Calculation method of expected following distance in driver following behavior analysis
A technology of following distance and behavior analysis, applied in design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as traffic safety hazards, poor test repeatability, poor safety, etc., achieve low cost, improve active adaptability, The effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] Preferred embodiments of the present invention are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Those skilled in the art should understand that these embodiments are only used to explain the technical principles of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
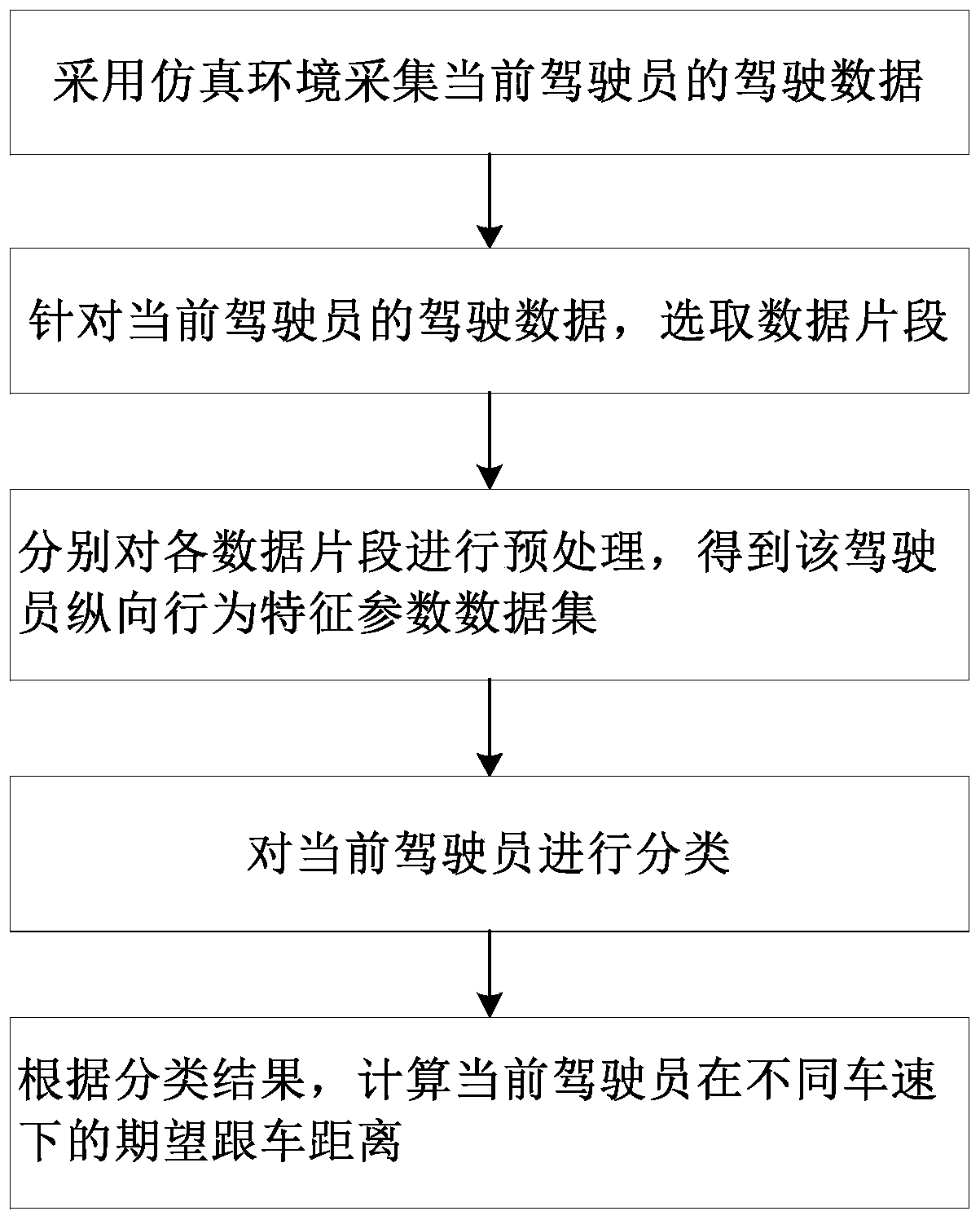
