Method for inducing T cells for immunocytotherapy from pluripotent stem cells
A technology for pluripotent stem cells and immunotherapy, which is applied in the field of T cells for inducing cellular immunotherapy, and can solve problems such as TCR specific loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
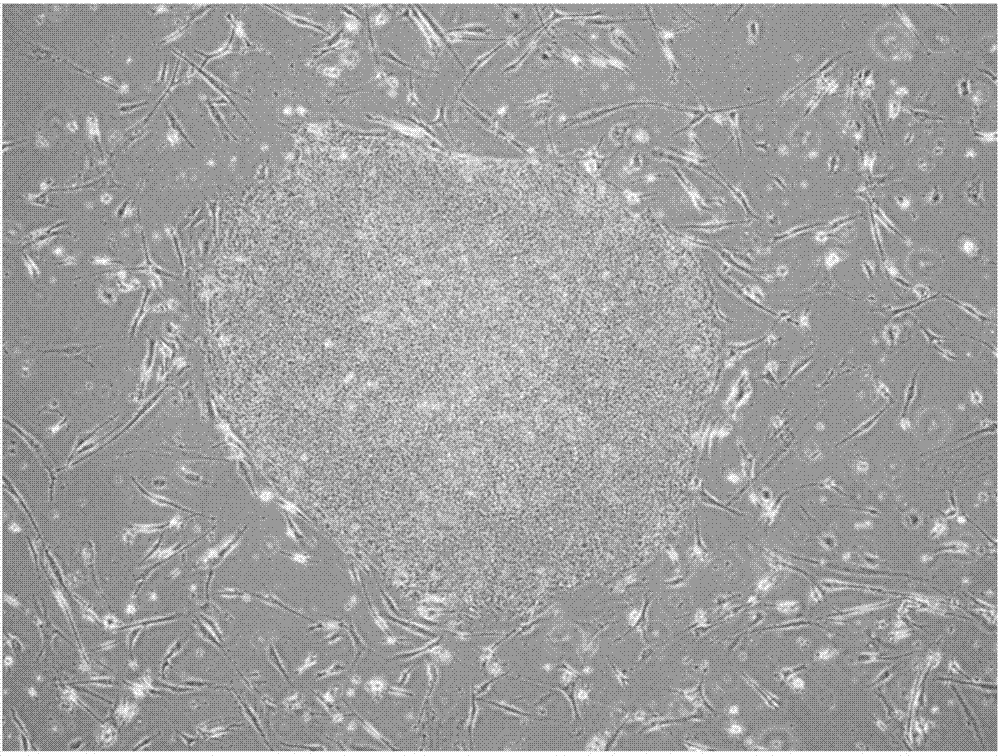
[0111] Establishment of iPS cells from T cells with a homozygous HLA haplotype and regeneration of T cells from iPS cells thus obtained.
[0112] Peripheral blood obtained from a donor homozygous for HLA-A*3303-B*4403-C*1403-ERB1*1302 was used.
[0113] 1) Establishment of Homo-T-iPS cells
[0114] The culture medium used is as follows:
[0115] 【Table 1】
[0116] Culture medium for T cells (T cell culture medium)
[0117] quantity final concentration RPMI 45ml human AB serum 5ml 10% Total 50ml
[0118] A. Activation of CD8-positive T cells
[0119] 1. Use Ficoll to refine peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from healthy volunteers, and use MACS beads to enrich CD8-positive cells.
[0120] 2. Disperse the enriched cells in T cell culture medium and add IL-2 (final concentration: 30U / mL), IL-7 (final concentration: 5ng / mL) and IL-15 (final concentration: 1ng / mL ). Dynabeads Human T-Activator CD3 / CD28 was added to form a be...
