Method and device for checking cabinet correction effect
A technology for correcting effects and cabinets, which is applied to the device for viewing the correction effects of cabinets, and in the field of viewing the correction effects of cabinets, which can solve the problems that random cabinet splicing is not easy to achieve, and the operation is not convenient.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
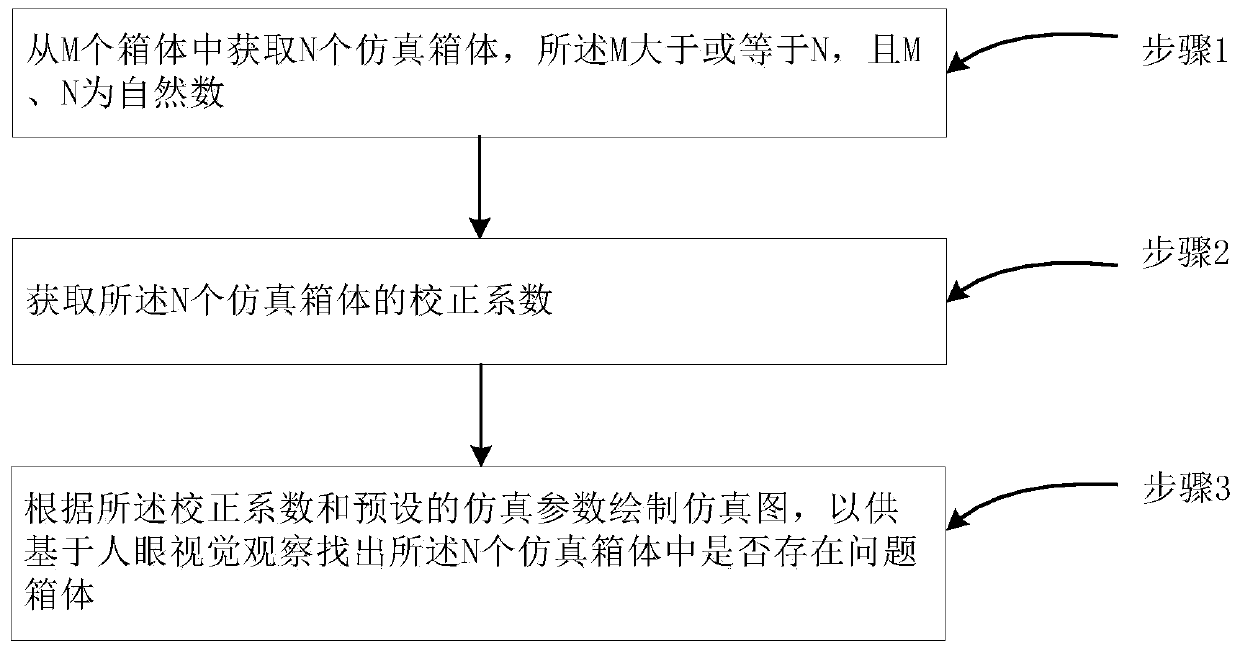
[0031] Such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a flow chart of a method for checking the effect of cabinet correction provided by the first embodiment of the present invention. The method includes the following steps:
[0032]Step 1. Obtain N simulated cabinets from M cabinets, where M is greater than or equal to N, and M and N are natural numbers;
[0033] Step 2, obtaining the correction coefficients of the N simulated cabinets;
[0034] Step 3. Draw a simulation diagram according to the correction coefficient and preset simulation parameters, so as to find out whether there is a problematic cabinet among the N simulated cabinets based on human visual observation.
[0035] Wherein, for step 1, it may be to select all, random multiple, front multiple, rear multiple or intermediate multiple cabinets as the N simulated cabinets from the M corrected cabinets.
[0036] Among them, for step 2, for the RGB full-color LED cabinet, each pixel includes red (R), green (G) and blue...
no. 2 example
[0047] This embodiment describes in detail the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention on the basis of the foregoing embodiments. Specifically, the method includes:
[0048] (1) Load the cabinet database, which can be a single database containing all cabinet correction coefficients, or multiple databases or a folder;
[0049] (2) Select the box to be simulated. The box can be selected arbitrarily, for example, you can choose all, multiple random, multiple in front, multiple in the back, multiple in the middle, etc., please refer to figure 2 , figure 2 A schematic diagram of the selection of a simulated box provided for the embodiment of the present invention;
[0050] (3) Read the box number and correction coefficient of each box;
[0051] (4) Set the number of cabinets in the row direction and column direction of the entire screen after the cabinets are spliced;
[0052] (5) To set simulation parameters, please refer to image 3 , image 3 A sc...
no. 3 example
[0064] See Figure 8 , Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of a device for checking the effect of cabinet correction provided by the embodiment of the present invention. The device includes: a first acquisition module 001, a second acquisition module 002, a drawing module 003, a color setting module 004, a mode setting module 005 and a third acquisition module 006;
[0065] The first obtaining module 001 is used to obtain N simulated cabinets from M cabinets, where M is greater than or equal to N, and M and N are natural numbers;
[0066] The second obtaining module 002 is used to obtain the correction coefficients of the N simulated cabinets;
[0067] The drawing module 003 is used to draw a simulation diagram according to the correction coefficient and preset simulation parameters, so as to find out whether there is a problem box in the N simulation boxes based on human visual observation;
[0068] The color setting module 004 is used for setting the color of the simulati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com