Energy efficient satellite maneuvering
A satellite and maneuvering technology, applied in the field of satellites, can solve the problems of requiring payload space and weight, increasing the sensitivity of inertia moment, gravity gradient moment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
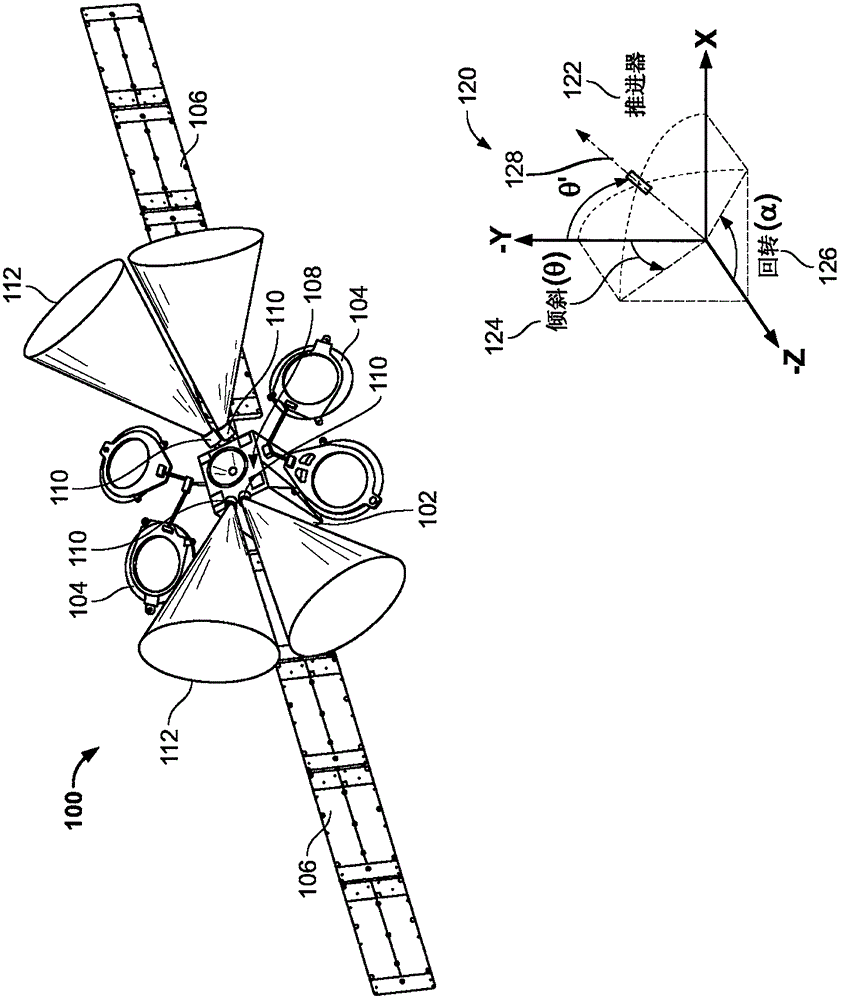
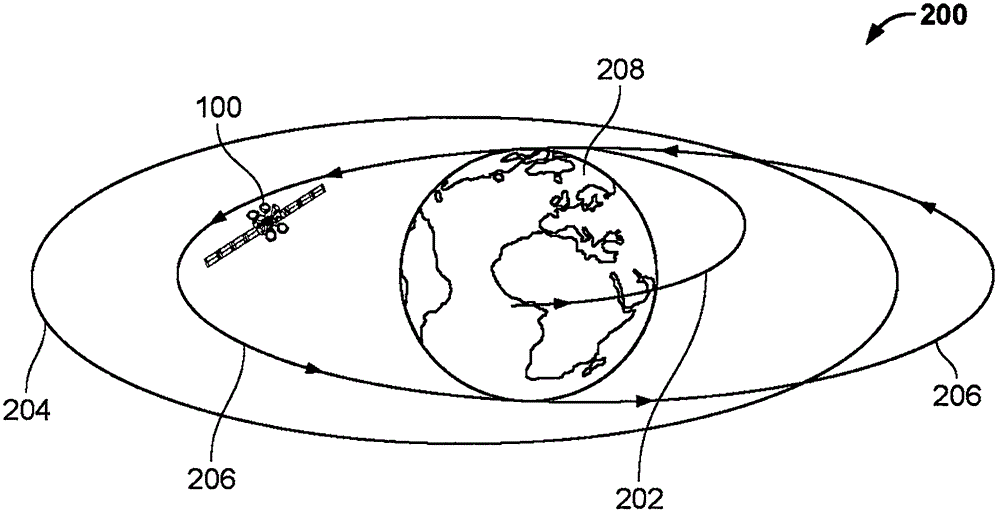
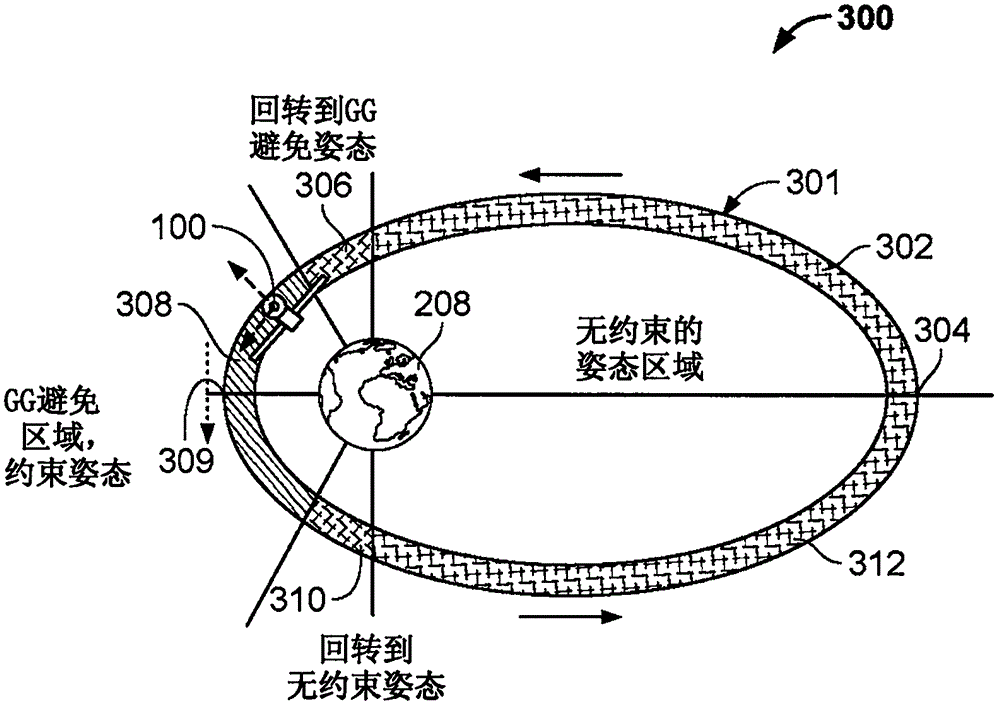
[0029] Energy efficient satellite maneuvers are disclosed herein. Typically, Earth-orbiting satellites or resident space objects (RSOs) may be positioned in a parking orbit or initial orbit ( such as the first track). The satellite can then perform the final maneuver to maintain the final orbit. For example, a satellite may start in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and maneuver through a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) to reach a final Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO). During such maneuvers, satellites may experience gravitational gradient moments and / or increased momentum buildup. Further, even in a given orbit (eg, final orbit), satellites may encounter gravitational gradient moments (eg, during perigee of the orbit) caused by the satellite's inertial properties.
[0030]During these maneuvers and / or orbit maintenance, the satellite's gravitational moment and / or momentum buildup may require significant use of thrusters or other momentum devices, and thus consume fuel / propulsion resour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com