Embodiment 2
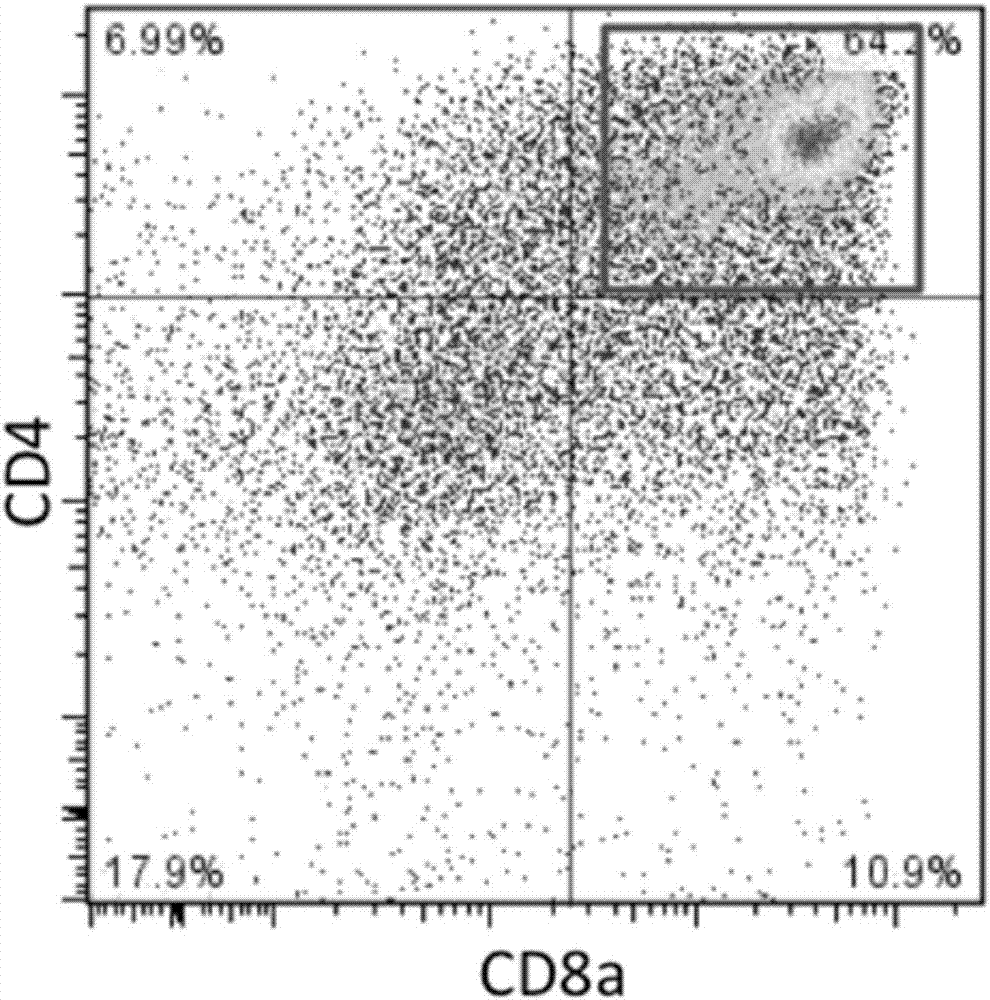
[0169] 1. Induction of CD8 positive T cells from T-iPS cells generated in Example 1.
[0170] 2. Using the iPS cell clones obtained in Example 1 with homozygous HLA haplotypes. Donor A (whose HLA haplotype has at least one match with the HLA haplotype of the iPS cell) and donor B (whose HLA haplotype does not match the HLA haplotype of the iPS cell at all) are selected.
[0171] Donor A: HLA-A*31:01 / 33:03; B*44:03 / 48:01; C*04:01 / 14:03; DRB1*04:03 / 13:02
[0172] Donor B: HLA-A*24:02 / 24:02; B*07:02 / 52:01; C*07:02 / 12:02; DRB1*01:01 / 15:02
[0173] 3. Using Ficoll to purify monocytes from the peripheral blood of donor A and donor B, and enrich CD8 positive cells by CD8 microbeads.
