Data transmission control method and system, data transmission method and device
A data transmission and control method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems that cannot guarantee the delay requirement of ultra-real-time service flow, does not involve QoS delay guarantee resource reservation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
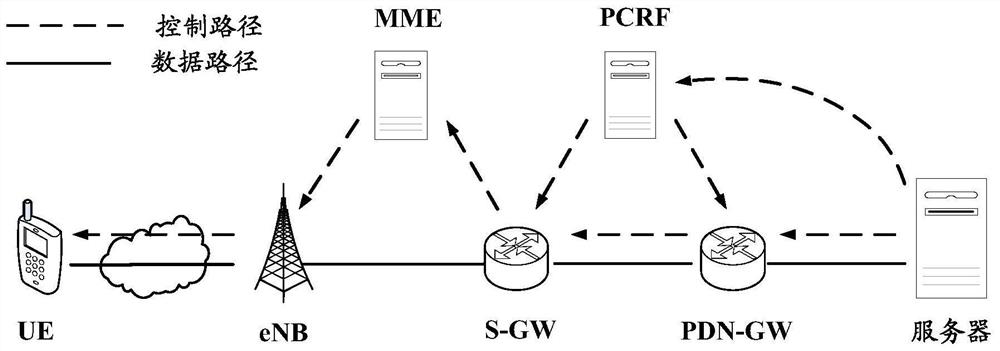
[0131] This embodiment describes a static bearer reservation scenario under a non-SDN architecture. This scenario is mainly aimed at multiple terminals (UEs) under the non-SDN architecture that have the same type of ultra-real-time service flow data transmission requirements of less than 50ms, and this ultra-real-time service flow is a service flow with relatively small bandwidth requirements. Typical applications It is a sudden emergency business flow. The network topology in this scenario is as follows: Figure 10 As shown, UE1 and UE2 have the requirement of sending the same type of service flow (corresponding to Content1) to an application function (AF, Application Function) server.
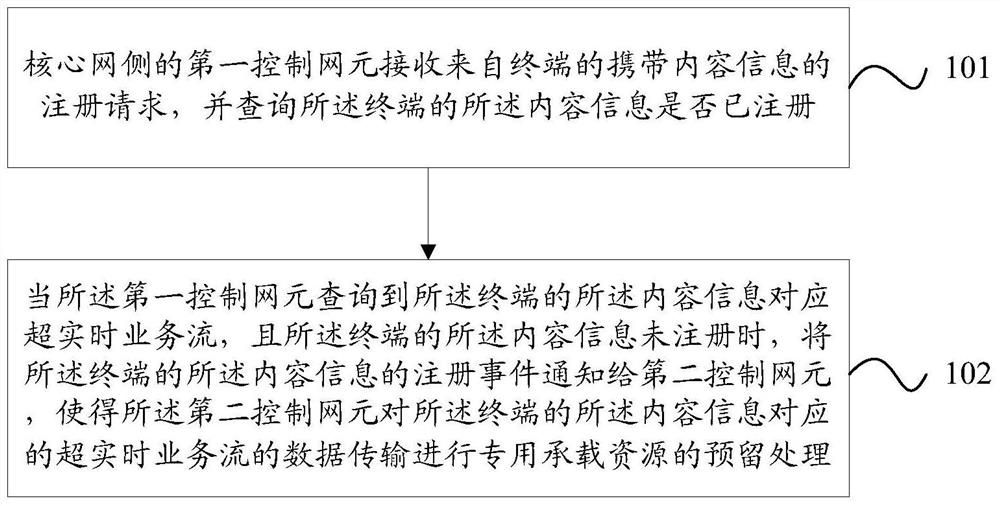
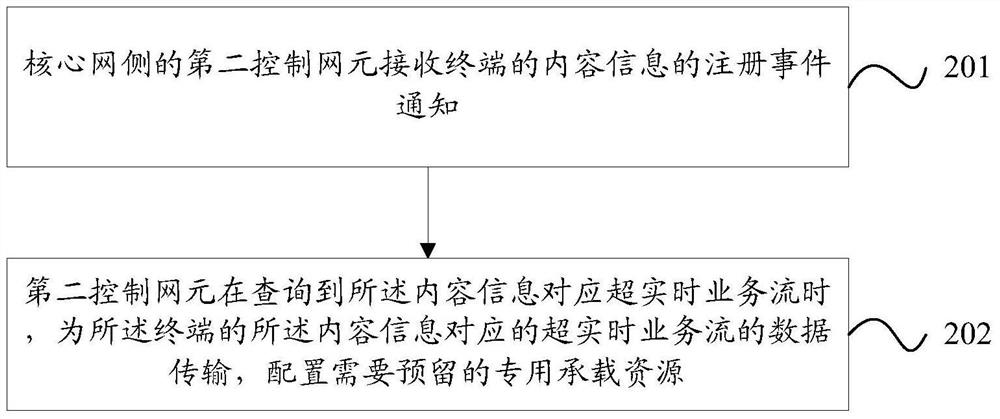
[0132] In this embodiment, the content1 registration and resource reservation process of UE1 is as follows Figure 11 shown. Specifically, UE1 first sends a registration request (Flow Register (Content1)) to the base station (eNB) for Content1, and the eNB forwards the registration request...
Embodiment 2
[0136] This embodiment describes a dynamic bearer reservation scenario under a non-SDN architecture. This scenario is mainly aimed at multiple terminals (UEs) in a non-SDN architecture that have the same type of ultra-real-time service flow data transmission requirements of less than 50ms, and this ultra-real-time service flow is a service flow with relatively large bandwidth requirements. Typical applications For telemedicine scenarios, the network topology of this scenario is as follows Figure 14 As shown, UE1 and UE2 have the requirement of sending the same type of service flow (corresponding to Content2) to the AF server.
[0137] In this embodiment, the content2 registration and resource reservation process of UE1 is as follows Figure 15 shown. UE1 first sends a registration request (Flow Register (Content2)) to eNB for Content2, and eNB forwards the registration request to MME to query the corresponding Content2; MME will first obtain the Subscription Profile templat...
Embodiment 3
[0142] This embodiment describes the static bearer reservation scenario under the SDN architecture. This scenario is mainly aimed at multiple terminals (UEs) under the SDN architecture that have the same type of ultra-real-time service flow data transmission requirements of less than 50ms, and this ultra-real-time service flow is a service flow with relatively small bandwidth requirements. Typical applications are For sudden emergency traffic, the network topology of this scenario is as follows: Figure 18As shown, UE1 and UE2 have the requirement of sending the same type of service flow (corresponding to Content1) to the AF server.
[0143] In this embodiment, the content1 registration and resource reservation process of UE1 is as follows Figure 19 shown. UE1 first sends a registration request (Flow Register (Content1)) to eNB for Content1, and eNB forwards the registration request to MME to query the corresponding Content1. MME will first obtain the Subscription Profile t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com