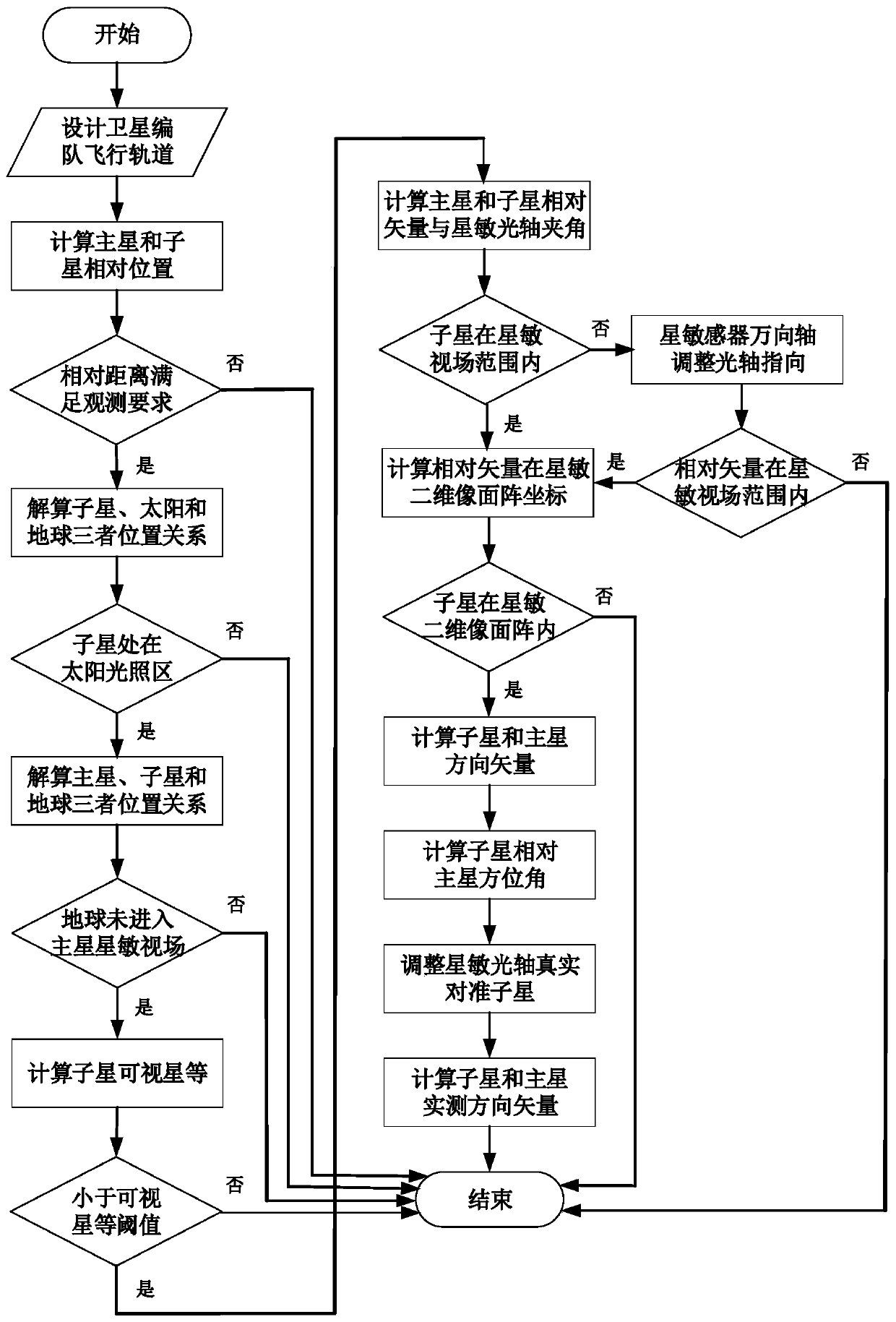
[0079] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention is a kind of space multi-robot relative observation method facing GEO satellite on-orbit service. In the stage of GEO satellite on-orbit service, space multi-robots (set as main star and sub-star) utilize star sensors to independently and continuously observe the relative direction The vector method is a space multi-robot relative observation method that is very suitable for on-orbit service. It includes the following steps:
[0080] (1) Design two space robots (set as main star and sub-star) formation flight configuration and orbital parameters (including orbital semi-major axis a, orbital eccentricity e, orbital inclination i, right ascension of ascending node Ω, argument of perigee ω, perigee time t p ), design the best installation orientation of the main star sensor to observe the sub-star; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com