Systems and methods to determine the age of cells
一种细胞、红血细胞的技术,应用在颗粒和沉降分析、仪器、分析材料等方向,能够解决未显示出红细胞寿命或平均年龄的确定等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
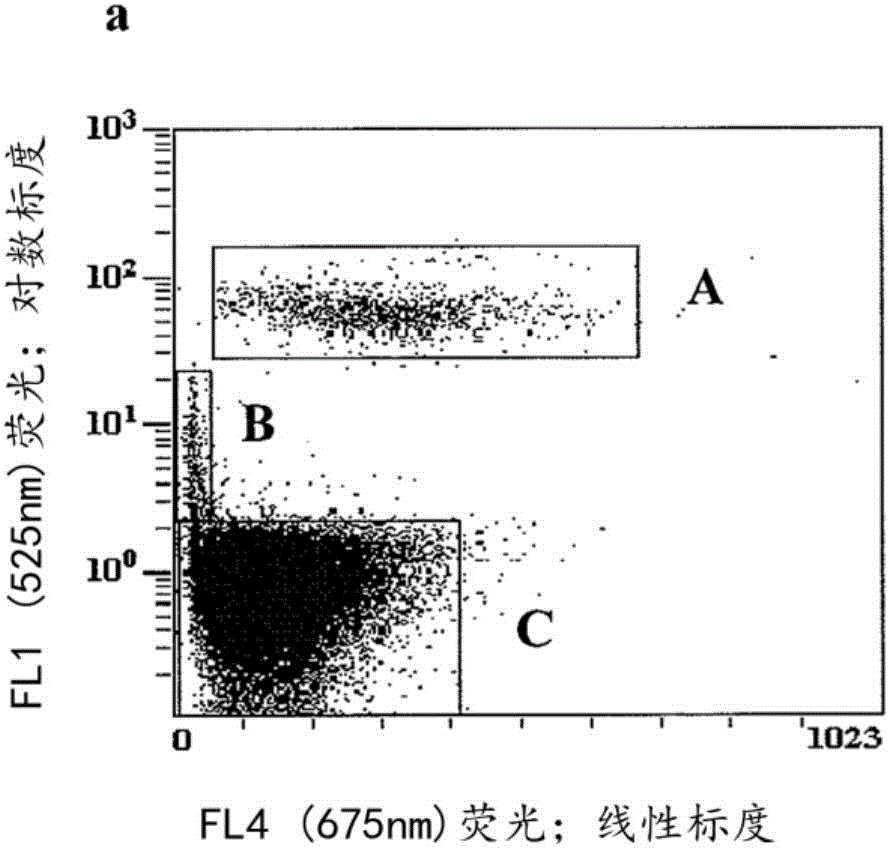
[0205] An assay is described that measures the cellular hemoglobin and HbA1c percentages of blood samples and fractionates the cells into reticulocytes and ten fractions of mature erythrocytes. Glucose and hemoglobin react irreversibly together to form HbA1c (Amadori product). This response is a continuous phenomenon as a function of time and glucose concentration. The formation of HbA1c is a controlling element of blood sugar balance in diabetic patients. Normal value of HbA1c: 5% of total hemoglobin.
[0206] Materials and Methods .
[0207] The following materials were used in this assay:
[0208] 1. Blood samples treated with 0.7 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as an anticoagulant and stored at 4°C for no more than ten days.
[0209] 2. Spheroidizing reagent: 0.137M sodium chloride, 0.005M HEPES, 0.0005M (D+) trehalose, 0.083M formaldehyde, 0.04mM n-dodecyl β-D-maltoside, 0.5ml / l Proclin-300, 0.5 mg / l acridine orange and a certain amount of sodium hydroxid...
example 2
[0224] Percentage HbA1c data from a reference laboratory using three different assays compared to a flow cytometry procedure Comparison of the correlation curves of HbA1c percentage data derived from the sequence .
[0225] Percent HbA1c was determined on 120 samples by reference laboratories using three different HbA1c assay methods; (Primus Ultra2: affinity chromatography, Roche Unimate: immunoturbidimetry, and Tosoh G7 variant: cation exchange chromatography). Flow cytometry percent HbAlc values were determined in the presence of reference control cells of known percent HbAlc. This document describes the conversion of arbitrary HbA1c percent units to percent HbA1c values.
