A Brain Fiber Clustering Method Based on Spatial Path Similarity
A clustering method and spatial path technology, applied in the research field of brain nerve fibers, can solve the problems of intricate fibers and the inability to visualize and analyze fiber trajectories, and achieve the effect of reducing errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
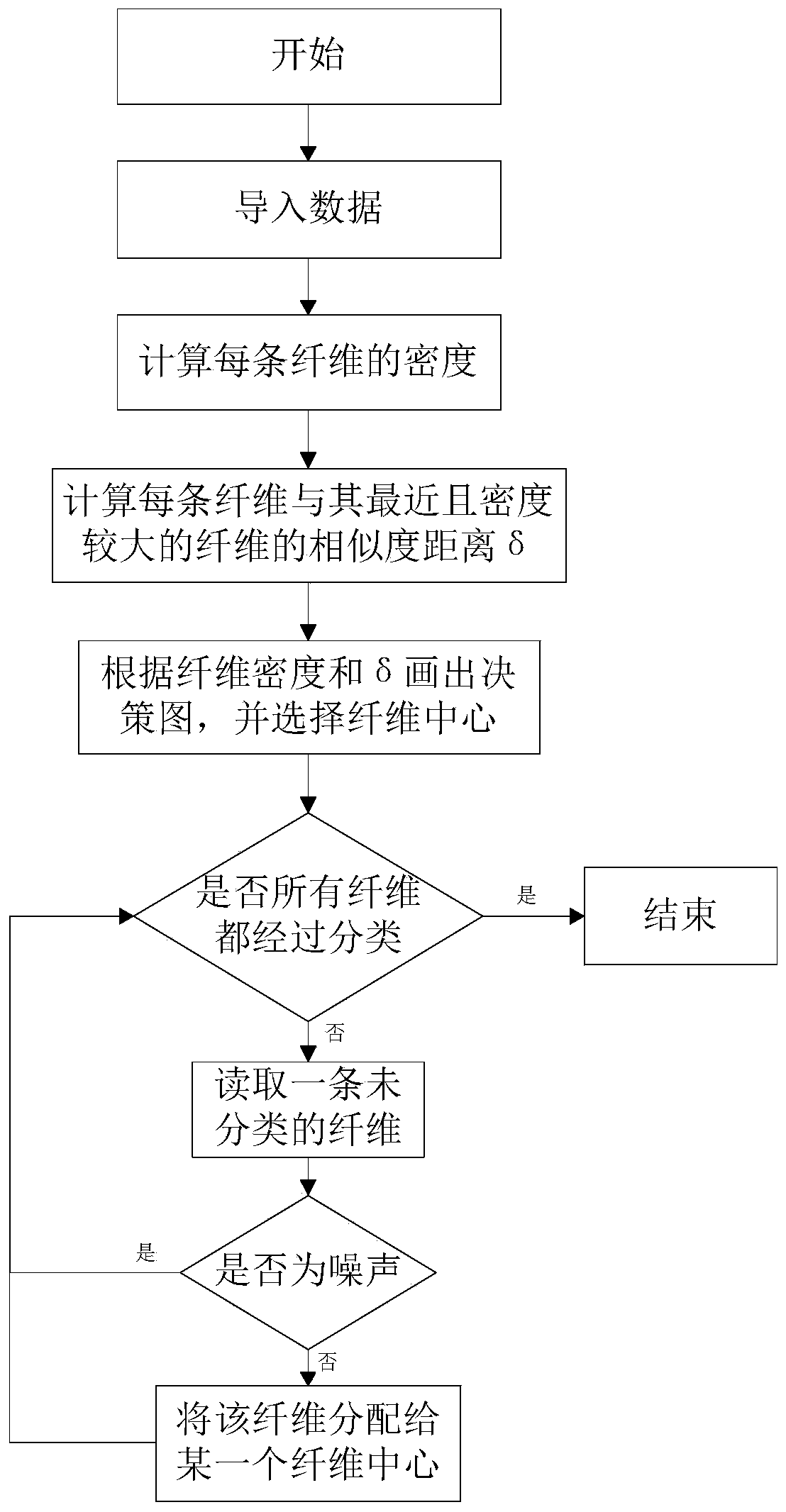
[0038] A method for clustering brain fibers based on spatial path similarity of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0039] 1), import fiber data, track out the fiber path, and calculate the similarity of each fiber;
[0040] 2) Due to the diversity of fiber data, some tissues have relatively scattered fibers and a small number of fibers, and some tissues have relatively dense fibers and a large number of fibers. According to the size of fiber data, two different fiber clustering methods are used: DPC(NGK) fiber clustering method and DPC(GK) fiber clustering method.
