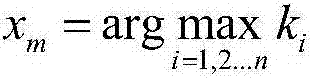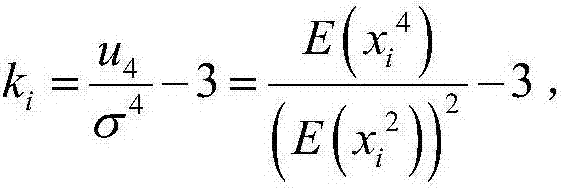Causal network inference method based on kurtosis
A causal network and kurtosis technology, applied in the field of causal network inference based on kurtosis, can solve the problems of initial value sensitivity, local convergence, unreliable measurement standards, etc., and achieve high accuracy, stability, and high recognition rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The specific embodiment of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
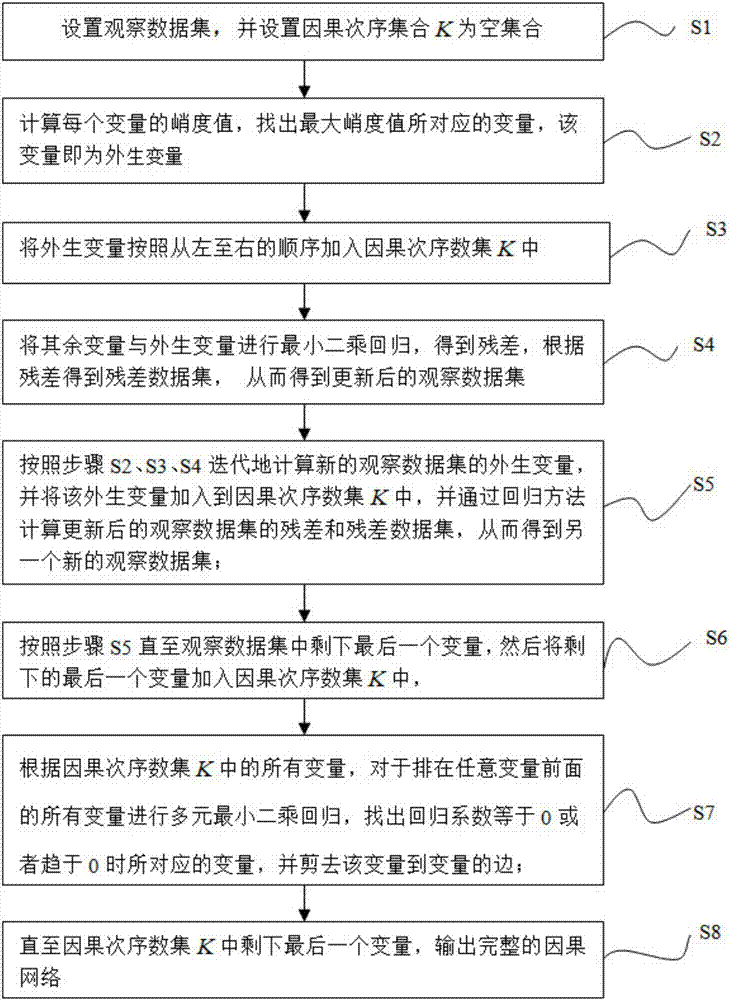
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, a causal network inference method based on kurtosis, through the three processes of selecting exogenous variables based on kurtosis, finding out the causal order layer by layer, and using the least square method to cut edges, includes the following steps:
[0030] 1), set the observation data set X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...x n ], each variable x i (i=1,2,...n) contains p sample data, and sets the causal sequence set K as an empty set;
[0031] 2), calculate each variable x i kurtosis value k for (i=1,2,...n) i (i=1,2,...n), find the maximum kurtosis value max k i The corresponding variable x m , variable x m It is an exogenous variable, and its calculation formula is:
[0032]
[0033]
[0034] Among them, E(x i 4 ) for the variable x i Fourth order center distance, (E(x i 2 )) 2 for x i the square of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com