[0226] Methods and Results
[0227] In the first case, we show that fluorescently labeled antibodies have free access to HbA1c molecules inside immobilized erythrocytes. Red blood cells are fixed with formaldehyde and lysed in water and further disintegrated in the presence of detergent. The l...
example 3
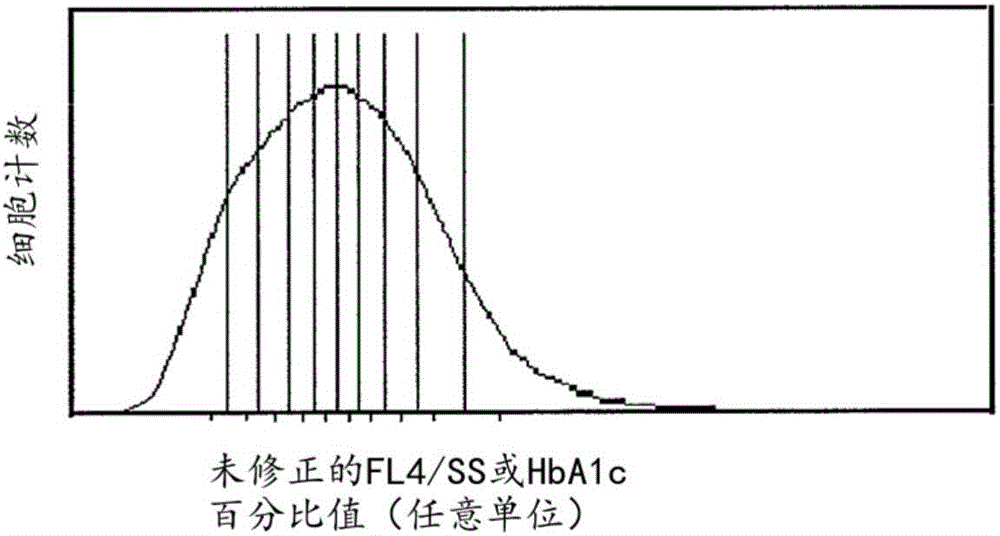
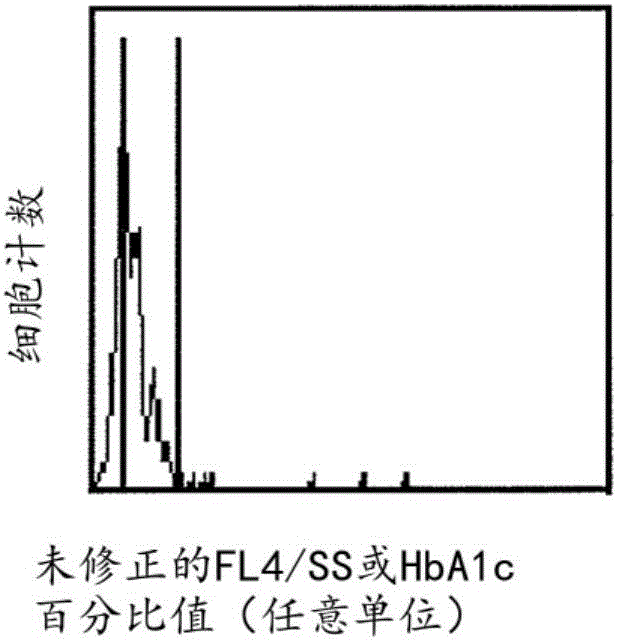
[0244] Data from six normal subjects; representation of FL4 / SS values and corrected FL4 / SS values in different fractions, and conversion of percentage HbA1c to time in each fraction .
[0245] This example presents data from six normal subjects and the conversion of fraction limit FL4 / SS values to time. For reasons of comparison with blood samples taken from diabetic individuals, in the first method, blood samples were selected that were representative of normal non-diabetic individuals who were considered to experience a constant blood glucose concentration. To further confirm that the parameters derived from normal samples represent constant blood glucose concentrations, the parameters of 6 normal samples were averaged.
[0246] Raw data generated by flow cytometry were used to fractionate mature cell populations into fractions containing equal numbers of cells as described in Example 1 . Cells were organized on the HbA1c percentage axis according to their increas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com