Anchor node optimal selection algorithm in wireless positioning
A technology for optimal selection and wireless positioning, applied in the field of high-precision distance estimation and wireless positioning technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
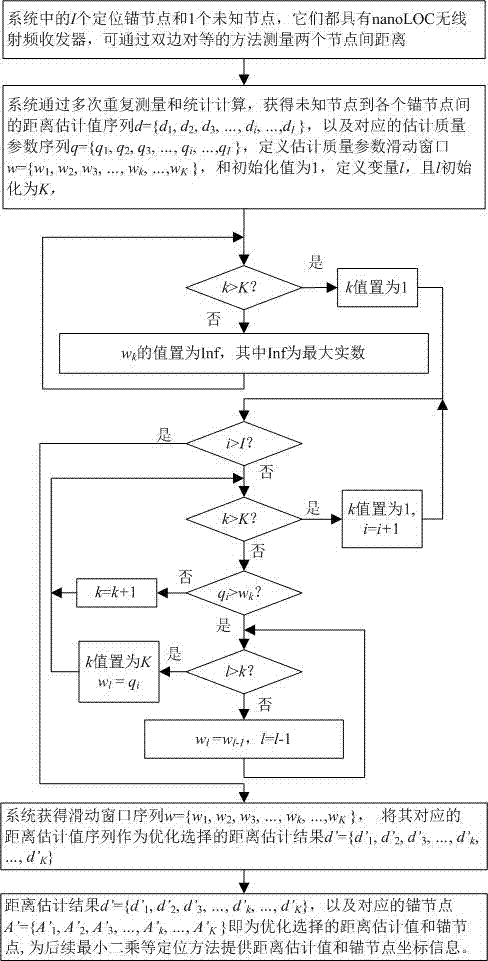
[0017] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, an anchor node optimal selection algorithm in wireless positioning described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0018] Step 1. There are I+1 wireless sensor nodes in the system, which are respectively I anchor nodes A={A 1 ,A 2 ,A 3 ,...,A i ,...,A I} and 1 unknown node, they all have nanoLOC radio frequency transceivers, and can use the bilateral peer-to-peer method to measure the estimated distance between any two nodes, where i is a positive integer, and 1≤i≤I, I is The parameter set by the user is a positive integer, and 6≤I≤15, in the present invention, I takes a value of 10;
[0019] Step 2. The system obtains the estimated distance sequence d={d from the unknown node to each anchor node through repeated measurement and statistical calculation 1 , d 2 , d 3 ,...,d i ,...,d I}, and the corresponding estimated quality parameter sequence q={q 1 ,q 2 ,q 3 ,.....
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Specific embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further description of the anchor node optimal selection algorithm in the wireless positioning described in the specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the strategy of sliding window and single-pass scanning is adopted, and no sorting is required. Thus, efficient distance estimation and optimal selection of anchor nodes can be realized.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific embodiment 3, this embodiment is to further explain the anchor node optimal selection algorithm in the wireless positioning described in specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the estimated quality parameter used can be statistical standard deviation, or are other parameters that characterize the quality of the distance estimate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com