[0062] The present invention proposes a method for calculating the expected following distance in the analysis of the driver's following behavior, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0063] Step A1, using the simulation environment to collect the driving data of the current driver;
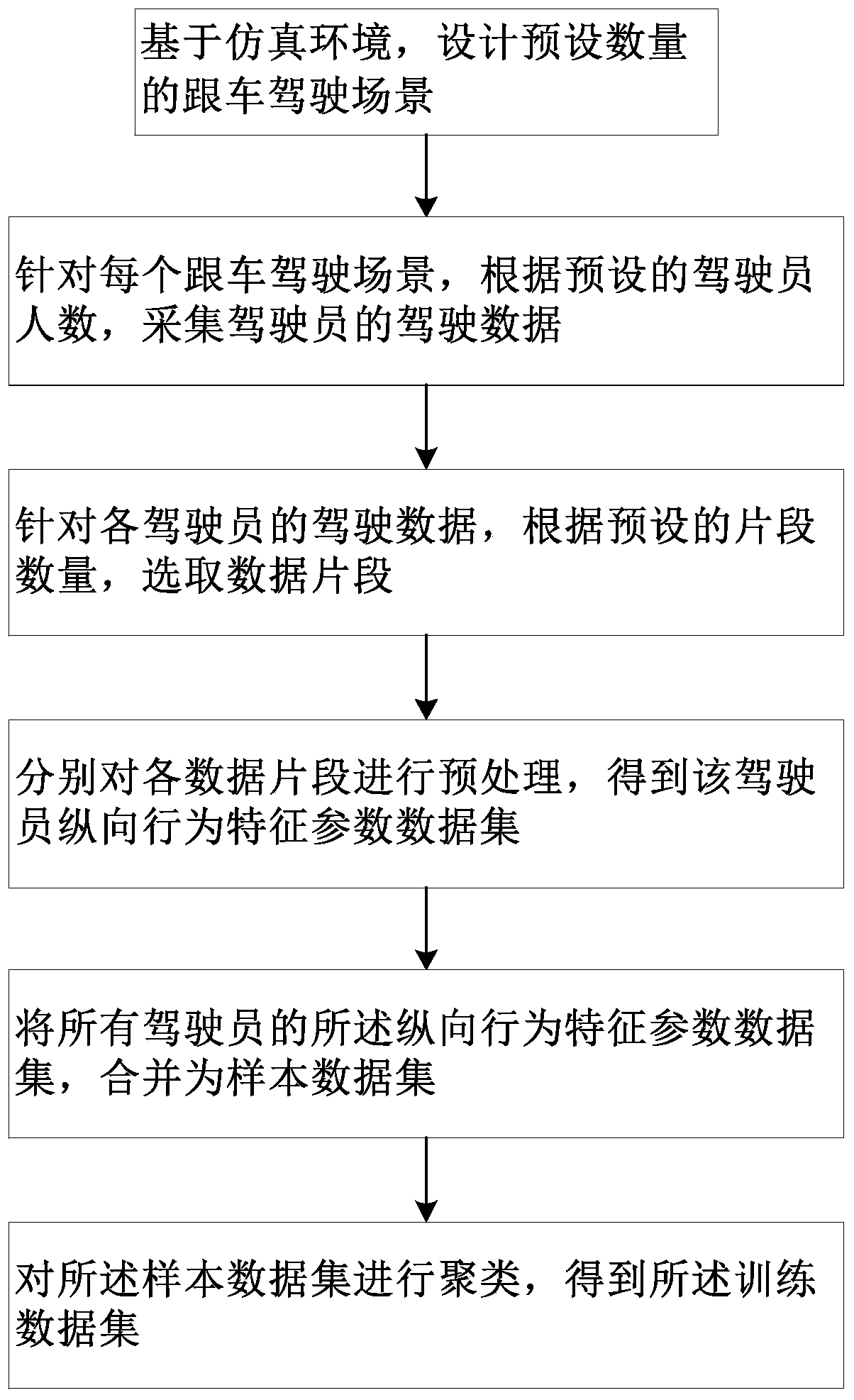
[0064] Step A2, for the driving data of the current driver, according to the preset number of segments, select the data segments of approximately steady-state car following; respectively preprocess each data segment to obtain the driver's longitudinal behavior characteristic parameter data set; The data segment of approximately steady-state ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com