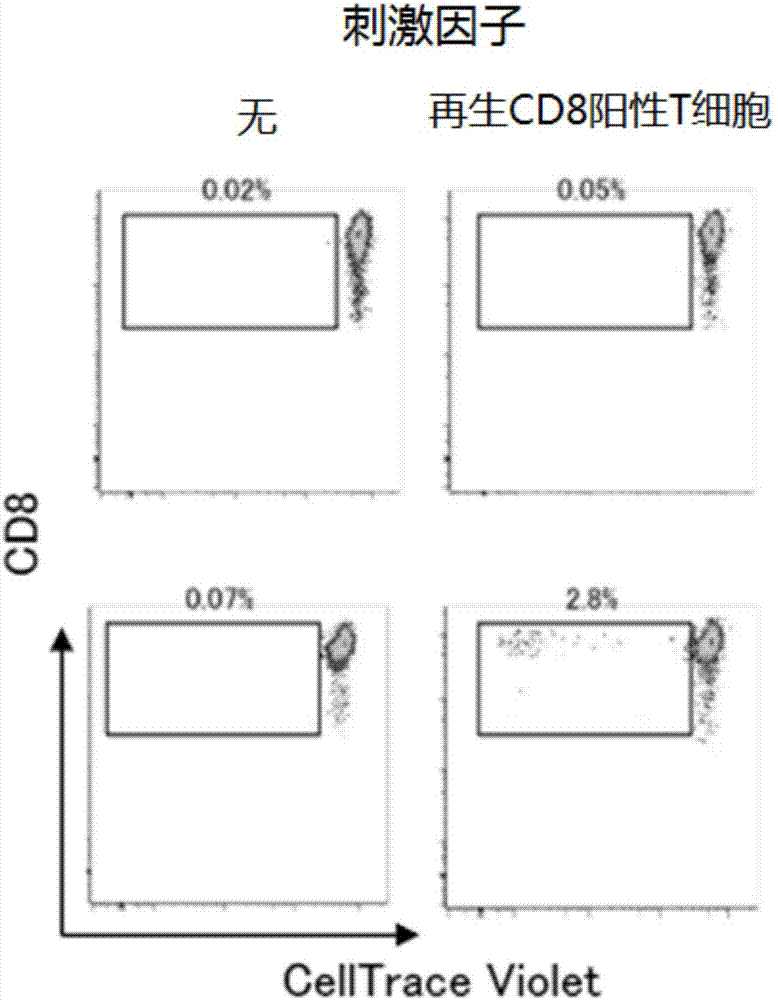
[0174] 4. Perform mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) using CD8-positive T cells regenerated from T-iPS cells as a stimulating factor. CD8 cells obtained from donors were used as effectors. Effector cells were fluorescently labeled using the CellTrace Violet Cell Proliferation Kit. Cell Trace CFSF Cell...
Embodiment 3
[0180] The T-iPS cells having a homozygous HLA haplotype obtained in Example 1 were differentiated into CD8-positive T cells (CTL) by conventional methods. It was examined whether CTLs would activate NK cells derived from peripheral blood of subjects with heterozygous HLA haplotypes, one of which matched the HLA haplotype of iPS cells.
[0181] 1. The CD8-positive T cells differentiated from iPS cells with a homozygous HLA haplotype by conventional methods in Example 1 were used as stimulators.
[0182] 2. Establish iPS cells from cells of donor A with heterozygous HLA haplotypes (one of which matches the HLA haplotype of the stimulator cell) by conventional methods, and differentiate the resulting iPS cells into CD8 positive T cells. And the obtained CD8 positive T cells were also used as stimulatory factors.
[0183] 3. Obtain peripheral blood from donor A, and use Ficoll to separate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). NK cells were enriched from PBMCs by negative ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com