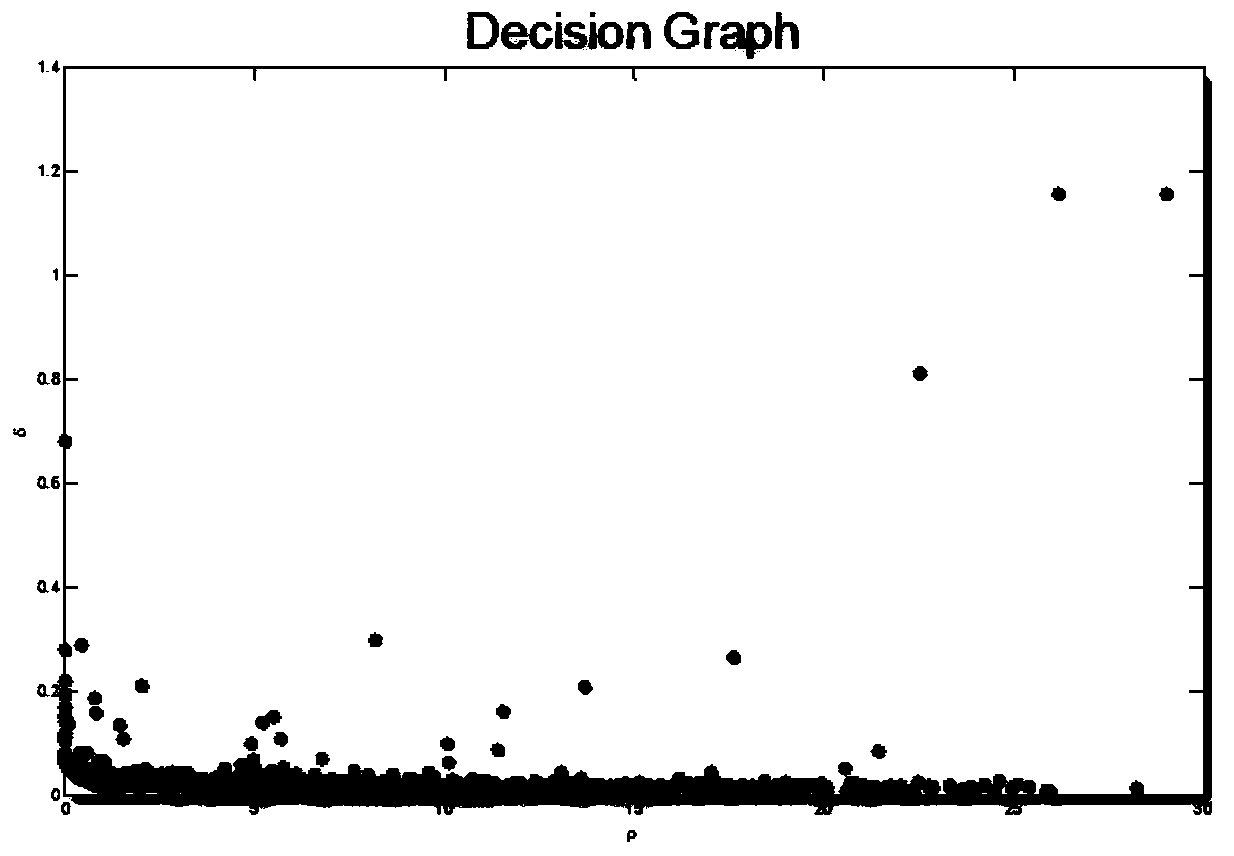
[0041] 2.1) For simple fiber data, the amount of fiber data is small, and the DPC (NGK) fiber clustering method is used: according to the density peak point, the clustering algorithm is quickly searched, that is, the DPC algorithm, and the corresponding density...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com