Sleeve shaft type differential locking mechanism
A technology of locking mechanism and differential, which is applied in the direction of differential transmission, mechanical equipment, belt/chain/gear, etc. It can solve the problems of unfavorable drive axle layout and increase in drive axle volume, so as to avoid abnormal wear and tear, The effect of reducing the overall size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
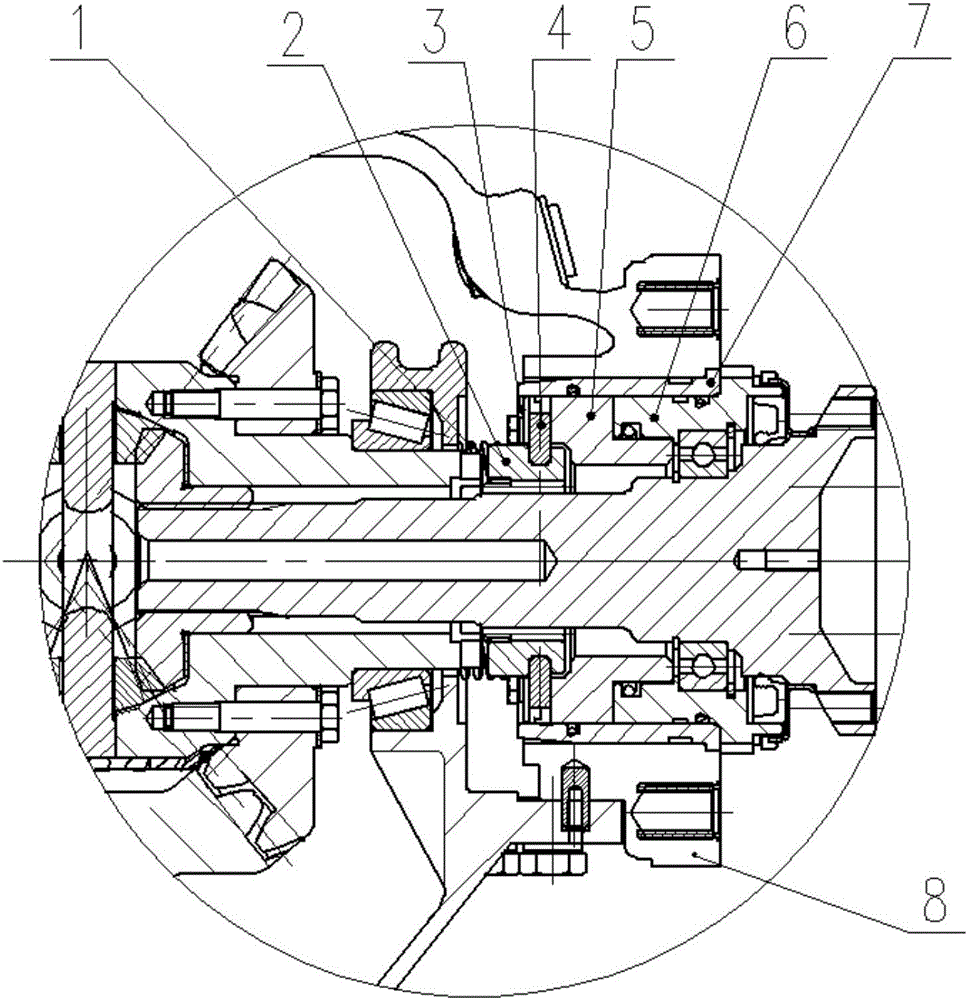
[0030] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, it is a sleeve-type differential locking mechanism provided by the present invention. The locking mechanism is arranged on the internal half shaft of the drive axle and connected with the differential case, and includes springs 1, 1, Crankshaft 2, crankshaft support 3 for fixing the crankshaft 2, slider 4, piston 5, bearing seat 6 and steel sleeve 7 located on the outside of the above-mentioned parts, the crankset 2 and the piston 5, the piston 5 and the bearing seat 6 all adopt a coaxial structure, the piston 5 and the steel sleeve 7 are radially positioned by positioning pins, the spring 1 is connected to the tooth plate support 3, and the tooth plate 2 is fixed on the tooth plate support 3, The end of the chain plate 2 away from the spring 1 is provided with a groove, the shape of the groove is adapted to the shape of the slider 4, and the piston 5 is composed of a stepped cylinder, and the axial direction is larger than the half axis. ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The present invention is realized in this way. When the differential gear is locked, the driver turns on the ventilation switch, and the gas with a certain pressure passes through the axle housing 8, the steel sleeve 7, and the bearing seat 6, and pushes the piston 5 to drive the tooth plate 2 and other compression springs. 1. Move towards the direction of the differential case, and the chain plate 2 is combined with the end face teeth on the differential case to realize the differential lock. When the differential lock is not needed, disconnect the air source, and the original compressed spring 1 Automatically return to the position under the action of elastic force, push the piston 5, chainring support 3, and chainring 2 to move away from the differential until the piston 5 is close to the end face of the bearing seat 6, and the teeth on the end face of the piston 5 are in contact with the end face of the differential case The teeth are separated. When the differential...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com